Basic BJT Amplifier
... If BJT with VBE=0.7 V is used, IB=9.5 μA & IC=0.95 mA But, if new BJT with VBE=0.6 V is used, IB=26 μA & BJT goes into saturation; which is not acceptable Previous circuit is not practical So, the emitter resistor is included: Q-point is stabilized against variations in β, as will the voltage gain ...
... If BJT with VBE=0.7 V is used, IB=9.5 μA & IC=0.95 mA But, if new BJT with VBE=0.6 V is used, IB=26 μA & BJT goes into saturation; which is not acceptable Previous circuit is not practical So, the emitter resistor is included: Q-point is stabilized against variations in β, as will the voltage gain ...
L6370
... deactivates itself. The following actions are taken: all the output stage is switched off; the signal DIAG2 is activated (active low). Normal operation is resumed as soon as (typically after some seconds) the chip temperature monitored goes back below Θlim-ΘH. The different thresholds with hystereti ...
... deactivates itself. The following actions are taken: all the output stage is switched off; the signal DIAG2 is activated (active low). Normal operation is resumed as soon as (typically after some seconds) the chip temperature monitored goes back below Θlim-ΘH. The different thresholds with hystereti ...
2350 POWER SERIES Selector Guide
... The 2350 Power Series offers a full range of power measurement instruments with unsurpassed accuracy in a compact DIN case. Single function 3 1/2 digit panel meters are available in a 1/8 DIN case with optional isolated analog output and fixed zeros as display multipliers. The model 2354 multifunct ...
... The 2350 Power Series offers a full range of power measurement instruments with unsurpassed accuracy in a compact DIN case. Single function 3 1/2 digit panel meters are available in a 1/8 DIN case with optional isolated analog output and fixed zeros as display multipliers. The model 2354 multifunct ...
Very wide input voltage range 6 W SMPS for metering
... Base drive circuit design Let's have a closer look at the very simple base drive network used in this application. Normally in applications such SMPS, where the load is variable, the collector current varies as well. It is very important to provide a base current to the device that is correlated wit ...
... Base drive circuit design Let's have a closer look at the very simple base drive network used in this application. Normally in applications such SMPS, where the load is variable, the collector current varies as well. It is very important to provide a base current to the device that is correlated wit ...
RC Filter Networks
... experimental error. The frequency corresponding to the half-power point of the low-pass filter was found to be at f = 1102Hz, while the phase difference at this frequency was found to be HPP 0.748 0.003 . While the latter result does not agree with the theory, the experimental error is very sm ...
... experimental error. The frequency corresponding to the half-power point of the low-pass filter was found to be at f = 1102Hz, while the phase difference at this frequency was found to be HPP 0.748 0.003 . While the latter result does not agree with the theory, the experimental error is very sm ...
LT6236/LT6237 - Rail-to-Rail Output 215MHz, 1.1nV/√Hz Op Amp/SAR ADC Driver
... output op amps that feature 1.1nV/√Hz input referred noise voltage density and draw only 3.5mA of supply current per amplifier. These amplifiers combine very low noise and supply current with a 215MHz gain bandwidth product and a 70V/μs slew rate. Low noise, fast settling time and low offset voltage ...
... output op amps that feature 1.1nV/√Hz input referred noise voltage density and draw only 3.5mA of supply current per amplifier. These amplifiers combine very low noise and supply current with a 215MHz gain bandwidth product and a 70V/μs slew rate. Low noise, fast settling time and low offset voltage ...
Data Sheet Features General Description
... 5.1 The VIN quiescent current loss comprises two parts: the DC bias current as given in the electrical characteristics and the internal MOSFET switch gate charge currents. The gate charge current results from switching the gate capacitance of the internal power MOSFET switches. Each cycle the gate i ...
... 5.1 The VIN quiescent current loss comprises two parts: the DC bias current as given in the electrical characteristics and the internal MOSFET switch gate charge currents. The gate charge current results from switching the gate capacitance of the internal power MOSFET switches. Each cycle the gate i ...
