Data sheet General Description
... Figure 18 shows a typical start up interval for AP3586A/B/C where the COMP/EN pin has been released from a grounded (system shutdown) state. The internal 120µA current source starts charge the compensation network after the COMP/EN pin is released from ground at T1. The COMP/EN exceeds 0.3V and enab ...
... Figure 18 shows a typical start up interval for AP3586A/B/C where the COMP/EN pin has been released from a grounded (system shutdown) state. The internal 120µA current source starts charge the compensation network after the COMP/EN pin is released from ground at T1. The COMP/EN exceeds 0.3V and enab ...
FUTURE DIRECTIONS IN BEHAVIORAL MODELING
... • Register – holds values passed between processes • Events – changes in the value of a register – @ statements make processes sensitive to events – Processes create events when they assign values to registers ...
... • Register – holds values passed between processes • Events – changes in the value of a register – @ statements make processes sensitive to events – Processes create events when they assign values to registers ...
Current Ripple Factor of a Buck Converter
... to load directly. When Q1 turns off, D1 is forward biased by inductor current iL. Switching voltage waveform shown as in Figure 1(b) is pulsating rectangular. After LC filtering, assuming corner frequency of LC is much lower than switching frequency, output voltage appears almost pure dc. It can be ...
... to load directly. When Q1 turns off, D1 is forward biased by inductor current iL. Switching voltage waveform shown as in Figure 1(b) is pulsating rectangular. After LC filtering, assuming corner frequency of LC is much lower than switching frequency, output voltage appears almost pure dc. It can be ...
Power Efficient Level Shifter for 16 nm FinFET Near Threshold Circuits
... CMOS microprocessors [1]. A standard method to reduce dynamic power consumption is to lower the supply voltage due to the quadratic dependence of dynamic power on voltage. A negative temperature coefficient has, therefore, become an attractive methodology for sub-30-nm CMOS circuits [2]. This mode o ...
... CMOS microprocessors [1]. A standard method to reduce dynamic power consumption is to lower the supply voltage due to the quadratic dependence of dynamic power on voltage. A negative temperature coefficient has, therefore, become an attractive methodology for sub-30-nm CMOS circuits [2]. This mode o ...
MAX882/MAX883/MAX884 5V/3.3V or Adjustable, Low-Dropout, Low I , 200mA Linear Regulators
... The MAX882/MAX883/MAX884 are micropower, lowdropout linear regulators designed primarily for batterypowered applications. They feature Dual Mode operation, allowing a fixed output of 5V for the MAX883 and 3.3V for the MAX882/MAX884, or an adjustable output from 1.25V to 11V. These devices supply up ...
... The MAX882/MAX883/MAX884 are micropower, lowdropout linear regulators designed primarily for batterypowered applications. They feature Dual Mode operation, allowing a fixed output of 5V for the MAX883 and 3.3V for the MAX882/MAX884, or an adjustable output from 1.25V to 11V. These devices supply up ...
Giuliano, D.M., M.E. D’Asaro, J. Zwart and D.J. Perreault, “Miniaturized Low-Voltage Power Converters with Fast Transient Response,” IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics , Vol. 2, No. 3, pp. 395-405, Sept. 2014.
... Two-stage converters have recently been developed to try to address the fundamental limitations of single-stage converters in this general space. We begin by reviewing examples of this general approach, some of which have only been published in academic journals while others are in commercial produc ...
... Two-stage converters have recently been developed to try to address the fundamental limitations of single-stage converters in this general space. We begin by reviewing examples of this general approach, some of which have only been published in academic journals while others are in commercial produc ...
1.8V to 28V Input, PWM Step-Up Controllers in µMAX General Description Features
... minimum-current comparator threshold is 15mV, or 15% of the full-load value (IMAX) of 100mV. When the controller is synchronized to an external clock, Idle Mode occurs only at very light loads. ...
... minimum-current comparator threshold is 15mV, or 15% of the full-load value (IMAX) of 100mV. When the controller is synchronized to an external clock, Idle Mode occurs only at very light loads. ...
FEATURES GENERAL DESCRIPTION AD7195 e
... contrast, and read the offset and gain registers. The function of each button is listed at the bottom of the LCD display. To operate the weigh scale demonstration, connect the load cell to Header J4 as shown in Figure 5. Apply power to the AD7195 evaluation board using either a 9 V battery or a 9 V ...
