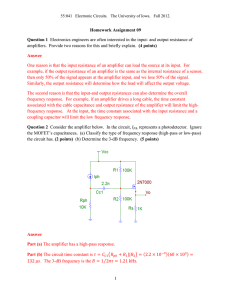
Cascaded Op Amp Circuits
... Op amp circuits have the advantage that they can be cascaded without changing their input-output relationships. This is due to the fact that each (ideal) op amp circuit has infinite input resistance and zero output resistance. Although the cascade connection does not affect the op amp input-ou ...
... Op amp circuits have the advantage that they can be cascaded without changing their input-output relationships. This is due to the fact that each (ideal) op amp circuit has infinite input resistance and zero output resistance. Although the cascade connection does not affect the op amp input-ou ...
Capacitor and EMI Considerations for New High Frequency
... large footprint, and limited temperature range. They are probably best suited for input bypassing at higher voltages, and very high frequency (≥1MHz) applications. Note that at high frequencies, most of the capacitors approach an inductive line of about 1nH to 5nH. Smaller units in parallel will re ...
... large footprint, and limited temperature range. They are probably best suited for input bypassing at higher voltages, and very high frequency (≥1MHz) applications. Note that at high frequencies, most of the capacitors approach an inductive line of about 1nH to 5nH. Smaller units in parallel will re ...
35MHz Standard Oscilloscope HM303-6
... worldwide). The bandwidth has been extended from 20 to 35MHz, the sweep speed increased to 10ns/div. and improvements added to the already legendary HAMEG auto triggering system. The HM303 is the ideal instrument for waveform display in the DC to 100MHz frequency range. A key feature of this oscillo ...
... worldwide). The bandwidth has been extended from 20 to 35MHz, the sweep speed increased to 10ns/div. and improvements added to the already legendary HAMEG auto triggering system. The HM303 is the ideal instrument for waveform display in the DC to 100MHz frequency range. A key feature of this oscillo ...
No Slide Title
... Usually specified as the conversion rate or sampling rate. It is the rate at which the input register is updated. High speed DACs are defined as operating at greater than 1 MHz. Some state of the art 12-16 bit DAC can reach speeds of 1GHz The conversion of the digital input signal is limited b ...
... Usually specified as the conversion rate or sampling rate. It is the rate at which the input register is updated. High speed DACs are defined as operating at greater than 1 MHz. Some state of the art 12-16 bit DAC can reach speeds of 1GHz The conversion of the digital input signal is limited b ...
AVOP-ELEKTRO-HOL-001
... Measured physical quantities, which can be found all around us, are almost always analog (temperature, pressure, voltage, current). Circuits processing signals can be divided into two basic groups: 1. Analog circuits 2. Numerical circuits Analog circuits - process signals, which are functions of ti ...
... Measured physical quantities, which can be found all around us, are almost always analog (temperature, pressure, voltage, current). Circuits processing signals can be divided into two basic groups: 1. Analog circuits 2. Numerical circuits Analog circuits - process signals, which are functions of ti ...
7- to 13-Bit Variable Resolution Incremental ADC Datasheet
... initialized only before the first reading. After the Compare and Period registers are set once, they do not have to be reinitialized unless resolution or calculation time is changed. When the PWM count is less than or equal to the integrate value, the output goes high, enabling the 8-bit counter to ...
... initialized only before the first reading. After the Compare and Period registers are set once, they do not have to be reinitialized unless resolution or calculation time is changed. When the PWM count is less than or equal to the integrate value, the output goes high, enabling the 8-bit counter to ...
High Speed Amps Roadmap
... Supply operation from 4 to 5.25 V @ 71 mA Split supply capable Fabricated on CBC8 Complementary SiGe process 3.0 x 3.0 mm2 16 lead QFN package ...
... Supply operation from 4 to 5.25 V @ 71 mA Split supply capable Fabricated on CBC8 Complementary SiGe process 3.0 x 3.0 mm2 16 lead QFN package ...
Full Wave Rectifier with LPF - EP58437
... Corporation assumes no responsibility for the use of any circuitry other than circuitry embodied in a Cypress product. Nor does it convey or imply any license under patent or other rights. Cypress products are not warranted nor intended to be used for medical, life support, life saving, critical con ...
... Corporation assumes no responsibility for the use of any circuitry other than circuitry embodied in a Cypress product. Nor does it convey or imply any license under patent or other rights. Cypress products are not warranted nor intended to be used for medical, life support, life saving, critical con ...
AN-726 APPLICATION NOTE
... three supplies do not come up simultaneously but in a staggered fashion, it’s evident that the trip point on the final supply to come up will depend on the voltage levels at which the other two supplies have settled. Figure 2 illustrates what happens when the 12 V supply is the last to come up. It i ...
... three supplies do not come up simultaneously but in a staggered fashion, it’s evident that the trip point on the final supply to come up will depend on the voltage levels at which the other two supplies have settled. Figure 2 illustrates what happens when the 12 V supply is the last to come up. It i ...
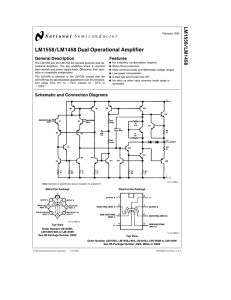
LM1558/LM1458 Dual Operational Amplifier
... bias network and power supply leads. Otherwise, their operation is completely independent. The LM1458 is identical to the LM1558 except that the LM1458 has its specifications guaranteed over the temperature range from 0§ C to a 70§ C instead of b55§ C to a 125§ C. ...
... bias network and power supply leads. Otherwise, their operation is completely independent. The LM1458 is identical to the LM1558 except that the LM1458 has its specifications guaranteed over the temperature range from 0§ C to a 70§ C instead of b55§ C to a 125§ C. ...
cmos differential amplifier
... Three problems in single-transistor amplifier stages: Bias and gain sensitive to device parameters (µCox,VT ); sensitivity can be mitigated but often paying price in performance or cost (gain, power, device area, etc.) Vulnerable to ground and power-supply noise (in dense IC’s there is cross-tal ...
... Three problems in single-transistor amplifier stages: Bias and gain sensitive to device parameters (µCox,VT ); sensitivity can be mitigated but often paying price in performance or cost (gain, power, device area, etc.) Vulnerable to ground and power-supply noise (in dense IC’s there is cross-tal ...
NTE823 Integrated Circuit Low Voltage Audio
... With Pin1 and Pin8 open the 1.35kΩ resistor sets the gain at 20 (26dB). If a capacitor is put from Pin1 to Pin8, bypassing the 1.35kΩ resistor, the gain will go up to 200 (46dB). If a resistor is placed in series with the capacitor, the gain can be set to any value from 20 to 200. Gain control can a ...
... With Pin1 and Pin8 open the 1.35kΩ resistor sets the gain at 20 (26dB). If a capacitor is put from Pin1 to Pin8, bypassing the 1.35kΩ resistor, the gain will go up to 200 (46dB). If a resistor is placed in series with the capacitor, the gain can be set to any value from 20 to 200. Gain control can a ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).