ADM1276 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... amplifier that measures the voltage across a sense resistor in the power path via the SENSE+ and SENSE− pins. A default limit of 20 mV is set, but this limit can be adjusted, if required, using a resistor divider network from the internal reference voltage to the ISET pin. The ADM1276 limits the cur ...
... amplifier that measures the voltage across a sense resistor in the power path via the SENSE+ and SENSE− pins. A default limit of 20 mV is set, but this limit can be adjusted, if required, using a resistor divider network from the internal reference voltage to the ISET pin. The ADM1276 limits the cur ...
MAX9321/MAX9321A Differential LVPECL/LVECL/HSTL Receiver/Drivers General Description
... When using the VBB reference output, bypass it with a 0.01µF ceramic capacitor to VCC. If the VBB reference is not used, it can be left open. The VBB reference can source or sink 0.5mA. Use VBB only for an input on the same device as the VBB reference. The maximum magnitude of the differential input ...
... When using the VBB reference output, bypass it with a 0.01µF ceramic capacitor to VCC. If the VBB reference is not used, it can be left open. The VBB reference can source or sink 0.5mA. Use VBB only for an input on the same device as the VBB reference. The maximum magnitude of the differential input ...
XHRA-2HPA Datasheet
... It is our intention to provide you with accurate and comprehensive documentation for the hardware and software components used in this product. To subscribe to receive updates, visit http://www.xmos.com/. XMOS Ltd. is the owner or licensee of the information in this document and is providing it to y ...
... It is our intention to provide you with accurate and comprehensive documentation for the hardware and software components used in this product. To subscribe to receive updates, visit http://www.xmos.com/. XMOS Ltd. is the owner or licensee of the information in this document and is providing it to y ...
LT1995 - 30MHz, 1000V/µs Gain Selectable Amplifier
... The LT®1995 is a high speed, high slew rate, gain selectable amplifier with excellent DC performance. Gains from –7 to 8 with a gain accuracy of 0.2% can be achieved using no external components. The device is particularly well suited for use as a difference amplifier, where the excellent resistor m ...
... The LT®1995 is a high speed, high slew rate, gain selectable amplifier with excellent DC performance. Gains from –7 to 8 with a gain accuracy of 0.2% can be achieved using no external components. The device is particularly well suited for use as a difference amplifier, where the excellent resistor m ...
TPS54200, TPS54201 4.5-V TO 28-V Input
... The TPS54200 is a 1.5-A synchronous buck LED driver up to 28-V input. Current-mode operation provides fast transient response. The optimized internal compensation network minimizes the external component counts and simplifies the control loop design. Fixed 600-kHz switching frequency is chosen for a ...
... The TPS54200 is a 1.5-A synchronous buck LED driver up to 28-V input. Current-mode operation provides fast transient response. The optimized internal compensation network minimizes the external component counts and simplifies the control loop design. Fixed 600-kHz switching frequency is chosen for a ...
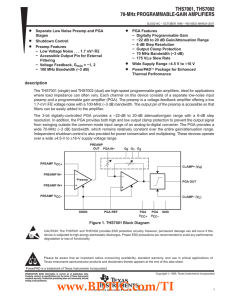
71M6541DT/71M6541FT/71M6541GT/ Energy Meter ICs 71M6542FT/71M6542GT General Description
... Our Single Converter Technology® with a 22-bit deltasigma ADC, three or four analog inputs, digital temperature compensation, precision voltage reference, and a 32-bit computation engine (CE) support a wide range of metering applications with very few external components. The 71M654xT devices suppor ...
... Our Single Converter Technology® with a 22-bit deltasigma ADC, three or four analog inputs, digital temperature compensation, precision voltage reference, and a 32-bit computation engine (CE) support a wide range of metering applications with very few external components. The 71M654xT devices suppor ...
THS7002 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... 1.7-nV/√Hz voltage noise with a 100-MHz (−3 dB) bandwidth. The output pin of the preamp is accessible so that filters can be easily added to the amplifier. The 3-bit digitally-controlled PGA provides a −22-dB to 20-dB attenuation/gain range with a 6-dB step resolution. In addition, the PGA provides ...
... 1.7-nV/√Hz voltage noise with a 100-MHz (−3 dB) bandwidth. The output pin of the preamp is accessible so that filters can be easily added to the amplifier. The 3-bit digitally-controlled PGA provides a −22-dB to 20-dB attenuation/gain range with a 6-dB step resolution. In addition, the PGA provides ...
