A Multi-Channel Discriminator IC George Engel IC Design Research Laboratory
... ”fast” shaper output is applied to the inverting input of the zero-cross discriminator circuit along with a delayed version of the input pulse connected to the non-inverting input. It is well-known that the time at which the differential voltage crosses through zero is independent of the input pulse ...
... ”fast” shaper output is applied to the inverting input of the zero-cross discriminator circuit along with a delayed version of the input pulse connected to the non-inverting input. It is well-known that the time at which the differential voltage crosses through zero is independent of the input pulse ...
Signals - theParticle.com
... and data rate. Usually they are related. More bandwidth usually implies higher data rate. It turns out (due to Nyquist), we can get about 2bps for every 1Hz. Each wave has an upside (the 1bit), and a down side (the 0bit). So if a channel has say 8000Hz bandwidth, we can transfer bits at 16000bps. Th ...
... and data rate. Usually they are related. More bandwidth usually implies higher data rate. It turns out (due to Nyquist), we can get about 2bps for every 1Hz. Each wave has an upside (the 1bit), and a down side (the 0bit). So if a channel has say 8000Hz bandwidth, we can transfer bits at 16000bps. Th ...
β τ β - Hacettepe University, Department of Electrical and Electronics
... 1. PURPOSE: To investigate the sweep generator implemented with BJT 2. THEORY : The function of the sweep generator is to produce a voltage waveform changing linearly with time. They are widely used in Cathode Ray Oscilloscopes, radars and television circuits. An ideal sweep generator has a sawtooth ...
... 1. PURPOSE: To investigate the sweep generator implemented with BJT 2. THEORY : The function of the sweep generator is to produce a voltage waveform changing linearly with time. They are widely used in Cathode Ray Oscilloscopes, radars and television circuits. An ideal sweep generator has a sawtooth ...
Analog or digital? Chapter 12 12.1 Is the world ‘analog’?
... could we tell? Of course, we could probably decide by looking to see if the circuit contained any integrated circuits, reading their type numbers, and looking them up in a book! (We can also guess that if the circuit doesn't contain any integrated circuits, it's probably not digital) However for ou ...
... could we tell? Of course, we could probably decide by looking to see if the circuit contained any integrated circuits, reading their type numbers, and looking them up in a book! (We can also guess that if the circuit doesn't contain any integrated circuits, it's probably not digital) However for ou ...
ADIS16060 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... All of the output data is in an offset-binary format, which in this case, means that the ideal output for a zero rate condition is 8192 codes. If the sensitivity is equal to +0.0122°/sec/LSB, a rate of +10°/sec results in a change of 820 codes, and a digital rate output of 9012 codes. If an offset e ...
... All of the output data is in an offset-binary format, which in this case, means that the ideal output for a zero rate condition is 8192 codes. If the sensitivity is equal to +0.0122°/sec/LSB, a rate of +10°/sec results in a change of 820 codes, and a digital rate output of 9012 codes. If an offset e ...
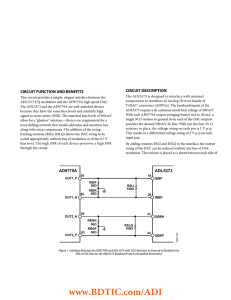
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
... The value of this ac swing-limiting resistor is chosen based on the desired ac voltage swing. Figure 2 shows the relationship between the swing-limiting resistor and the peak-to-peak ac swing that it produces when 50 Ω bias-setting resistors are used. Note that all Analog Devices I/Q modulators pres ...
... The value of this ac swing-limiting resistor is chosen based on the desired ac voltage swing. Figure 2 shows the relationship between the swing-limiting resistor and the peak-to-peak ac swing that it produces when 50 Ω bias-setting resistors are used. Note that all Analog Devices I/Q modulators pres ...
