LM111/LM211/LM311 Voltage Comparator
... crossing-point. This is due to the high gain and wide bandwidth of comparators like the LM111. To avoid oscillation or instability in such a usage, several precautions are recommended, as shown in Figure 1 below. 1. The trim pins (pins 5 and 6) act as unwanted auxiliary inputs. If these pins are not ...
... crossing-point. This is due to the high gain and wide bandwidth of comparators like the LM111. To avoid oscillation or instability in such a usage, several precautions are recommended, as shown in Figure 1 below. 1. The trim pins (pins 5 and 6) act as unwanted auxiliary inputs. If these pins are not ...
Section H5: High-Frequency Amplifier Response
... slightly different notation and taking a different approach than your author. As usual, if this results in confusion, or you are more comfortable with his technique, let me know and we’ll work it out. High Frequency Response of the CE and ER Amplifier The generic common-emitter amplifier circuit of ...
... slightly different notation and taking a different approach than your author. As usual, if this results in confusion, or you are more comfortable with his technique, let me know and we’ll work it out. High Frequency Response of the CE and ER Amplifier The generic common-emitter amplifier circuit of ...
Evaluates: MAX5072 MAX5072 Evaluation Kit General Description Features
... necessary to evaluate the performance of the MAX5072. The MAX5072 is a dual-output DC-DC converter. One of the outputs is configured as a step-down converter (converter 1), while converter 2 is configured as a step-up converter. The EV kit is powered from a DC supply providing 5.5V to 16V. The EV ki ...
... necessary to evaluate the performance of the MAX5072. The MAX5072 is a dual-output DC-DC converter. One of the outputs is configured as a step-down converter (converter 1), while converter 2 is configured as a step-up converter. The EV kit is powered from a DC supply providing 5.5V to 16V. The EV ki ...
AD96685 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... should not be allowed to “float.” The high internal gain may cause the output to oscillate (possibly affecting the other comparator which is being used) unless the output is forced into a fixed state. This is easily accomplished by ensuring that the two inputs are at least one diode drop apart, whil ...
... should not be allowed to “float.” The high internal gain may cause the output to oscillate (possibly affecting the other comparator which is being used) unless the output is forced into a fixed state. This is easily accomplished by ensuring that the two inputs are at least one diode drop apart, whil ...
ElektorElectronics-1..
... noise voltage is directly proportional to the bandwidth. This allows a lower amount of IF gain to be used, which also results in less noise. In this way we manage to achieve a noise floor of approximately –80 dBm. The mixer must have an output impedance of 50 Ω in order to properly match the impedan ...
... noise voltage is directly proportional to the bandwidth. This allows a lower amount of IF gain to be used, which also results in less noise. In this way we manage to achieve a noise floor of approximately –80 dBm. The mixer must have an output impedance of 50 Ω in order to properly match the impedan ...
MAX5436–MAX5439 ±15V, 128-Tap, Low-Drift Digital Potentiometers General Description Features
... +5.25V supply voltage (VCC). The resistor string uses its own analog supplies (V DD and V SS ) that require VDD - VSS to be greater than 9V and less than 31.5V. This allows for greater flexibility in voltage ranges that can be used with these devices. Examples of analog supply ranges include not onl ...
... +5.25V supply voltage (VCC). The resistor string uses its own analog supplies (V DD and V SS ) that require VDD - VSS to be greater than 9V and less than 31.5V. This allows for greater flexibility in voltage ranges that can be used with these devices. Examples of analog supply ranges include not onl ...
LMV851 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... National’s LMV851/LMV852/LMV854 are CMOS input, low power op amp ICs, providing a low input bias current, a wide temperature range of −40°C to +125°C and exceptional performance, making them robust general purpose parts. Additionally, the LMV851/LMV852/LMV854 are EMI hardened to minimize any interfe ...
... National’s LMV851/LMV852/LMV854 are CMOS input, low power op amp ICs, providing a low input bias current, a wide temperature range of −40°C to +125°C and exceptional performance, making them robust general purpose parts. Additionally, the LMV851/LMV852/LMV854 are EMI hardened to minimize any interfe ...
Action PAK AP4351 ® Thermocouple-Input,
... The AP4351 isolating thermocouple conditioner offers wide ranging input and output capability. The AP4351 can be field configured by the user to accept input from thermocouple types J, K, T, R, S, E, and B and to provide current or voltage output. The output is linearized to temperature according to ...
... The AP4351 isolating thermocouple conditioner offers wide ranging input and output capability. The AP4351 can be field configured by the user to accept input from thermocouple types J, K, T, R, S, E, and B and to provide current or voltage output. The output is linearized to temperature according to ...
AD8038
... a high slew rate of 425 V/µs and low input offset voltage of 3 mV max. ADI’s proprietary XFCB process allows low noise operation (8 nV/√Hz and 600 fA/√Hz) at extremely low quiescent currents. Given a wide supply voltage range (3 V to 12 V), wide bandwidth, and small packaging, the AD8038 and AD8039 ...
