200400045 VECTRON ELEKTRONIK MANUAL
... Means free choice of the most suitable control method for specific applications - up to positioning and synchronous drives - using the key pad or any other control unit. ...
... Means free choice of the most suitable control method for specific applications - up to positioning and synchronous drives - using the key pad or any other control unit. ...
Research Proposal - Sacramento
... All signals in the real world are analog, and vary continuously in both time and amplitude with an infinite number of possible values. However, most of the time digital systems are used for data analysis, for example to analyze ECG data by inputting the data into a computer or other digital analysis ...
... All signals in the real world are analog, and vary continuously in both time and amplitude with an infinite number of possible values. However, most of the time digital systems are used for data analysis, for example to analyze ECG data by inputting the data into a computer or other digital analysis ...
The Analog Lock
... amplifiers will be operating near to their maximum gain. However, at mid-range sensitivity settings the same overall sensitivity can be obtained by different combinations of AC and DC gain. Lower values of DC gain give better output stability, but at the expense of reducing the instrument’s dynamic ...
... amplifiers will be operating near to their maximum gain. However, at mid-range sensitivity settings the same overall sensitivity can be obtained by different combinations of AC and DC gain. Lower values of DC gain give better output stability, but at the expense of reducing the instrument’s dynamic ...
Representations of any two different signals
... Effect of Finite Gain A • Drop the assumption of “virtual short circuit” vO ...
... Effect of Finite Gain A • Drop the assumption of “virtual short circuit” vO ...
ASDBLR02_pads
... 2 Discriminator negative supply. 1 may be used. VEDR 2 Output Drive negative supply. Both should be used. Pads for supplies connect internally across the ASIC we have only utilized the ASDBLR with all pads redundantly connected. It may be possible to connect from only one side. Grounds - The ASDBLR ...
... 2 Discriminator negative supply. 1 may be used. VEDR 2 Output Drive negative supply. Both should be used. Pads for supplies connect internally across the ASIC we have only utilized the ASDBLR with all pads redundantly connected. It may be possible to connect from only one side. Grounds - The ASDBLR ...
... .c. )The ability to measure wider ranges of voltage and resistances d). None 12. In an Ntype semiconductor, the position of the fermi level – .a. )Is lower than the centre of the energy gap b.) Is at the centre of the energy gap c.)Is higher than the centre of the energy gap .d. )Can be anywhere dep ...
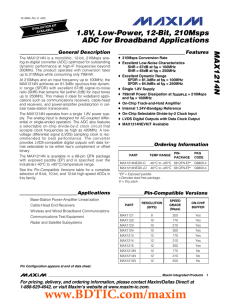
MAX1214N 1.8V, Low-Power, 12-Bit, 210Msps ADC for Broadband Applications General Description
... At 210Msps and an input frequency up to 100MHz, the MAX1214N achieves an 81.3dBc spurious-free dynamic range (SFDR) with excellent 67dB signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) that remains flat (within 2dB) for input tones up to 250MHz. This makes it ideal for wideband applications such as communications receiv ...
... At 210Msps and an input frequency up to 100MHz, the MAX1214N achieves an 81.3dBc spurious-free dynamic range (SFDR) with excellent 67dB signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) that remains flat (within 2dB) for input tones up to 250MHz. This makes it ideal for wideband applications such as communications receiv ...
EE_115AL_Experiment_7
... Set the frequency to 10kHz and increase the input voltage until the output voltage becomes distorted. Note the maximum. When the input is at 0.61 volts, the output is at 5.85 volts. Further increase of the input voltage distorts the output. Thus 5.85 volts is the max output swing. d) AC Voltage and ...
... Set the frequency to 10kHz and increase the input voltage until the output voltage becomes distorted. Note the maximum. When the input is at 0.61 volts, the output is at 5.85 volts. Further increase of the input voltage distorts the output. Thus 5.85 volts is the max output swing. d) AC Voltage and ...
Low-power, Low-noise, Low -voltage Amplifier for Very Low
... • The amplified output is amplitude modulated with the same carrier signal as the original low power, low frequency signal. • The second modulation stage demodulates the amplified neural signal back to its baseband frequency, while modulating the noise and offset voltage signals up to the carrier fr ...
... • The amplified output is amplitude modulated with the same carrier signal as the original low power, low frequency signal. • The second modulation stage demodulates the amplified neural signal back to its baseband frequency, while modulating the noise and offset voltage signals up to the carrier fr ...
Operational amplifier
... When Vin=0, Vout is NOT 0 due to mismatch of transistors in real circuit design. It is more meaningful to specify input-referred offset voltage, defined as Vos,in=Vos,out / A. Offset voltage may causes a DC shift of later stages, also causes limited precision in signal comparison. ...
... When Vin=0, Vout is NOT 0 due to mismatch of transistors in real circuit design. It is more meaningful to specify input-referred offset voltage, defined as Vos,in=Vos,out / A. Offset voltage may causes a DC shift of later stages, also causes limited precision in signal comparison. ...
MAX1121 1.8V, 8-Bit, 250Msps Analog-to-Digital Converter with LVDS Outputs for Wideband Applications
... up to 250Msps while consuming only 477mW. At 250Msps and an input frequency of 100MHz, the MAX1121 achieves a spurious-free dynamic range (SFDR) of 68dBc. Its excellent signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of 48.9dB at 10MHz remains flat (within 0.5dB) for input tones up to 500MHz. This makes the MAX1121 ide ...
... up to 250Msps while consuming only 477mW. At 250Msps and an input frequency of 100MHz, the MAX1121 achieves a spurious-free dynamic range (SFDR) of 68dBc. Its excellent signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of 48.9dB at 10MHz remains flat (within 0.5dB) for input tones up to 500MHz. This makes the MAX1121 ide ...
AN-653: Improving Temperature, Stability, and Linearity of High Dynamic Range RMS RF Power Detectors
... broadband signal is applied as an input to the circuit, the output of the error amplifier contains significant noise but is still centered on the correct rms output level. The noise level at the output of the error amplifier is set to a level of at least 300 mV p-p, 300 mV being the distance in dB b ...
... broadband signal is applied as an input to the circuit, the output of the error amplifier contains significant noise but is still centered on the correct rms output level. The noise level at the output of the error amplifier is set to a level of at least 300 mV p-p, 300 mV being the distance in dB b ...
ppt
... transmitter and the nature of the transmission medium in cycles/sec (hertz) • channel capacity (C) – the rate at which data can be transmitted over a given channel under given conditions. ...
... transmitter and the nature of the transmission medium in cycles/sec (hertz) • channel capacity (C) – the rate at which data can be transmitted over a given channel under given conditions. ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).