SMP18
... Note that several specifications, including acquisition time, offset and output voltage compliance, will degrade for supply voltages of less than 7 V. If split supplies are used, the negative supply should be bypassed with a 0.1 µF capacitor in parallel with a 10 µF to ground. The internal hold capa ...
... Note that several specifications, including acquisition time, offset and output voltage compliance, will degrade for supply voltages of less than 7 V. If split supplies are used, the negative supply should be bypassed with a 0.1 µF capacitor in parallel with a 10 µF to ground. The internal hold capa ...
AN614: A Simple Alternative to Analog Isolation
... ISOamps are hybridized devices that contain linear input and output circuits separated by an internal isolation barrier. ISOamps typically modulate the linear input signal and transmit the resulting digital information across the isolation barrier to a demodulator where it is converted back to analo ...
... ISOamps are hybridized devices that contain linear input and output circuits separated by an internal isolation barrier. ISOamps typically modulate the linear input signal and transmit the resulting digital information across the isolation barrier to a demodulator where it is converted back to analo ...
DN254 - LT1806: 325MHz Low Noise Rail-to-Rail SOT-23 Op Amp Saves Board Space
... bandwidth and noise performance achieved with several large-area photodiodes (and a small-area SFH213 for comparison). Note that large-area detectors also place extra demands on the gain bandwidth of an amplifier. The final case in Table 1 shows a 1MΩ transimpedance amplifier with 650kHz bandwidth f ...
... bandwidth and noise performance achieved with several large-area photodiodes (and a small-area SFH213 for comparison). Note that large-area detectors also place extra demands on the gain bandwidth of an amplifier. The final case in Table 1 shows a 1MΩ transimpedance amplifier with 650kHz bandwidth f ...
FAQs for SmartLEWIS RX+ family: TDA5240, TDA5235, TDA5225
... The 5V-to-3.3V regulator needs a slew rate limitation at power-up. Steep slew rates at VDD5V in 5V supply mode cannot be regulated and therefore higher voltages than allowed could result across voltage regulator. For avoiding this, slew rate limitation can be applied with an RC low-pass (22Ohm + 1µF ...
... The 5V-to-3.3V regulator needs a slew rate limitation at power-up. Steep slew rates at VDD5V in 5V supply mode cannot be regulated and therefore higher voltages than allowed could result across voltage regulator. For avoiding this, slew rate limitation can be applied with an RC low-pass (22Ohm + 1µF ...
ADS7834 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... manner, synchronous to the CLK input. The result is provided most significant bit first and represents the result of the conversion currently in progress—there is no pipeline delay. By properly controlling the CONV and CLK inputs, it is possible to obtain the digital result least significant bit fir ...
... manner, synchronous to the CLK input. The result is provided most significant bit first and represents the result of the conversion currently in progress—there is no pipeline delay. By properly controlling the CONV and CLK inputs, it is possible to obtain the digital result least significant bit fir ...
Introduction to Comparators
... A basic circuit for TPD measurement is shown in Figure 16. One DC power supply is used for VCC biasing, and a second one for VICM voltage. If the measurement is performed at VICM = 0 V, the source can be removed and the inverting pin directly connected to ground. To keep low source impedance and pre ...
... A basic circuit for TPD measurement is shown in Figure 16. One DC power supply is used for VCC biasing, and a second one for VICM voltage. If the measurement is performed at VICM = 0 V, the source can be removed and the inverting pin directly connected to ground. To keep low source impedance and pre ...
OP-AMP
... when the feedback resistor (Rf) is zero. The Op-Amp operates as a comparator and not as a linear amplifier. ...
... when the feedback resistor (Rf) is zero. The Op-Amp operates as a comparator and not as a linear amplifier. ...
Frequency input signal conditioner
... pushes the CAL button while the INPUT LED is lit. The low input frequency is then input and pushing the CAL button again stores the low frequency input. The high and low ranges are stored in non-volatile memory and correspond to the high and low output range which is selected via DIP switches. To pr ...
... pushes the CAL button while the INPUT LED is lit. The low input frequency is then input and pushing the CAL button again stores the low frequency input. The high and low ranges are stored in non-volatile memory and correspond to the high and low output range which is selected via DIP switches. To pr ...
OPA177 Precision OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER FEATURES
... free from oscillations in the widest range of circuitry. Applications with noisy or high impedance power supply lines may require decoupling capacitors close to the device pins. In most cases 0.1µF ceramic capacitors are adequate. The OPA177 has very low offset voltage and drift. To achieve highest ...
... free from oscillations in the widest range of circuitry. Applications with noisy or high impedance power supply lines may require decoupling capacitors close to the device pins. In most cases 0.1µF ceramic capacitors are adequate. The OPA177 has very low offset voltage and drift. To achieve highest ...
Lab 16 - ece.unm.edu
... and 16-2 respectively. The JFET CS and CD amplifiers are comparable in operation to the MOSFET CS and CD configurations. The amplifier characteristics of the JFET CS and CD circuits can also be compared to the BJT CE and CC circuits respectively. The main advantage JFET amplifiers have over BJT ampl ...
... and 16-2 respectively. The JFET CS and CD amplifiers are comparable in operation to the MOSFET CS and CD configurations. The amplifier characteristics of the JFET CS and CD circuits can also be compared to the BJT CE and CC circuits respectively. The main advantage JFET amplifiers have over BJT ampl ...
TRF2052 - uri=media.digikey
... channel for IF frequencies. The current-output charge pumps directly drive passive RC filter networks, to generate VCO control voltages. Fast main-channel frequency switching is achieved with a charge pump arrangement that increases the current drive and alters the loop-filter frequency response dur ...
... channel for IF frequencies. The current-output charge pumps directly drive passive RC filter networks, to generate VCO control voltages. Fast main-channel frequency switching is achieved with a charge pump arrangement that increases the current drive and alters the loop-filter frequency response dur ...
Power Meter PM800
... D IN (Digital Input) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A OUT (Analog Output) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A IN (Analog Input) . . . . . . . . . ...
... D IN (Digital Input) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A OUT (Analog Output) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A IN (Analog Input) . . . . . . . . . ...
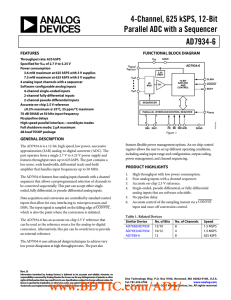
4-Channel, 625 kSPS, 12-Bit Parallel ADC with a Sequencer AD7934-6
... mode just prior to the falling edge of BUSY, on the 13th rising edge of CLKIN (see Figure 34). Master Clock Input. The clock source for the conversion process is applied to this pin. Conversion time for the AD7934-6 takes 13 clock cycles + t2. The frequency of the master clock input therefore determ ...
... mode just prior to the falling edge of BUSY, on the 13th rising edge of CLKIN (see Figure 34). Master Clock Input. The clock source for the conversion process is applied to this pin. Conversion time for the AD7934-6 takes 13 clock cycles + t2. The frequency of the master clock input therefore determ ...
AD6630 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... filters are largely capacitive in nature. Normally a conjugate match to the load is desired for maximum power transfer. Another way to treat the problem is to make the SAW filter look purely resistive. If the SAW filter load looks resistive there is no lead or lag in the current vs. voltage. This ma ...
... filters are largely capacitive in nature. Normally a conjugate match to the load is desired for maximum power transfer. Another way to treat the problem is to make the SAW filter look purely resistive. If the SAW filter load looks resistive there is no lead or lag in the current vs. voltage. This ma ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).