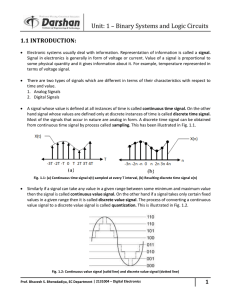
Safety, Protection, and Modification of the Product n
... Note: User’s Manual can be downloaded from a website. ...
... Note: User’s Manual can be downloaded from a website. ...
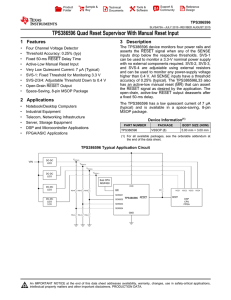
MAX15062 60V, 300mA, Ultra-Small, High-Efficiency, Synchronous Step-Down DC-DC Converters General Description
... step-down DC-DC converter with integrated MOSFETs operates over a 4.5V to 60V input voltage range. The converter delivers output current up to 300mA at 3.3V (MAX15062A), 5V (MAX15062B), and adjustable output voltages (MAX15062C). The device operates over the -40°C to +125°C temperature range and is ...
... step-down DC-DC converter with integrated MOSFETs operates over a 4.5V to 60V input voltage range. The converter delivers output current up to 300mA at 3.3V (MAX15062A), 5V (MAX15062B), and adjustable output voltages (MAX15062C). The device operates over the -40°C to +125°C temperature range and is ...
MAX17000 Complete DDR2 and DDR3 Memory Power-Management Solution General Description
... The VDDQ rail is supplied by a step-down converter using Maxim’s proprietary Quick-PWM™ controller. The high-efficiency, constant-on-time PWM controller handles wide input/output voltage ratios (low duty-cycle applications) with ease and provides 100ns response to load transients while maintaining a ...
... The VDDQ rail is supplied by a step-down converter using Maxim’s proprietary Quick-PWM™ controller. The high-efficiency, constant-on-time PWM controller handles wide input/output voltage ratios (low duty-cycle applications) with ease and provides 100ns response to load transients while maintaining a ...
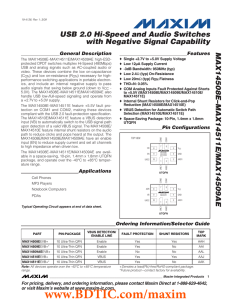
MAX14508E–MAX14511E/MAX14509AE USB 2.0 Hi-Speed and Audio Switches with Negative Signal Capability General Description
... USB and analog signals such as AC-coupled audio or video. These devices combine the low on-capacitance (CON) and low on-resistance (RON) necessary for highperformance switching applications in portable electronics, and include an internal negative supply to pass audio signals that swing below ground ...
... USB and analog signals such as AC-coupled audio or video. These devices combine the low on-capacitance (CON) and low on-resistance (RON) necessary for highperformance switching applications in portable electronics, and include an internal negative supply to pass audio signals that swing below ground ...
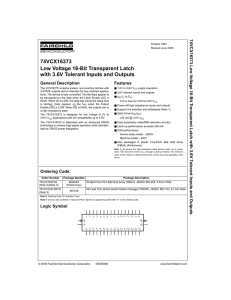
74VCX16373 Low Voltage 16-Bit Transparent Latch with 3.6V Tolerant Inputs and Outputs 7
... HIGH Voltage Level LOW Voltage Level Immaterial (HIGH or LOW, inputs may not float) High Impedance Previous O0 before HIGH-to-LOW of Latch Enable ...
... HIGH Voltage Level LOW Voltage Level Immaterial (HIGH or LOW, inputs may not float) High Impedance Previous O0 before HIGH-to-LOW of Latch Enable ...
UCC28510 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... amplifier output capacitance when the output voltage falls outside a certain regulation window. A number of additional features such as UVLO circuit with selectable hysteresis levels, an accurate reference voltage for the voltage amplifier, zero power detect, OVP/enable, peak current limit, power li ...
... amplifier output capacitance when the output voltage falls outside a certain regulation window. A number of additional features such as UVLO circuit with selectable hysteresis levels, an accurate reference voltage for the voltage amplifier, zero power detect, OVP/enable, peak current limit, power li ...
3.0-V TO 20-V PMBus SYNCHRONOUS BUCK CONTROLLER TPS40400 FEATURES APPLICATIONS
... (9) All read backs are an average of 16 consecutive measurements – not a rolling average. Time is a delay between parameter updates. (10) Constrained by the resolution of READ_IOUT command. This presents as the greater of 122 µV/ IOUT_CAL_GAIN or 62.5 mA, the resolution of the READ_IOUT command (11) ...
... (9) All read backs are an average of 16 consecutive measurements – not a rolling average. Time is a delay between parameter updates. (10) Constrained by the resolution of READ_IOUT command. This presents as the greater of 122 µV/ IOUT_CAL_GAIN or 62.5 mA, the resolution of the READ_IOUT command (11) ...