AD22103 - Farnell
... operation without a precision voltage reference, it can still be used in such systems. Overall system requirements involving other sensors or signal inputs may dictate the need for a fixed precision ADC reference. The AD22103 can be converted to absolute voltage operation by using a precision refere ...
... operation without a precision voltage reference, it can still be used in such systems. Overall system requirements involving other sensors or signal inputs may dictate the need for a fixed precision ADC reference. The AD22103 can be converted to absolute voltage operation by using a precision refere ...
MAX1124 1.8V, 10-Bit, 250Msps Analog-to-Digital Converter with LVDS Outputs for Wideband Applications
... up to 250Msps while consuming only 477mW. At 250Msps and an input frequency of 100MHz, the MAX1124 achieves a spurious-free dynamic range (SFDR) of 71dBc. Its excellent signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of 57.1dB at 10MHz remains flat (within 1dB) for input tones up to 500MHz. This makes the MAX1124 ideal ...
... up to 250Msps while consuming only 477mW. At 250Msps and an input frequency of 100MHz, the MAX1124 achieves a spurious-free dynamic range (SFDR) of 71dBc. Its excellent signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of 57.1dB at 10MHz remains flat (within 1dB) for input tones up to 500MHz. This makes the MAX1124 ideal ...
Product data: Charge Amplifier
... Charge Amplifier Type 2634 is a very robust construction and is ideal for use in conditions where the preamplifier must be sited near to the transducer, in order to avoid noise pick-up in long transducer cables due to electromagnetic noise and triboelectric noise. Power Supply and output signal can ...
... Charge Amplifier Type 2634 is a very robust construction and is ideal for use in conditions where the preamplifier must be sited near to the transducer, in order to avoid noise pick-up in long transducer cables due to electromagnetic noise and triboelectric noise. Power Supply and output signal can ...
MAX125/MAX126 2x4-Channel, Simultaneous-Sampling 14-Bit DAS General Description
... conversions, data can be accessed by applying successive pulses to the RD pin. Four successive reads access four data words sequentially. The parallel interface’s data-access and bus-release timing specifications are compatible with most popular digital signal processors and 16-bit/32-bit microproce ...
... conversions, data can be accessed by applying successive pulses to the RD pin. Four successive reads access four data words sequentially. The parallel interface’s data-access and bus-release timing specifications are compatible with most popular digital signal processors and 16-bit/32-bit microproce ...
An Introduction to Circuits Excited with an AC Potential
... A: the amplitude, is the peak deviation of the function from its center position. "A" is always the zero-to- peak value of the sinusoid when the wave is expressed in the form of (1). ω: the angular frequency, specifies how many oscillations occur in a unit time interval, in radians per second ϴ: the ...
... A: the amplitude, is the peak deviation of the function from its center position. "A" is always the zero-to- peak value of the sinusoid when the wave is expressed in the form of (1). ω: the angular frequency, specifies how many oscillations occur in a unit time interval, in radians per second ϴ: the ...
Technical Info CMRR (Common Mode Rejection Ratio)
... Both of the signal cable and the signal source have impedances, therefore the simplified circuit diagram in the actual use of the differential amplifier is shown as follows. If there are no these impedances, the noise source is applied to the non inverting input terminal and the inverting input termina ...
... Both of the signal cable and the signal source have impedances, therefore the simplified circuit diagram in the actual use of the differential amplifier is shown as follows. If there are no these impedances, the noise source is applied to the non inverting input terminal and the inverting input termina ...
a high-efficiency resonant switched capacitor converter
... Switched capacitor converters (SCCs) have limited capabilities for voltage regulation due to the tight relationship between the voltage gain and the converter efficiency. Regulation can be obtained either by varying SCC parameters, or inserting a post regulation stage to match the required conversio ...
... Switched capacitor converters (SCCs) have limited capabilities for voltage regulation due to the tight relationship between the voltage gain and the converter efficiency. Regulation can be obtained either by varying SCC parameters, or inserting a post regulation stage to match the required conversio ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).