... contrast, and read the offset and gain registers. The function of each button is listed at the bottom of the LCD display. To operate the weigh scale demonstration, connect the load cell to Header J4 as shown in Figure 5. Apply power to the AD7195 evaluation board using either a 9 V battery or a 9 V ...
AD9851 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... The DAC’s external RSET connection—nominally a 3.92 k resistor to ground for 10 mA out. This sets the DAC full-scale output current available from IOUT and IOUTB. RSET = 39.93/IOUT. Voltage Output Negative. The comparator’s complementary CMOS logic level output. Voltage Output Positive. The compara ...
... The DAC’s external RSET connection—nominally a 3.92 k resistor to ground for 10 mA out. This sets the DAC full-scale output current available from IOUT and IOUTB. RSET = 39.93/IOUT. Voltage Output Negative. The comparator’s complementary CMOS logic level output. Voltage Output Positive. The compara ...
ADA4960-1 数据手册DataSheet 下载
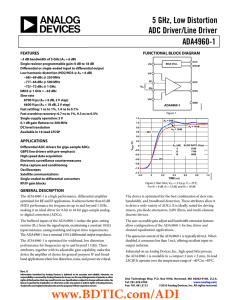
... The ADA4960-1 is a high performance, differential amplifier optimized for RF and IF applications. It achieves better than 63 dB IMD3 performance for frequencies up to and beyond 1 GHz, making it an ideal driver for 8-bit to 10-bit giga-sample analogto-digital converters (ADCs). ...
... The ADA4960-1 is a high performance, differential amplifier optimized for RF and IF applications. It achieves better than 63 dB IMD3 performance for frequencies up to and beyond 1 GHz, making it an ideal driver for 8-bit to 10-bit giga-sample analogto-digital converters (ADCs). ...
AD5063 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... part uses a versatile 3-wire serial interface that operates at clock rates up to 30 MHz and that is compatible with standard SPI®, QSPI™, MICROWIRE™, and DSP interface standards. The reference for the AD5063 is supplied from an external VREF pin. A reference buffer is also provided on-chip. The part ...
... part uses a versatile 3-wire serial interface that operates at clock rates up to 30 MHz and that is compatible with standard SPI®, QSPI™, MICROWIRE™, and DSP interface standards. The reference for the AD5063 is supplied from an external VREF pin. A reference buffer is also provided on-chip. The part ...
DX-40 DX-45 Lynx Panel Meter 4 DIGIT 0.8” LED
... Pin Descriptions Pins 1 to 6 - Input Module: See the individual pin out of the input signal conditioning module selected. Usually Pin 1 is the Signal Input High pin and Pin 3 is the Signal Input Low pin. All calibration and scaling functions are performed on the individual input signal conditioner m ...
... Pin Descriptions Pins 1 to 6 - Input Module: See the individual pin out of the input signal conditioning module selected. Usually Pin 1 is the Signal Input High pin and Pin 3 is the Signal Input Low pin. All calibration and scaling functions are performed on the individual input signal conditioner m ...
II. The Equivalent Input Circuit
... was not presented in [1], as well. The transducer consists of a probe and a signal-processing unit connected to the probe via coaxial extension cable. The probe is a simple, usually coreless coil placed in the tip of a suitable probe body. The purpose of signal-processing unit is to excite the probe ...
... was not presented in [1], as well. The transducer consists of a probe and a signal-processing unit connected to the probe via coaxial extension cable. The probe is a simple, usually coreless coil placed in the tip of a suitable probe body. The purpose of signal-processing unit is to excite the probe ...
nb6l14 - 2.5 V/3.3 V 3.0 GHz Differential 1:4
... NOTE: Device will meet the specifications after thermal equilibrium has been established when mounted in a test socket or printed circuit board with maintained transverse airflow greater than 500 lfpm. Electrical parameters are guaranteed only over the declared operating temperature range. Functiona ...
... NOTE: Device will meet the specifications after thermal equilibrium has been established when mounted in a test socket or printed circuit board with maintained transverse airflow greater than 500 lfpm. Electrical parameters are guaranteed only over the declared operating temperature range. Functiona ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).