30A - SynQor
... is a next-generation, board-mountable, isolated, fixed switching frequency DC/DC converter that uses synchronous rectification to achieve extremely high conversion efficiency. The power dissipated by the converter is so low that a heatsink is not required, which saves cost, weight, height, and appli ...
... is a next-generation, board-mountable, isolated, fixed switching frequency DC/DC converter that uses synchronous rectification to achieve extremely high conversion efficiency. The power dissipated by the converter is so low that a heatsink is not required, which saves cost, weight, height, and appli ...
+3 V/+5 V, Dual, Serial Input 12-Bit DAC AD7394
... The AD7394 is a pin compatible, dual, 12-bit digital-to-analog converter. This single-supply operation device consumes less than 200 microamps of current while operating from power supplies in the 2.7 V to 5.5 V range, making it ideal for batteryoperated applications. The AD7394 contains a voltage-s ...
... The AD7394 is a pin compatible, dual, 12-bit digital-to-analog converter. This single-supply operation device consumes less than 200 microamps of current while operating from power supplies in the 2.7 V to 5.5 V range, making it ideal for batteryoperated applications. The AD7394 contains a voltage-s ...
TPS54917 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... regulators, the TPS54917 low-input voltage high-output current synchronous buck PWM converter offers the same features as the TPS54910 in a smaller package and higher switching frequency, which allows for a smaller total solution. Included on the substrate with the listed features are a true, high p ...
... regulators, the TPS54917 low-input voltage high-output current synchronous buck PWM converter offers the same features as the TPS54910 in a smaller package and higher switching frequency, which allows for a smaller total solution. Included on the substrate with the listed features are a true, high p ...
HMC678LC3C 数据资料DataSheet下载
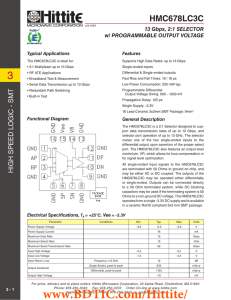
... The HMC678LC3C is a 2:1 Selector designed to support data transmission rates of up to 13 Gbps, and selector port operation of up to 13 GHz. The selector routes one of the two single-ended inputs to the differential output upon assertion of the proper select port. The HMC678LC3C also features an outp ...
... The HMC678LC3C is a 2:1 Selector designed to support data transmission rates of up to 13 Gbps, and selector port operation of up to 13 GHz. The selector routes one of the two single-ended inputs to the differential output upon assertion of the proper select port. The HMC678LC3C also features an outp ...
MAX5102 +2.7V to +5.5V, Low-Power, Dual, Parallel General Description
... Note 2: Gain error is: [100 (VF0,meas - ZCE - VF0,ideal) / VREF]. Where VF0,meas is the DAC output voltage with input code F0 hex, and VF0,ideal is the ideal DAC output voltage with input code F0 hex (i.e., VREF · 240 / 256). Note 3: Output settling time is measured from the 50% point of the falling ...
... Note 2: Gain error is: [100 (VF0,meas - ZCE - VF0,ideal) / VREF]. Where VF0,meas is the DAC output voltage with input code F0 hex, and VF0,ideal is the ideal DAC output voltage with input code F0 hex (i.e., VREF · 240 / 256). Note 3: Output settling time is measured from the 50% point of the falling ...
AK4687EQ Datasheet
... The AK4687 has two audio serial interfaces (PORT1 and PORT2) which can be operated asynchronously. The PORT2 is the audio data interface for DAC, and the PORT1 is for ADC. At each PORT, the external clocks, which are required to operate the AK4687 in slave mode, are MCLK1 (MCLK2), LRCK1 (LRCK2) and ...
... The AK4687 has two audio serial interfaces (PORT1 and PORT2) which can be operated asynchronously. The PORT2 is the audio data interface for DAC, and the PORT1 is for ADC. At each PORT, the external clocks, which are required to operate the AK4687 in slave mode, are MCLK1 (MCLK2), LRCK1 (LRCK2) and ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).