... Stresses beyond those listed under absolute maximum ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under recommended operating conditions is not implied. Exposure to absol ...
MAX13170E +5V Multiprotocol, 3Tx/3Rx, Software- Selectable Clock/Data Transceiver General Description
... Transmitter Outputs T_OUT_, T3OUT_/R1IN_ (No Cable Mode or V.28) ..........................................................-15V to +15V Short-Circuit Duration to GND...............................Continuous ...
... Transmitter Outputs T_OUT_, T3OUT_/R1IN_ (No Cable Mode or V.28) ..........................................................-15V to +15V Short-Circuit Duration to GND...............................Continuous ...
MAX1980 Quick-PWM Slave Controller with Driver Disable for Multiphase DC-DC Converter General Description
... The MAX1980 provides the same high-efficiency, ultralow duty factor capability, and excellent transient response as other Quick-PWM controllers. The MAX1980 differentially senses the inductor currents of both the master and the slave across current-sense resistors. These differential inputs and the ...
... The MAX1980 provides the same high-efficiency, ultralow duty factor capability, and excellent transient response as other Quick-PWM controllers. The MAX1980 differentially senses the inductor currents of both the master and the slave across current-sense resistors. These differential inputs and the ...
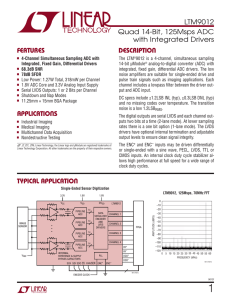
LTM9012 - Quad 14-Bit, 125Msps ADC with Integrated Drivers
... The LTM®9012 is a 4-channel, simultaneous sampling 14-bit µModule® analog-to-digital converter (ADC) with integrated, fixed gain, differential ADC drivers. The low noise amplifiers are suitable for single-ended drive and pulse train signals such as imaging applications. Each channel includes a lowpa ...
... The LTM®9012 is a 4-channel, simultaneous sampling 14-bit µModule® analog-to-digital converter (ADC) with integrated, fixed gain, differential ADC drivers. The low noise amplifiers are suitable for single-ended drive and pulse train signals such as imaging applications. Each channel includes a lowpa ...
AVTRON ACCel500 FREQUENCY CONVERTERS Frames 4-12
... the cover before this time has expired. • The control I/O terminals are isolated from the mains potential. However, the relay outputs and other I/O terminals may have a dangerous control voltage present even when the ACCel500 frequency converter is disconnected from mains. • Before connecting the fr ...
... the cover before this time has expired. • The control I/O terminals are isolated from the mains potential. However, the relay outputs and other I/O terminals may have a dangerous control voltage present even when the ACCel500 frequency converter is disconnected from mains. • Before connecting the fr ...
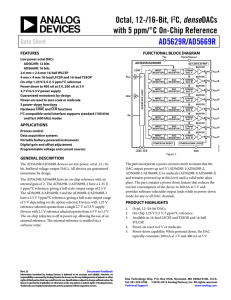
AD5629R/AD5669R - produktinfo.conrad.com
... The AD5629R/AD5669R have an on-chip reference with an internal gain of 2. The AD5629R-1/AD5669R-1 have a 1.25 V, 5 ppm/°C reference, giving a full-scale output range of 2.5 V. The AD5629R-2/AD5629R-3 and the AD5669R-2/AD5669R-3 have a 2.5 V 5 ppm/°C reference, giving a full-scale output range of 5 V ...
... The AD5629R/AD5669R have an on-chip reference with an internal gain of 2. The AD5629R-1/AD5669R-1 have a 1.25 V, 5 ppm/°C reference, giving a full-scale output range of 2.5 V. The AD5629R-2/AD5629R-3 and the AD5669R-2/AD5669R-3 have a 2.5 V 5 ppm/°C reference, giving a full-scale output range of 5 V ...
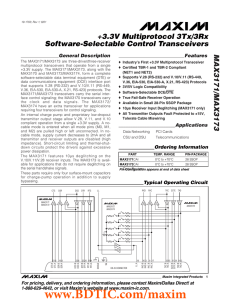
MAX3171/MAX3173 +3.3V Multiprotocol 3Tx/3Rx Software-Selectable Control Transceivers General Description
... An internal charge pump and proprietary low-dropout transmitter output stage allow V.28, V.11, and V.10 compliant operation from a single +3.3V supply. A nocable mode is entered when all mode pins (M0, M1, and M2) are pulled high or left unconnected. In nocable mode, supply current decreases to 2mA ...
... An internal charge pump and proprietary low-dropout transmitter output stage allow V.28, V.11, and V.10 compliant operation from a single +3.3V supply. A nocable mode is entered when all mode pins (M0, M1, and M2) are pulled high or left unconnected. In nocable mode, supply current decreases to 2mA ...
Modulation and Demodulation
... rier itself and two other steady frequencies i.e. fc + fs and fc − fs. Let us illustrate sideband frequencies with an example. Suppose the carrier frequency is 400 kHz and the signal frequency is 1 kHz. The AM wave will contain three frequencies viz 400 kHz, 401 kHz and 399 kHz. It is clear that upp ...
