Paper
... the cleft have a bandwidth of approximately 10 Hz–1 kHz and an amplitude of approximately 100 V . Another suitable model system for such applications is given by snail neurons (invertebrates). Snail cells with diameters of approximately 50 m provide signals of below 3 mV . Bandwidth is 10 Hz–1 kHz. ...
... the cleft have a bandwidth of approximately 10 Hz–1 kHz and an amplitude of approximately 100 V . Another suitable model system for such applications is given by snail neurons (invertebrates). Snail cells with diameters of approximately 50 m provide signals of below 3 mV . Bandwidth is 10 Hz–1 kHz. ...
MAX3291,92 - Part Number Search
... limiting and a fail-safe receiver input that guarantees a logic-high output if the input is open circuit. A 1/4-unitload receiver input impedance allows up to 128 transceivers on the bus. Inter-symbol interference (ISI) causes significant problems for UARTs if the total RS-485/RS-422 signal jitter b ...
... limiting and a fail-safe receiver input that guarantees a logic-high output if the input is open circuit. A 1/4-unitload receiver input impedance allows up to 128 transceivers on the bus. Inter-symbol interference (ISI) causes significant problems for UARTs if the total RS-485/RS-422 signal jitter b ...
MAX5084/MAX5085 65V, 200mA, Low-Quiescent-Current Linear Regulators in TDFN General Description
... 65V, 200mA, Low-Quiescent-Current Linear Regulators in TDFN The MAX5084/MAX5085 are high-voltage linear regulators with a 6.5V to 65V input voltage range. The devices guarantee 200mA output current and are available with preset output voltages of 3.3V or 5V. Both devices can be used to provide adju ...
... 65V, 200mA, Low-Quiescent-Current Linear Regulators in TDFN The MAX5084/MAX5085 are high-voltage linear regulators with a 6.5V to 65V input voltage range. The devices guarantee 200mA output current and are available with preset output voltages of 3.3V or 5V. Both devices can be used to provide adju ...
Application Note AN-6014 Green Current Mode PWM Controller FAN7602 1. Introduction www.fairchildsemi.com
... If the input voltage of the converter is lower than the minimum operating voltage, the converter input current increases too much, causing component failure. Therefore if the input voltage is low, the converter should be protected. In the FAN7602, the LUVP circuit senses the input voltage using the ...
... If the input voltage of the converter is lower than the minimum operating voltage, the converter input current increases too much, causing component failure. Therefore if the input voltage is low, the converter should be protected. In the FAN7602, the LUVP circuit senses the input voltage using the ...
AD8055
... The AD8055 and AD8056 require only 5 mA typ/amplifier of supply current and operate on a dual ±5 V or a single +12 V power supply, while capable of delivering over 60 mA of load current. The AD8055 is available in a small 8-lead PDIP, an 8-lead SOIC, and a 5-lead SOT-23, while the AD8056 is availabl ...
... The AD8055 and AD8056 require only 5 mA typ/amplifier of supply current and operate on a dual ±5 V or a single +12 V power supply, while capable of delivering over 60 mA of load current. The AD8055 is available in a small 8-lead PDIP, an 8-lead SOIC, and a 5-lead SOT-23, while the AD8056 is availabl ...
Thermocouple Measurements with ΔΣ ADCs
... Thermocouples are widely used in a range of industrial and commercial settings, and the temperature/voltage response for thermocouples is fully characterized. The small voltage output is well-suited to the high resolution capability provided by ∆Σ (Delta-Sigma) analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) wi ...
... Thermocouples are widely used in a range of industrial and commercial settings, and the temperature/voltage response for thermocouples is fully characterized. The small voltage output is well-suited to the high resolution capability provided by ∆Σ (Delta-Sigma) analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) wi ...
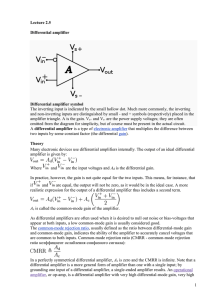
Differential amplifier
... omitted from the diagram for simplicity, but of course must be present in the actual circuit. A differential amplifier is a type of electronic amplifier that multiplies the difference between two inputs by some constant factor (the differential gain). Theory Many electronic devices use differential ...
... omitted from the diagram for simplicity, but of course must be present in the actual circuit. A differential amplifier is a type of electronic amplifier that multiplies the difference between two inputs by some constant factor (the differential gain). Theory Many electronic devices use differential ...
3_conductivity_sensor_intro
... if the voltage drop across the conductivity sensor decreases, then how does this influence the voltage drop across the 10kΩ resistor? it increases ...
... if the voltage drop across the conductivity sensor decreases, then how does this influence the voltage drop across the 10kΩ resistor? it increases ...
1 - DCC
... Each high voltage channel of the LV ESD Driver (bias, UR, LR, UL, and LL) must operate reliably without high voltage breakdown up to the operating limit of the high voltage power amplifier driving each of these channels (430V). The circuit components used in the LV ESD Driver are rated for continuou ...
... Each high voltage channel of the LV ESD Driver (bias, UR, LR, UL, and LL) must operate reliably without high voltage breakdown up to the operating limit of the high voltage power amplifier driving each of these channels (430V). The circuit components used in the LV ESD Driver are rated for continuou ...
TPS40057-Q1 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... 1.55 V. The controller is considered shut down when VSS/SD is 125 mV or less. All internal circuitry is inactive. The internal circuitry is enabled when VSS/SD is 210 mV or greater. When VSS/SD is less than approximately 0.85 V, the outputs cease switching and the output voltage (VOUT) decays while ...
... 1.55 V. The controller is considered shut down when VSS/SD is 125 mV or less. All internal circuitry is inactive. The internal circuitry is enabled when VSS/SD is 210 mV or greater. When VSS/SD is less than approximately 0.85 V, the outputs cease switching and the output voltage (VOUT) decays while ...
PWM
... its speed. • This method was inefficient • PWM provided a great way to have compact and low cost means for applying adjustable power for many devices. ...
... its speed. • This method was inefficient • PWM provided a great way to have compact and low cost means for applying adjustable power for many devices. ...
OPA684 Low-Power, Current Feedback OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER With Disable FEATURES
... output headroom requirement is complemented by a similar 1.2V input stage headroom giving exceptional capability for single +5V operation. The OPA684’s low 1.7mA supply current is precisely trimmed at 25°C. This trim, along with low shift over temperature and supply voltage, gives a very robust desi ...
... output headroom requirement is complemented by a similar 1.2V input stage headroom giving exceptional capability for single +5V operation. The OPA684’s low 1.7mA supply current is precisely trimmed at 25°C. This trim, along with low shift over temperature and supply voltage, gives a very robust desi ...
MAX14920/MAX14921 High-Accuracy 12-/16-Cell Measurement AFEs EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE General Description
... Both devices simultaneously sample all cell voltages, allowing accurate state-of-charge and source-resistance determination. All cell voltages are level shifted to ground reference with unity gain, simplifying external ADC data conversion. The devices have a low-noise, low-offset amplifier that buff ...
... Both devices simultaneously sample all cell voltages, allowing accurate state-of-charge and source-resistance determination. All cell voltages are level shifted to ground reference with unity gain, simplifying external ADC data conversion. The devices have a low-noise, low-offset amplifier that buff ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).