Tiny boost converter with adjustable input current limit
... an application to be interfaced directly to its load, without overloading the input source due to appropriate set average input current limit . High values of output capacitance are mainly achieved by putting capacitors in parallel. This reduces the overall series resistance (ESR) to very low values ...
... an application to be interfaced directly to its load, without overloading the input source due to appropriate set average input current limit . High values of output capacitance are mainly achieved by putting capacitors in parallel. This reduces the overall series resistance (ESR) to very low values ...
Rev. 0
... DMAX is determined for the VR controller being used with the driver. Note this current gets divided roughly equally between MOSFETs if more than one is used (assume a worst-case mismatch of 30% for design margin). LOUT is the output inductor value. ...
... DMAX is determined for the VR controller being used with the driver. Note this current gets divided roughly equally between MOSFETs if more than one is used (assume a worst-case mismatch of 30% for design margin). LOUT is the output inductor value. ...
Design and Manufacture of the UIM Driver Unit
... output current by a factor of 2 (6dB) at 100Hz. Simulation also shows that the attenuation factor for each filter stage at 100Hz is 0.093 (-20.5dB). With two filter stages switched in, the total attenuation at 100 Hz will therefore be 0.0172 (35dB). The low frequency output current will therefore be ...
... output current by a factor of 2 (6dB) at 100Hz. Simulation also shows that the attenuation factor for each filter stage at 100Hz is 0.093 (-20.5dB). With two filter stages switched in, the total attenuation at 100 Hz will therefore be 0.0172 (35dB). The low frequency output current will therefore be ...
Electronics circuits I
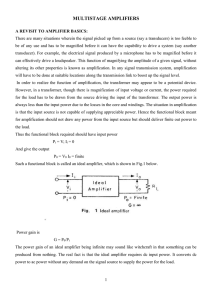
... There are many situations wherein the signal picked up from a source (say a transducers) is too feeble to be of any use and has to be magnified before it can have the capability to drive a system (say another transducer). For example, the electrical signal produced by a microphone has to be magnifie ...
... There are many situations wherein the signal picked up from a source (say a transducers) is too feeble to be of any use and has to be magnified before it can have the capability to drive a system (say another transducer). For example, the electrical signal produced by a microphone has to be magnifie ...
UC2907 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... (–) SENSE: (Pin 4) This is a high-impedance pin allowing remote sensing of the system ground, bypassing any voltage drops which might appear in the power return line. This point should be considered as the true ground. Unless otherwise stated, all voltages are with respect to this point. Artificial ...
... (–) SENSE: (Pin 4) This is a high-impedance pin allowing remote sensing of the system ground, bypassing any voltage drops which might appear in the power return line. This point should be considered as the true ground. Unless otherwise stated, all voltages are with respect to this point. Artificial ...
Dual Wideband, High Output Current Operational Amplifier with
... All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. ...
... All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. ...
PDF
... The conventional converters provide high voltage but does so at high duty cycle and the parasitic elements present in the passive elements effects reduces the voltage gain. The high voltages can also be obtained at lower duty cycle by making use of an isolated transformer or coupled inductors but th ...
... The conventional converters provide high voltage but does so at high duty cycle and the parasitic elements present in the passive elements effects reduces the voltage gain. The high voltages can also be obtained at lower duty cycle by making use of an isolated transformer or coupled inductors but th ...
ISO35T 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... RS-422 applications that can easily be configured for half-duplex operation by connecting pin 11 to pin 14, and pin 12 to pin 13. These devices are ideal for long transmission lines since the ground loop is broken to allow for a much larger common-mode voltage range. The symmetrical isolation barrie ...
... RS-422 applications that can easily be configured for half-duplex operation by connecting pin 11 to pin 14, and pin 12 to pin 13. These devices are ideal for long transmission lines since the ground loop is broken to allow for a much larger common-mode voltage range. The symmetrical isolation barrie ...
High Frequency, High Precision CMOS Half-Wave Rectifier Montree Kumngern and Kobchai Dejhan
... mode rectifier circuit based on the use of one current conveyor and bipolar transistors operating in class-B, this circuit is a realization that enjoys the high precision rectifier. However, the two grounded resistors are used and the high frequency performance is limited in this scheme. In [8]-[9] ...
... mode rectifier circuit based on the use of one current conveyor and bipolar transistors operating in class-B, this circuit is a realization that enjoys the high precision rectifier. However, the two grounded resistors are used and the high frequency performance is limited in this scheme. In [8]-[9] ...
AD9221 数据手册DataSheet下载
... The first code transition should occur at an analog value 1/2 LSB above negative full scale. The last transition should occur at an analog value 1 1/2 LSB below the nominal full scale. Gain error is the deviation of the actual difference between first and last code transitions and the ideal differen ...