TANGO PCIe | Operating Manual
... when the status LED lights up. Make sure that during this period of time the joystick doesn't get shifted. The result would be that the zero point would also be shifted and axes would move when letting go of the joystick! ● Connect PC with socket and switch on, if necessary together with the externa ...
... when the status LED lights up. Make sure that during this period of time the joystick doesn't get shifted. The result would be that the zero point would also be shifted and axes would move when letting go of the joystick! ● Connect PC with socket and switch on, if necessary together with the externa ...
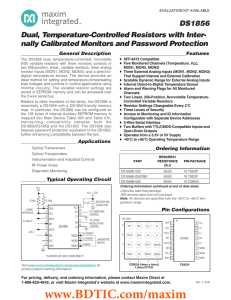
DS1856 Dual, Temperature-Controlled Resistors with Inter- nally Calibrated Monitors and Password Protection
... I/O pins of fast-mode devices must not obstruct the SDA and SCL lines if VCC is switched off. SDA and SCL are connected to VCC and all other input signals are connected to well-defined logic levels. Full scale is user programmable. The maximum voltage that the MON inputs read is approximately full s ...
... I/O pins of fast-mode devices must not obstruct the SDA and SCL lines if VCC is switched off. SDA and SCL are connected to VCC and all other input signals are connected to well-defined logic levels. Full scale is user programmable. The maximum voltage that the MON inputs read is approximately full s ...
HOTLink® CY7B923/CY7B933 to HOTLink II™ Migration
... ENA input is sometimes set LOW permanently. This allows an even simpler configuration where TXCTx[0] can be connected to GND and TXCTx[1] used to select between encoding a data or a special character. HOTLink II does not have the Enable Next Parallel Data (ENN ¯¯¯¯ and the Send Violation Symbol (SVS ...
... ENA input is sometimes set LOW permanently. This allows an even simpler configuration where TXCTx[0] can be connected to GND and TXCTx[1] used to select between encoding a data or a special character. HOTLink II does not have the Enable Next Parallel Data (ENN ¯¯¯¯ and the Send Violation Symbol (SVS ...
MAX1816/MAX1994 Dual Step-Down Controllers Plus Linear- Regulator Controller for Notebook Computers General Description
... for notebook computer applications. BUCK1 is a CPU core regulator with dynamically adjustable output, ultrafast transient response, high DC accuracy, and high efficiency. BUCK2 is an adjustable step-down regulator for I/O and memory supplies. Both regulators employ Maxim’s proprietary Quick-PWM™ con ...
... for notebook computer applications. BUCK1 is a CPU core regulator with dynamically adjustable output, ultrafast transient response, high DC accuracy, and high efficiency. BUCK2 is an adjustable step-down regulator for I/O and memory supplies. Both regulators employ Maxim’s proprietary Quick-PWM™ con ...
MAX1907A/MAX1981A Quick-PWM Master Controllers for Voltage- Positioned CPU Core Power Supplies (IMVP-IV)
... The MAX1907A/MAX1981A meet the IMVP-IV specifications and include logic to interface with the CPU power good signals from the VCCP and VCCMCH rails within the system. The regulator features power-up sequencing, automatically ramping up to the Intel-specified boot voltage. The MAX1907A/MAX1981A featu ...
... The MAX1907A/MAX1981A meet the IMVP-IV specifications and include logic to interface with the CPU power good signals from the VCCP and VCCMCH rails within the system. The regulator features power-up sequencing, automatically ramping up to the Intel-specified boot voltage. The MAX1907A/MAX1981A featu ...
Range and General Features ClassA HEADENDS
... a) “Input Channel o IF” conversion. Includes a delayed AGC circuitry that operates in the 50-90 dBmV (analog) or 40-80 dBmV (digital) input level ranges. b) IF filtering. A double SAW filter is used, what provides very high selectivity (>70 dB at ±5.25 MHz from the centre for 8MHz-wide channels). c) “ ...
... a) “Input Channel o IF” conversion. Includes a delayed AGC circuitry that operates in the 50-90 dBmV (analog) or 40-80 dBmV (digital) input level ranges. b) IF filtering. A double SAW filter is used, what provides very high selectivity (>70 dB at ±5.25 MHz from the centre for 8MHz-wide channels). c) “ ...
S1L50000 Series 2.5 Voltage Library Design Guide
... 2.5 Voltage Library DESIGN GUIDE S1L50000 Series 2.5 Voltage Library DESIGN GUIDE First issue April,1998 D Printed June, 2002 in Japan C A ...
... 2.5 Voltage Library DESIGN GUIDE S1L50000 Series 2.5 Voltage Library DESIGN GUIDE First issue April,1998 D Printed June, 2002 in Japan C A ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).