... rier itself and two other steady frequencies i.e. fc + fs and fc − fs. Let us illustrate sideband frequencies with an example. Suppose the carrier frequency is 400 kHz and the signal frequency is 1 kHz. The AM wave will contain three frequencies viz 400 kHz, 401 kHz and 399 kHz. It is clear that upp ...
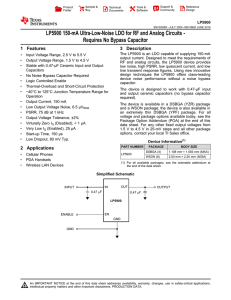
LP5900 - Texas Instruments
... JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process. ...
... JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process. ...
HS2313011312
... stage that is comprised of the two cross coupled inverters, where each input is connected to the output of the other. It operates in two phases.1) Interface phase and 2) Regeneration phase. It consists of single nmos tail transistor connected to ground. When clock is low tail transistor is off and d ...
... stage that is comprised of the two cross coupled inverters, where each input is connected to the output of the other. It operates in two phases.1) Interface phase and 2) Regeneration phase. It consists of single nmos tail transistor connected to ground. When clock is low tail transistor is off and d ...
LTC4370 - Two-Supply Diode-OR Current
... approximately 10 to 50 times the gate capacitance (CISS) of the MOSFET switch. Maintain low board leakage on this pin for best load sharing accuracy. For example, 100nA of leakage current (equal to 1V across 10MΩ) increases the error amplifier offset by 0.7mV. Leave this pin open if only using ideal ...
... approximately 10 to 50 times the gate capacitance (CISS) of the MOSFET switch. Maintain low board leakage on this pin for best load sharing accuracy. For example, 100nA of leakage current (equal to 1V across 10MΩ) increases the error amplifier offset by 0.7mV. Leave this pin open if only using ideal ...
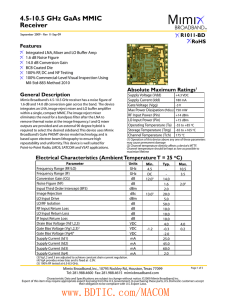
4.5-10.5 GHz GaAs MMIC Receiver Features
... Mimix Broadband’s 4.5-10.5 GHz receiver has a noise figure of 1.6 dB and 14.0 dB conversion gain across the band. The device integrates an LNA, image reject mixer and LO buffer amplifier within a single, compact MMIC. The image reject mixer eliminates the need for a bandpass filter after the LNA to ...
... Mimix Broadband’s 4.5-10.5 GHz receiver has a noise figure of 1.6 dB and 14.0 dB conversion gain across the band. The device integrates an LNA, image reject mixer and LO buffer amplifier within a single, compact MMIC. The image reject mixer eliminates the need for a bandpass filter after the LNA to ...
J. Santiago-Gonzalez, K.M. Elbaggari, K.K. Afridi and D.J. Perreault, “Design of Class E Resonant Rectifiers and Diode Evaluation for VHF Power Conversion,” IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, Vol.30, No. 9, pp. 4960-4972, 2015.
... impedance [3,11]. This paper introduces a design method for realizing class E rectifiers that provide near-resistive input impedance over a wide range of output power levels. Experimental validation of the proposed method is also provided along with its limitations. The selection of a diode is also ...
... impedance [3,11]. This paper introduces a design method for realizing class E rectifiers that provide near-resistive input impedance over a wide range of output power levels. Experimental validation of the proposed method is also provided along with its limitations. The selection of a diode is also ...
SIMULATION OF THREE, FIVE, SEVEN, NINE, ELEVEN, THIRTEEN
... multilevel converters are neither operable nor complete for real (active) power conversion because they all depend on outside circuits for voltage balancing. For the number of levels (M) no greater than 3 (i.e., M13), or some applications such as reactive and harmonic compensation in power systems, ...
... multilevel converters are neither operable nor complete for real (active) power conversion because they all depend on outside circuits for voltage balancing. For the number of levels (M) no greater than 3 (i.e., M13), or some applications such as reactive and harmonic compensation in power systems, ...
A Designer`s Guide to Instrumentation Amplifiers, 3rd Edition
... A High Speed In-Amp Circuit for Data Acquisition . ............................................................................... 7-8 APPENDIX A—INSTRUMENTATION AMPLIFIER SPECIFICATIONS ......................................... A-1 (A) Specifications (Conditions) .............................. ...
... A High Speed In-Amp Circuit for Data Acquisition . ............................................................................... 7-8 APPENDIX A—INSTRUMENTATION AMPLIFIER SPECIFICATIONS ......................................... A-1 (A) Specifications (Conditions) .............................. ...
LTM8029 - 36VIN, 600mA Step-Down μModule Converter with 5μA Quiescent Current
... typically 5μA at no load and 12VIN. Since the LTM8029 is mostly shut down between bursts, the effective switching frequency will be lower than that programmed at the RT pin. For the same reason, the output ripple will be different than when the part is running at the full programmed frequency. The L ...
... typically 5μA at no load and 12VIN. Since the LTM8029 is mostly shut down between bursts, the effective switching frequency will be lower than that programmed at the RT pin. For the same reason, the output ripple will be different than when the part is running at the full programmed frequency. The L ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).