... The first code transition should occur at an analog value 1/2 LSB above negative full scale. The last transition should occur at an analog value 1 1/2 LSB below the nominal full scale. Gain error is the deviation of the actual difference between first and last code transitions and the ideal differen ...
MAX9375 Single LVDS/Anything-to-LVPECL Translator General Description Features
... VOL or VOH with fast transition edges between state levels. Output current always flows into the termination during proper operation. ...
... VOL or VOH with fast transition edges between state levels. Output current always flows into the termination during proper operation. ...
MAX5251 +3V, Quad, 10-Bit Voltage-Output DAC with Serial Interface __________________General Description
... and a DAC register (see Functional Diagram). In addition to the four voltage outputs, each amplifier’s negative input is available to the user. The DACs are inverted R-2R ladder networks that convert a digital input (10 data bits plus 2 sub-bits) into equivalent analog output voltages in proportion ...
... and a DAC register (see Functional Diagram). In addition to the four voltage outputs, each amplifier’s negative input is available to the user. The DACs are inverted R-2R ladder networks that convert a digital input (10 data bits plus 2 sub-bits) into equivalent analog output voltages in proportion ...
ics8543.pdf
... While the information presented herein has been checked for both accuracy and reliability, Integrated Circuit Systems, Incorporated (ICS) assumes no responsibility for either its use or for infringement of any patents or other rights of third parties, which would result from its use. No other circui ...
... While the information presented herein has been checked for both accuracy and reliability, Integrated Circuit Systems, Incorporated (ICS) assumes no responsibility for either its use or for infringement of any patents or other rights of third parties, which would result from its use. No other circui ...
IDT23S09E - Integrated Device Technology
... The IDT23S09E is a high-speed phase-lock loop (PLL) clock buffer, designed to address high-speed clock distribution applications. The zero delay is achieved by aligning the phase between the incoming clock and the output clock, operable within the range of 10 to 200MHz. The IDT23S09E is a 16-pin ver ...
... The IDT23S09E is a high-speed phase-lock loop (PLL) clock buffer, designed to address high-speed clock distribution applications. The zero delay is achieved by aligning the phase between the incoming clock and the output clock, operable within the range of 10 to 200MHz. The IDT23S09E is a 16-pin ver ...
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-ISSN: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331,
... these large voltage spikes. For example, for a 400V output DC supply a 1200V voltage appears across the output diodes. Thus, the component rating increases and the topology is not practical for the high voltage high frequency applications. In the battery charging applications, after the battery is c ...
... these large voltage spikes. For example, for a 400V output DC supply a 1200V voltage appears across the output diodes. Thus, the component rating increases and the topology is not practical for the high voltage high frequency applications. In the battery charging applications, after the battery is c ...
Simulation and Performance Analysis of Parallel Resonant Inverter
... density. The resonant tank can be of various topologies including the commonly used ones such as parallel resonant tank, series resonant tank, LCC, LLC and LC-LC resonant tanks. Class D is one of the power stage prototypes of electronic ballast. Also half bridge topology has extensively applications ...
... density. The resonant tank can be of various topologies including the commonly used ones such as parallel resonant tank, series resonant tank, LCC, LLC and LC-LC resonant tanks. Class D is one of the power stage prototypes of electronic ballast. Also half bridge topology has extensively applications ...
System-Level Protection for High-Voltage
... Figure 8. MUX36S08 Overvoltage Performance With Input Series Resistor Protection and Zener Clamping on the Off Channel Figure 8 shows how the Zener diode on the input can be used to prevent an overvoltage condition on the off channel from impacting the operation of the on channel. This example uses ...
... Figure 8. MUX36S08 Overvoltage Performance With Input Series Resistor Protection and Zener Clamping on the Off Channel Figure 8 shows how the Zener diode on the input can be used to prevent an overvoltage condition on the off channel from impacting the operation of the on channel. This example uses ...
MAX9621 Dual, 2-Wire Hall-Effect Sensor Interface with Analog and Digital Outputs
... The MAX9621, an interface between two 2-wire Halleffect sensors and a low-voltage microprocessor, supplies and monitors current through IN1 and IN2 to two Hall sensors. The MAX9621 complements Maxim’s existing family of Hall-effect sensor interfaces that includes the MAX9921. The MAX9621 provides tw ...
... The MAX9621, an interface between two 2-wire Halleffect sensors and a low-voltage microprocessor, supplies and monitors current through IN1 and IN2 to two Hall sensors. The MAX9621 complements Maxim’s existing family of Hall-effect sensor interfaces that includes the MAX9921. The MAX9621 provides tw ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).