Timer and switching relay
... Upon excitation of the motor and the magnet, the immediate contact is moved to the operating position, and the time elapse begins. If the preselected time is attained, the time contact is activated and the motor is powered off. After the de-excitation, the magnet, the timing element and all contacts ...
... Upon excitation of the motor and the magnet, the immediate contact is moved to the operating position, and the time elapse begins. If the preselected time is attained, the time contact is activated and the motor is powered off. After the de-excitation, the magnet, the timing element and all contacts ...
XENON FLASH LAMPS
... In the actual circuit, the delay time is several micro seconds, though it differs depending on the components making up the trigger power supply section (response time of photocoupler and thyristor etc.), as well as the lamp preliminary ionization time and main discharge voltage. The main discharge ...
... In the actual circuit, the delay time is several micro seconds, though it differs depending on the components making up the trigger power supply section (response time of photocoupler and thyristor etc.), as well as the lamp preliminary ionization time and main discharge voltage. The main discharge ...
AN-940 APPLICATION NOTE
... Choose low noise resistive element material Resistive elements composed of pure metals and/or metal alloys in bulk exhibits low noise characteristics. Such as Vishay Bulk Metal® foil technology resistors (such as, S102C, Z201) Wirewound technology resistors composed of metal alloys have similar nois ...
... Choose low noise resistive element material Resistive elements composed of pure metals and/or metal alloys in bulk exhibits low noise characteristics. Such as Vishay Bulk Metal® foil technology resistors (such as, S102C, Z201) Wirewound technology resistors composed of metal alloys have similar nois ...
A 3-Phase ac Induction Motor Control System Based on the
... One of the most important features of the PWMMC is its ability to “shut itself down” when a system fault is detected. When dealing with a system that potentially could have hundreds of amps of peak current, reacting to faults such as overcurrent or overvoltage conditions is an absolute necessity. Fa ...
... One of the most important features of the PWMMC is its ability to “shut itself down” when a system fault is detected. When dealing with a system that potentially could have hundreds of amps of peak current, reacting to faults such as overcurrent or overvoltage conditions is an absolute necessity. Fa ...
MAX8973A 9A, Three-Phase Step-Down Switching Regulator General Description
... allowing the use of small magnetic components. Maxim Integrated’s proprietary Rotational Phase Spreading algorithm optimizes efficiency at low output currents. Software-selectable forced-PWM mode allows either fixed-frequency operation, or improved efficiency at light load with a variable frequency ...
... allowing the use of small magnetic components. Maxim Integrated’s proprietary Rotational Phase Spreading algorithm optimizes efficiency at low output currents. Software-selectable forced-PWM mode allows either fixed-frequency operation, or improved efficiency at light load with a variable frequency ...
E. Receiver Gain and AGC
... But, we find that almost always the demodulator dynamic range (IDR) is much less than the receiver dynamic range (TDR), thus Gmax is almost never larger than Gmin . Typically, ...
... But, we find that almost always the demodulator dynamic range (IDR) is much less than the receiver dynamic range (TDR), thus Gmax is almost never larger than Gmin . Typically, ...
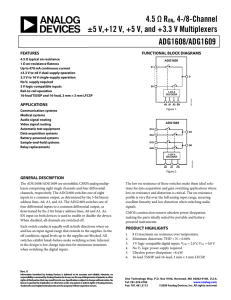
4.5 Ω RON, 4-/8-Channel ±5 V,+12 V, +5 V, and +3.3 V Multiplexers
... The ADG1608/ADG1609 are monolithic CMOS analog multiplexers comprising eight single channels and four differential channels, respectively. The ADG1608 switches one of eight inputs to a common output, as determined by the 3-bit binary address lines, A0, A1, and A2. The ADG1609 switches one of four di ...
... The ADG1608/ADG1609 are monolithic CMOS analog multiplexers comprising eight single channels and four differential channels, respectively. The ADG1608 switches one of eight inputs to a common output, as determined by the 3-bit binary address lines, A0, A1, and A2. The ADG1609 switches one of four di ...
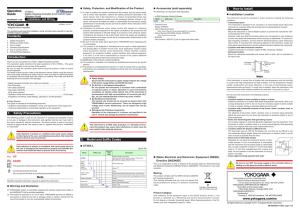
74VCX16374 Low Voltage 16-Bit D-Type Flip-Flops with 3.6V Tolerant Inputs and Outputs 7
... meet the setup and hold time requirements on the LOW-to-HIGH Clock (CPn) transition. With the Output Enable (OEn) LOW, the contents of the flip-flops are available at the outputs. When OEn is HIGH, the outputs go to the high impedance state. Operations of the OEn input does not affect the state of t ...
... meet the setup and hold time requirements on the LOW-to-HIGH Clock (CPn) transition. With the Output Enable (OEn) LOW, the contents of the flip-flops are available at the outputs. When OEn is HIGH, the outputs go to the high impedance state. Operations of the OEn input does not affect the state of t ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).