... a high slew rate of 425 V/µs and low input offset voltage of 3 mV max. ADI’s proprietary XFCB process allows low noise operation (8 nV/√Hz and 600 fA/√Hz) at extremely low quiescent currents. Given a wide supply voltage range (3 V to 12 V), wide bandwidth, and small packaging, the AD8038 and AD8039 ...
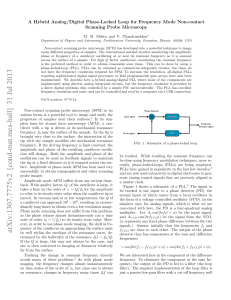
A Hybrid Analog/Digital Phase-Locked Loop for Frequency Mode
... reference mode, and the signal from the SPM transducer to the LIA input. The in-phase or ‘X’ output of the LIA is then the required output of the phase detector. In most cases, the LIA provides a low pass filter on this output whose time constant can be adjusted, so that in essence the LIA also inco ...
... reference mode, and the signal from the SPM transducer to the LIA input. The in-phase or ‘X’ output of the LIA is then the required output of the phase detector. In most cases, the LIA provides a low pass filter on this output whose time constant can be adjusted, so that in essence the LIA also inco ...
MAX44242 20V, Low Input Bias-Current, Low
... The device interfaces to both current-output sensors (photodiodes) (Figure 1), and high-impedance voltage sources (piezoelectric sensors). For current output sensors, a transimpedance amplifier is the most noise-efficient method for converting the input signal to a voltage. High-value feedback resis ...
... The device interfaces to both current-output sensors (photodiodes) (Figure 1), and high-impedance voltage sources (piezoelectric sensors). For current output sensors, a transimpedance amplifier is the most noise-efficient method for converting the input signal to a voltage. High-value feedback resis ...
Digital Electronics - Dr. Imtiaz Hussain
... common, high-speed data communications bus which interconnects any or all devices within the local area. LANs are commonly used in business applications to allow several users to share costly software packages and peripheral equipment such as printers and hard disk storage. ...
... common, high-speed data communications bus which interconnects any or all devices within the local area. LANs are commonly used in business applications to allow several users to share costly software packages and peripheral equipment such as printers and hard disk storage. ...
LTC1069-6 - Single Supply, Very Low Power, Elliptic Lowpass Filter
... (±10%) is an adequate clock source for the device. The power supply for the clock source should not necessarily be the filter’s power supply. The analog ground of the filter should be connected to the clock’s ground at a single point only. Table 1 shows the clock’s low and high level threshold value f ...
... (±10%) is an adequate clock source for the device. The power supply for the clock source should not necessarily be the filter’s power supply. The analog ground of the filter should be connected to the clock’s ground at a single point only. Table 1 shows the clock’s low and high level threshold value f ...
IEEE Transactions on Magnetics
... advantage that is evident from the figure is that the multiphase configuration allows the combination of output capacitor from each individual boost into just a single capacitor Co. Due to the frequency multiplication property of the multiphase, the output voltage will actually have ripple component ...
... advantage that is evident from the figure is that the multiphase configuration allows the combination of output capacitor from each individual boost into just a single capacitor Co. Due to the frequency multiplication property of the multiphase, the output voltage will actually have ripple component ...
Adaptive signal sampling for high throughput, broadband
... Having a high sampling frequency at the beginning is essential while with longer time after the step no further information appear. Therefore, the sampling rate can gradually cease (Fig.5) without losing information. An often underestimated problem is the high frequency noise present even at the slo ...
... Having a high sampling frequency at the beginning is essential while with longer time after the step no further information appear. Therefore, the sampling rate can gradually cease (Fig.5) without losing information. An often underestimated problem is the high frequency noise present even at the slo ...
A network analyzer (150MHz)
... The AD9951 needs a REFCLOCK (here 400MHz or 20MHz), 4 control lines SDIO_LO, SCLK, RESET, I/OUPDATE and two power supply : +3.3V and 1.8V . A transistor (BFR520) amplifies the differential signal present on the outputs ( IOUT and IOUT ). A low-pass filter (with a cut-off frequency of 150 MHz) keeps ...
... The AD9951 needs a REFCLOCK (here 400MHz or 20MHz), 4 control lines SDIO_LO, SCLK, RESET, I/OUPDATE and two power supply : +3.3V and 1.8V . A transistor (BFR520) amplifies the differential signal present on the outputs ( IOUT and IOUT ). A low-pass filter (with a cut-off frequency of 150 MHz) keeps ...
RPM971-H14
... Notes No technical content pages of this document may be reproduced in any form or transmitted by any means without prior permission of ROHM CO.,LTD. The contents described herein are subject to change without notice. The specifications for the product described in this document are for reference on ...
... Notes No technical content pages of this document may be reproduced in any form or transmitted by any means without prior permission of ROHM CO.,LTD. The contents described herein are subject to change without notice. The specifications for the product described in this document are for reference on ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).