ZXLD1374
... power MOSFET switch, load and ambient temperature conditions. To ensure best operation in Boost and Buck-boost modes with input voltages, VIN, between 6.5 and 12V a suitable boot-strap network on VAUX pin is recommended. Performance in Buck mode will be reduced at input voltages (VIN, VAUX) below 8V ...
... power MOSFET switch, load and ambient temperature conditions. To ensure best operation in Boost and Buck-boost modes with input voltages, VIN, between 6.5 and 12V a suitable boot-strap network on VAUX pin is recommended. Performance in Buck mode will be reduced at input voltages (VIN, VAUX) below 8V ...
AD9714 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... consumption reduces to 35 mW at 125 MSPS with a 1.8 V supply. Sleep and power-down modes are provided for low power idle periods. CMOS Clock Input. High speed, single-ended CMOS clock input supports a 125 MSPS conversion rate. Easy Interfacing to Other Components. Adjustable output common mode from ...
... consumption reduces to 35 mW at 125 MSPS with a 1.8 V supply. Sleep and power-down modes are provided for low power idle periods. CMOS Clock Input. High speed, single-ended CMOS clock input supports a 125 MSPS conversion rate. Easy Interfacing to Other Components. Adjustable output common mode from ...
Slide 1
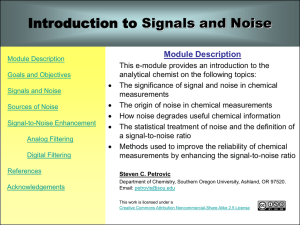
... Analog Filtering (Hardware-Based) Digital Filtering (Software-Based) Most of these S/N enhancement methods, whether analog or digital, are based on either: Bandwidth Reduction (i.e. decreasing Δf). Signal Averaging (i.e. decreasing Δf or averaging out random noise fluctuations) Bandwidth reduction i ...
... Analog Filtering (Hardware-Based) Digital Filtering (Software-Based) Most of these S/N enhancement methods, whether analog or digital, are based on either: Bandwidth Reduction (i.e. decreasing Δf). Signal Averaging (i.e. decreasing Δf or averaging out random noise fluctuations) Bandwidth reduction i ...
TAS5342A 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... noise, and low idle current. The TAS5342A has a complete protection system integrated on-chip, safeguarding the device against a wide range of fault conditions that could damage the system. These protection features are short-circuit protection, over-current protection, under voltage protection, ove ...
... noise, and low idle current. The TAS5342A has a complete protection system integrated on-chip, safeguarding the device against a wide range of fault conditions that could damage the system. These protection features are short-circuit protection, over-current protection, under voltage protection, ove ...
M I C -S
... glitches. In this work, two DAC architectures are developed. These are denoted the decomposed and partially decomposed architectures and utilize encoding strategies aiming at a high circuit performance by avoiding unnecessary switching of current sources. The developed architectures are compared wit ...
... glitches. In this work, two DAC architectures are developed. These are denoted the decomposed and partially decomposed architectures and utilize encoding strategies aiming at a high circuit performance by avoiding unnecessary switching of current sources. The developed architectures are compared wit ...
MAX4744/MAX4744H/MAX4745/MAX4745H/MAX4746H Low-Voltage, Dual SPDT, Audio Clickless Switches with Negative Rail Capability General Description
... Figure 3. Break-Before-Make Interval ...
... Figure 3. Break-Before-Make Interval ...
3-Channel, Low-Power Video Amplifier with I
... THS7303 is a low-power, single-supply, 2.7-V to 5-V, 3-channel integrated video buffer. It incorporates a selectable fifth-order Butterworth filter to eliminate data converter images. The 9-MHz filter is a perfect choice for SDTV video including composite (CVBS), S-Video, and 480i/576i Y'P'BP'R, and ...
... THS7303 is a low-power, single-supply, 2.7-V to 5-V, 3-channel integrated video buffer. It incorporates a selectable fifth-order Butterworth filter to eliminate data converter images. The 9-MHz filter is a perfect choice for SDTV video including composite (CVBS), S-Video, and 480i/576i Y'P'BP'R, and ...
TAS5342LA 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions is not implied. Exposure to absol ...
... Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions is not implied. Exposure to absol ...
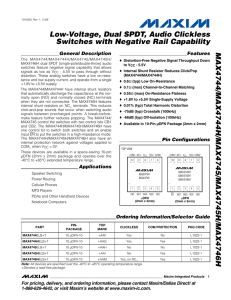
MAX9910–MAX9913 200kHz, 4µA, Rail-to-Rail I/O Op Amps with Shutdown General Description
... applications. These CMOS devices consume an ultralow 4µA (typ) supply current and a 200µV (typ) offset voltage. For additional power conservation, the MAX9911/MAX9913 feature a low-power shutdown mode that reduces supply current to 1nA (typ), and puts the amplifiers’ output in a high-impedance state ...
... applications. These CMOS devices consume an ultralow 4µA (typ) supply current and a 200µV (typ) offset voltage. For additional power conservation, the MAX9911/MAX9913 feature a low-power shutdown mode that reduces supply current to 1nA (typ), and puts the amplifiers’ output in a high-impedance state ...
TAS5342L 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... Stresses beyond those listed under "absolute maximum ratings" may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under "recommended operating conditions" is not implied. Exposure to a ...
... Stresses beyond those listed under "absolute maximum ratings" may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under "recommended operating conditions" is not implied. Exposure to a ...
2. The Low-Noise Amplifier
... steps: peak gain, or zero gain. Such LNAs are equipped with a bypass circuit leading to two modes of operation ...
... steps: peak gain, or zero gain. Such LNAs are equipped with a bypass circuit leading to two modes of operation ...
64-Position Up/Down Control Digital Potentiometer AD5227
... Resistor position nonlinearity error, R-INL, is the deviation from an ideal value measured between the maximum resistance and the minimum resistance wiper positions. R-DNL measures the relative step change from ideal between successive tap positions. Parts are guaranteed monotonic. ...
... Resistor position nonlinearity error, R-INL, is the deviation from an ideal value measured between the maximum resistance and the minimum resistance wiper positions. R-DNL measures the relative step change from ideal between successive tap positions. Parts are guaranteed monotonic. ...
TPS76901 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... inputs to reduce supply currents to 1 µA when the regulators are turned off. ...
... inputs to reduce supply currents to 1 µA when the regulators are turned off. ...
MAX17009 AMD Mobile Serial VID Dual-Phase Fixed-Frequency Controller General Description
... single-phase regulators for a dual CPU core application, or one high-current, dual-phase, combined-output regulator for a unified core application. A reference buffer output (NBV_BUF) sets the voltage-regulation level for a North Bridge (NB) regulator, completing the total CPU cores and NB power req ...
... single-phase regulators for a dual CPU core application, or one high-current, dual-phase, combined-output regulator for a unified core application. A reference buffer output (NBV_BUF) sets the voltage-regulation level for a North Bridge (NB) regulator, completing the total CPU cores and NB power req ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).