Ω MAX4741/MAX4742/MAX4743 0.8 , Low-Voltage, Single-Supply Dual SPST
... switches that operate from a single +1.6V to +3.6V supply. These devices have fast switching speeds (tON = 24ns, tOFF = 16ns max), handle rail-to-rail analog signals, and consume less than 1µW of quiescent power. The MAX4743 has break-before-make switching. When powered from a +3V supply, the MAX474 ...
... switches that operate from a single +1.6V to +3.6V supply. These devices have fast switching speeds (tON = 24ns, tOFF = 16ns max), handle rail-to-rail analog signals, and consume less than 1µW of quiescent power. The MAX4743 has break-before-make switching. When powered from a +3V supply, the MAX474 ...
Efficient Excitation Signals for the Fast Impedance Spectroscopy
... multifrequency excitation waveforms for fast bioimpedance spectroscopy. However, the solutions described here could be useful also in other fields of impedance spectroscopy. Theoretically, the useful excitation power of optimized binary multifrequency signals (BMS) exceeds the power of comparable mu ...
... multifrequency excitation waveforms for fast bioimpedance spectroscopy. However, the solutions described here could be useful also in other fields of impedance spectroscopy. Theoretically, the useful excitation power of optimized binary multifrequency signals (BMS) exceeds the power of comparable mu ...
MAX1700/MAX1701 1-Cell to 3-Cell, High-Power (1A), Low-Noise, Step-Up DC-DC Converters General Description
... Oscillator Maximum Duty Cycle ...
... Oscillator Maximum Duty Cycle ...
BDTIC www.BDTIC.com/infineon RF and Protection Devices BCR450, TDA4863
... This demo board shows a 40W offline AC-to-DC LED driving solution with power factor correction. The isolated concept ensures easy and safe installation and maintenance for street lights and Indoor lighting fixtures. The design utilizes a three step approach with a universal input PFC IC stage on the ...
... This demo board shows a 40W offline AC-to-DC LED driving solution with power factor correction. The isolated concept ensures easy and safe installation and maintenance for street lights and Indoor lighting fixtures. The design utilizes a three step approach with a universal input PFC IC stage on the ...
MAX4060/MAX4061/MAX4062 Differential Microphone Preamplifiers with Internal Bias and Complete Shutdown General Description
... resistance is 100kΩ (typ), so the capacitor size may be chosen accordingly to define the LF rolloff desired. This can be calculated as: CIN = 1 / (2πfCUTRIN) This assumes a low source impedance driving the inputs. A further consideration for the differential input is the effect of these series input ...
... resistance is 100kΩ (typ), so the capacitor size may be chosen accordingly to define the LF rolloff desired. This can be calculated as: CIN = 1 / (2πfCUTRIN) This assumes a low source impedance driving the inputs. A further consideration for the differential input is the effect of these series input ...
NCL30000 - Power Factor Corrected Dimmable LED Driver
... for low to medium power single stage power factor (PF) corrected LED Drivers. The device is designed to operate in critical conduction mode (CrM) and is suitable for flyback as well as buck topologies. Constant on time CrM operation is particularly suited for isolated flyback LED applications as the ...
... for low to medium power single stage power factor (PF) corrected LED Drivers. The device is designed to operate in critical conduction mode (CrM) and is suitable for flyback as well as buck topologies. Constant on time CrM operation is particularly suited for isolated flyback LED applications as the ...
mc34161d.pdf
... To be competitive in today’s electronic equipment market, new circuits must be designed to increase system reliability with minimal incremental cost. The circuit designer can take a significant step toward attaining these goals by implementing economical circuitry that continuously monitors critical ...
... To be competitive in today’s electronic equipment market, new circuits must be designed to increase system reliability with minimal incremental cost. The circuit designer can take a significant step toward attaining these goals by implementing economical circuitry that continuously monitors critical ...
SIMULATION OF LCC RESONANT CIRCUITS PURPOSE POWER ELECTRONICS ECE562 COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY
... Or by clicking the icons for each function. Notice how the vertical scale units of V. Note that the resonant frequency is nearly the same as the Zin peak. This makes sense, since the output voltage is the input current times Zpar, and the input current is a maximum when Zin is a minimum. Note that t ...
... Or by clicking the icons for each function. Notice how the vertical scale units of V. Note that the resonant frequency is nearly the same as the Zin peak. This makes sense, since the output voltage is the input current times Zpar, and the input current is a maximum when Zin is a minimum. Note that t ...
SAM3S8/SD8 Series Summary
... general-purpose 16-bit timers (with stepper motor and quadrature decoder logic support), an RTC, a 12-bit ADC, a 12-bit DAC and an analog comparator. The SAM3S8/SD8 series is ready for capacitive touch thanks to the QTouch® library, offering an easy way to implement buttons, wheels and sliders. The ...
