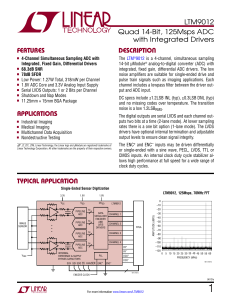
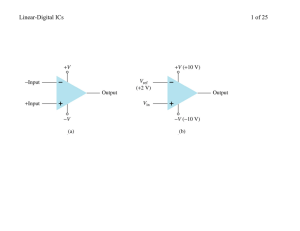
A Designer`s Guide to Instrumentation Amplifiers, 3rd Edition
... A High Speed In-Amp Circuit for Data Acquisition . ............................................................................... 7-8 APPENDIX A—INSTRUMENTATION AMPLIFIER SPECIFICATIONS ......................................... A-1 (A) Specifications (Conditions) .............................. ...
... A High Speed In-Amp Circuit for Data Acquisition . ............................................................................... 7-8 APPENDIX A—INSTRUMENTATION AMPLIFIER SPECIFICATIONS ......................................... A-1 (A) Specifications (Conditions) .............................. ...
UCC28950 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... • The voltage on the soft-start capacitor is not below 0.55 V typical. If all those conditions are met, an internal enable signal EN is generated that initiates the soft start process. The duty cycle during the soft start is defined by the voltage at the SS pin, and cannot be lower than the duty cyc ...
... • The voltage on the soft-start capacitor is not below 0.55 V typical. If all those conditions are met, an internal enable signal EN is generated that initiates the soft start process. The duty cycle during the soft start is defined by the voltage at the SS pin, and cannot be lower than the duty cyc ...
TM 11–6625–2781–14–6
... 1-16. Adjustment or repair of the opened instrument with the ac power connected should be avoided as much as possible and, when inevitable, should be performed only by a skilled person who knows the hazard involved. 1-17. Make sure only fuses of the required current rating and type (normal blow, tim ...
... 1-16. Adjustment or repair of the opened instrument with the ac power connected should be avoided as much as possible and, when inevitable, should be performed only by a skilled person who knows the hazard involved. 1-17. Make sure only fuses of the required current rating and type (normal blow, tim ...
RF Microelectronic
... Images of these noises also translated to IF 1/f noise here is not problematic because of the low frequency. It is up converted. Going to LO frequency, it is filtered IF filter sets the BW, so only this value is taken from noise (e.g. 30KHz in GSM) When each of the two switches in on instantaneously ...
... Images of these noises also translated to IF 1/f noise here is not problematic because of the low frequency. It is up converted. Going to LO frequency, it is filtered IF filter sets the BW, so only this value is taken from noise (e.g. 30KHz in GSM) When each of the two switches in on instantaneously ...
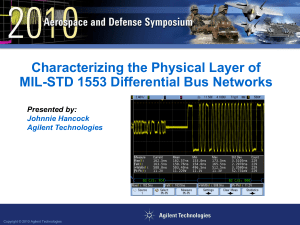
Triggering on MIL-STD 1553 Signals
... The electrical/physical layer of MIL-STD 1553 networks should be characterized to insure good signal integrity for reliable communication. Using an oscilloscope with built-in MIL-STD 1553 triggering and decoding will enhance your ability to quickly window-in on specific transmitted and received ...
... The electrical/physical layer of MIL-STD 1553 networks should be characterized to insure good signal integrity for reliable communication. Using an oscilloscope with built-in MIL-STD 1553 triggering and decoding will enhance your ability to quickly window-in on specific transmitted and received ...
LMV1088 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... 3.5Vpp at the output of the LMV1088. This level is higher then maximum level hat is allowed at the input of the Post Amp of the LMV1088. Therefore the Pre Amp gain has to be reduced, to 1.4Vpp minus 9dB = 0.5Vpp. This limits the Pre Amp gain to a maximum of 20dB. 5. The baseband chip limits the maxi ...
