MAX710/MAX711 3.3V/5V or Adjustable, Step-Up/Down DC
... voltage, the output will linear regulate down to the selected output voltage. The MAX711’s adjustable output voltage is set by two resistors, R1 and R2 (Figure 3), which form a voltage divider between the output and FB. Use the following equation to determine the resistor values: R1 = R2 [(VOUT / VR ...
... voltage, the output will linear regulate down to the selected output voltage. The MAX711’s adjustable output voltage is set by two resistors, R1 and R2 (Figure 3), which form a voltage divider between the output and FB. Use the following equation to determine the resistor values: R1 = R2 [(VOUT / VR ...
EDM-M - Duplomatic Oleodinamica
... ok OUTPUT”, located on pin 9 (referred to zero power supply, pin 15) with load resistance of 220 KΩ and max current 100 mA . When the card works normally, on this pin there is the same voltage as the power supply; when there is an anomaly, the output voltage is zero. The anomalies could be: - low vo ...
... ok OUTPUT”, located on pin 9 (referred to zero power supply, pin 15) with load resistance of 220 KΩ and max current 100 mA . When the card works normally, on this pin there is the same voltage as the power supply; when there is an anomaly, the output voltage is zero. The anomalies could be: - low vo ...
OP37
... OP37 Series units may be inserted directly into 725 and OP07 sockets with or without removal of external compensation or nulling components. Additionally, the OP37 may be fitted to unnulled 741type sockets; however, if conventional 741 nulling circuitry is in use, it should be modified or removed to ...
... OP37 Series units may be inserted directly into 725 and OP07 sockets with or without removal of external compensation or nulling components. Additionally, the OP37 may be fitted to unnulled 741type sockets; however, if conventional 741 nulling circuitry is in use, it should be modified or removed to ...
ADG752 数据手册DataSheet下载
... The ADG752 is designed on a submicron process that provides low power dissipation yet gives high switching speed and low on resistance. This part is a fully bidirectional switch and can handle signals up to and including the supply rails. Break-before-make switching action ensures the input signals ...
... The ADG752 is designed on a submicron process that provides low power dissipation yet gives high switching speed and low on resistance. This part is a fully bidirectional switch and can handle signals up to and including the supply rails. Break-before-make switching action ensures the input signals ...
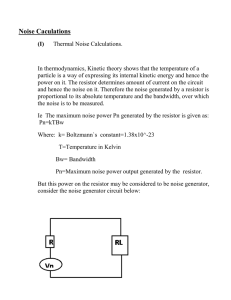
Noise Caculations (I) Thermal Noise Calculations. In
... The noise factor is expressed as a dimensionless ratio. “The noise factor, at a specified input frequency, is defined as the ratio of the total noise power per unit bandwidth available at the output port when noise temperature of the input termination is standard (290 K) to that portion produced a ...
... The noise factor is expressed as a dimensionless ratio. “The noise factor, at a specified input frequency, is defined as the ratio of the total noise power per unit bandwidth available at the output port when noise temperature of the input termination is standard (290 K) to that portion produced a ...
MAX4503/MAX4504 Low-Voltage, Dual-Supply, SPST, CMOS Analog Switches General Description
... two supply pins: V+ and V-. These voltages set the analog voltage limits of the switch. Reverse ESD-protection diodes are internally connected between IN and each analog signal pin and both V+ and V-. If any analog signal exceeds V+ or V-, one of these diodes will conduct. During normal operation, t ...
... two supply pins: V+ and V-. These voltages set the analog voltage limits of the switch. Reverse ESD-protection diodes are internally connected between IN and each analog signal pin and both V+ and V-. If any analog signal exceeds V+ or V-, one of these diodes will conduct. During normal operation, t ...
1 - Mouser
... functionally compatible with National’s LP2981, but offers performance advantages. The ADP3309 stands out from conventional LDOs with a novel architecture and an enhanced process. Its patented design requires only a 0.47 μF output capacitor for stability. This device is stable with any type of capac ...
... functionally compatible with National’s LP2981, but offers performance advantages. The ADP3309 stands out from conventional LDOs with a novel architecture and an enhanced process. Its patented design requires only a 0.47 μF output capacitor for stability. This device is stable with any type of capac ...
MK2059-01 - Integrated Device Technology
... a lower loop bandwidth. This enables the use of lower input clock reference frequencies and also input clock jitter attenuation capabilities. Larger loop filter capacitors also allow higher loop damping factors when less passband ...
... a lower loop bandwidth. This enables the use of lower input clock reference frequencies and also input clock jitter attenuation capabilities. Larger loop filter capacitors also allow higher loop damping factors when less passband ...
MAX4675/MAX4676 3 Single SPST Analog Switches ________________General Description
... 3Ω Single SPST Analog Switches ...
... 3Ω Single SPST Analog Switches ...
MAX551/MAX552 +3V/+5V, 12-Bit, Serial, Multiplying DACs in 10-Pin µMAX Package _______________General Description
... where V OS = is the op amp’s offset and R O is the DAC’s output resistance, which is code dependent. The maximum error voltage (RO = RFB) is 2VOS; the minimum error voltage (RO = ∞) is VOS. To minimize this error, use a low-offset amplifier such as the MAX4166 (unipolar output) or the MAX427 (bipola ...
... where V OS = is the op amp’s offset and R O is the DAC’s output resistance, which is code dependent. The maximum error voltage (RO = RFB) is 2VOS; the minimum error voltage (RO = ∞) is VOS. To minimize this error, use a low-offset amplifier such as the MAX4166 (unipolar output) or the MAX427 (bipola ...
LM747 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are sold subject to TI’s terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment. TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the speci ...
... obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are sold subject to TI’s terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment. TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the speci ...
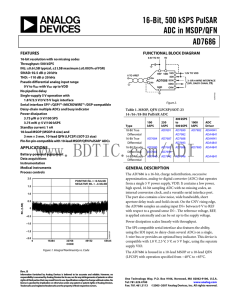
16-Bit, 500 kSPS PulSAR ADC in MSOP/QFN AD7686
... The AD7686 is a 16-bit, charge redistribution, successive approximation, analog-to-digital converter (ADC) that operates from a single 5 V power supply, VDD. It contains a low power, high speed, 16-bit sampling ADC with no missing codes, an internal conversion clock, and a versatile serial interface ...
... The AD7686 is a 16-bit, charge redistribution, successive approximation, analog-to-digital converter (ADC) that operates from a single 5 V power supply, VDD. It contains a low power, high speed, 16-bit sampling ADC with no missing codes, an internal conversion clock, and a versatile serial interface ...
LM193/LM293/LM393/LM2903 Low Power Low Offset Voltage Dual
... Positive excursions of input voltage may exceed the power supply level. As long as the other voltage remains within the common-mode range, the comparator will provide a proper output state. The low input voltage state must not be less than −0.3V (or 0.3V below the magnitude of the negative power sup ...
... Positive excursions of input voltage may exceed the power supply level. As long as the other voltage remains within the common-mode range, the comparator will provide a proper output state. The low input voltage state must not be less than −0.3V (or 0.3V below the magnitude of the negative power sup ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).