... general-purpose 16-bit timers (with stepper motor and quadrature decoder logic support), an RTC, a 12-bit ADC, a 12-bit DAC and an analog comparator. The SAM3S8/SD8 series is ready for capacitive touch thanks to the QTouch® library, offering an easy way to implement buttons, wheels and sliders. The ...
UCC28500 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... conditions. When enabled, SS2 charges an external capacitor with a current source. This voltage is used as the voltage error signal during start-up, enabling the PWM duty cycle to increase slowly. In the event of a disable command or a UVLO2 dropout, SS2 quickly discharges to disable the PWM. VAOUT: ...
... conditions. When enabled, SS2 charges an external capacitor with a current source. This voltage is used as the voltage error signal during start-up, enabling the PWM duty cycle to increase slowly. In the event of a disable command or a UVLO2 dropout, SS2 quickly discharges to disable the PWM. VAOUT: ...
MAX1895/MAX1995 High-Efficiency, Wide Brightness Range, CCFL Backlight Controllers General Description
... The MAX1895/MAX1995 include safety features that limit the transformer secondary voltage and protect against single-point fault conditions including lamp-out and short-circuit faults. The MAX1895/MAX1995 regulate the CCFL brightness in three ways: linearly controlling the lamp current, digital pulse ...
... The MAX1895/MAX1995 include safety features that limit the transformer secondary voltage and protect against single-point fault conditions including lamp-out and short-circuit faults. The MAX1895/MAX1995 regulate the CCFL brightness in three ways: linearly controlling the lamp current, digital pulse ...
MAX8643A 3A, 2MHz Step-Down Regulator with Integrated Switches General Description
... 0.6V to (0.9 x VIN). The IC operates from 2.35V to 3.6V, making it ideal for on-board point-of-load and postregulation applications. Total output error is less than ±1% over load, line, and temperature. The MAX8643A features fixed-frequency PWM mode operation with a switching frequency range of 500k ...
... 0.6V to (0.9 x VIN). The IC operates from 2.35V to 3.6V, making it ideal for on-board point-of-load and postregulation applications. Total output error is less than ±1% over load, line, and temperature. The MAX8643A features fixed-frequency PWM mode operation with a switching frequency range of 500k ...
BDTIC CoolSET -Q1 www.BDTIC.com/infineon
... The ZC counter has a minimum value of 0 and maximum value of 7. After the external MOSFET is turned off, every time when the falling voltage ramp of on ZC pin crosses the 100mV threshold, a zero crossing is detected and ZC counter will increase by 1. It is reset every time after the DRIVER output is ...
... The ZC counter has a minimum value of 0 and maximum value of 7. After the external MOSFET is turned off, every time when the falling voltage ramp of on ZC pin crosses the 100mV threshold, a zero crossing is detected and ZC counter will increase by 1. It is reset every time after the DRIVER output is ...
UCC28810 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... depending upon the VDD voltage being used. Below the UVLO threshold, the output is held low. ...
... depending upon the VDD voltage being used. Below the UVLO threshold, the output is held low. ...
$doc.title
... capabilities and its DC precision make it a design option for a wide variety of applications, including test and measurement, optical monitoring, transimpedance gain circuits, and high-impedance buffers. The applications section of the data sheet discusses these particular applications in addition t ...
... capabilities and its DC precision make it a design option for a wide variety of applications, including test and measurement, optical monitoring, transimpedance gain circuits, and high-impedance buffers. The applications section of the data sheet discusses these particular applications in addition t ...
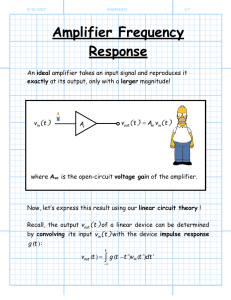
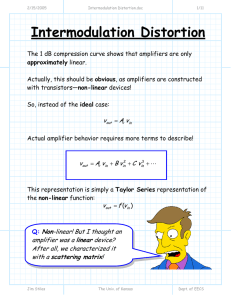
lec14
... capacitor are connected in series with each other in a closed loop. Then the switch is closed. The capacitor charges. A person measures the time it takes for the voltage across the capacitor to reach 99% of the battery voltage. The switch is opened and a person discharges the capacitor. Then, that s ...
... capacitor are connected in series with each other in a closed loop. Then the switch is closed. The capacitor charges. A person measures the time it takes for the voltage across the capacitor to reach 99% of the battery voltage. The switch is opened and a person discharges the capacitor. Then, that s ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).