... 3.5Vpp at the output of the LMV1088. This level is higher then maximum level hat is allowed at the input of the Post Amp of the LMV1088. Therefore the Pre Amp gain has to be reduced, to 1.4Vpp minus 9dB = 0.5Vpp. This limits the Pre Amp gain to a maximum of 20dB. 5. The baseband chip limits the maxi ...
Capacitor
... Whereas the resistor behaves all the “same” in AC or DC regimes, the capacitor doesn't - a capacitor will in general not conduct DC current, so it's influence becomes obvious only in AC and signal regime. ...
... Whereas the resistor behaves all the “same” in AC or DC regimes, the capacitor doesn't - a capacitor will in general not conduct DC current, so it's influence becomes obvious only in AC and signal regime. ...
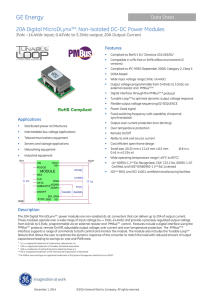
GE Energy 20A Digital MicroDLynx : Non-Isolated DC-DC Power Modules Data Sheet
... These modules operate over a wide range of input voltage (VIN = 3Vdc-14.4Vdc) and provide a precisely regulated output voltage from 0.6Vdc to 5.5Vdc, programmable via an external resistor and PMBusTM control. Features include a digital interface using the PMBusTM protocol, remote On/Off, adjustable ...
... These modules operate over a wide range of input voltage (VIN = 3Vdc-14.4Vdc) and provide a precisely regulated output voltage from 0.6Vdc to 5.5Vdc, programmable via an external resistor and PMBusTM control. Features include a digital interface using the PMBusTM protocol, remote On/Off, adjustable ...
SN74GTLPH16916 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... backplanes, unevenly distributed cards, or empty slots during low-to-high signal transitions. This improves signal integrity, which allows adequate noise margin to be maintained at higher frequencies. Active bus-hold circuitry holds unused or undriven LVTTL data inputs at a valid logic state. Use of ...
... backplanes, unevenly distributed cards, or empty slots during low-to-high signal transitions. This improves signal integrity, which allows adequate noise margin to be maintained at higher frequencies. Active bus-hold circuitry holds unused or undriven LVTTL data inputs at a valid logic state. Use of ...
Full PowerPoint
... • Now we can find “propagation delay” tp; the time between the input reaching 50% of its final value and the output to reaching 50% of final value. • Today’s case, using “perfect input” (50% reached at t=0): 0.5 = e-tp tp = - ln 0.5 = 0.69 It takes 0.69 time constants, or 0.69 RC. • We can find the ...
... • Now we can find “propagation delay” tp; the time between the input reaching 50% of its final value and the output to reaching 50% of final value. • Today’s case, using “perfect input” (50% reached at t=0): 0.5 = e-tp tp = - ln 0.5 = 0.69 It takes 0.69 time constants, or 0.69 RC. • We can find the ...
chapter 05 Low Noise Amplifiers
... In the circuit of figure below, the PMOS current source is converted to an “active load,” amplifying the input signal. The idea is that, if M2 amplifies the input in addition to injecting noise to the output, then the noise figure may be lower. Neglecting channel-length modulation, calculate the noi ...
... In the circuit of figure below, the PMOS current source is converted to an “active load,” amplifying the input signal. The idea is that, if M2 amplifies the input in addition to injecting noise to the output, then the noise figure may be lower. Neglecting channel-length modulation, calculate the noi ...
1.5A, 24V, 17MHz POWER OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER OPA564 FEATURES
... amplifier that is ideal for driving up to 1.5A into reactive loads. The high slew rate provides 1.3MHz full-power bandwidth and excellent linearity. These monolithic integrated circuits provide high reliability in demanding powerline communications and motor control applications. The OPA564 operates ...
... amplifier that is ideal for driving up to 1.5A into reactive loads. The high slew rate provides 1.3MHz full-power bandwidth and excellent linearity. These monolithic integrated circuits provide high reliability in demanding powerline communications and motor control applications. The OPA564 operates ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).