Design of a Charge Controller Circuit.pdf
... Solar energy is one of the most important renewable energy sources that have been gaining increased attention in recent years. Solar energy is plentiful; it has the greatest availability compared to other energy sources. The amount of energy supplied to the earth in one day by the sun is sufficient ...
... Solar energy is one of the most important renewable energy sources that have been gaining increased attention in recent years. Solar energy is plentiful; it has the greatest availability compared to other energy sources. The amount of energy supplied to the earth in one day by the sun is sufficient ...
DATA SHEET For a complete data sheet, please also download:
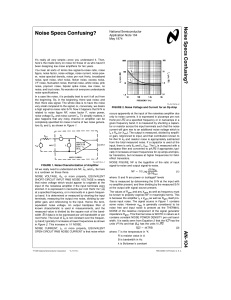
... When the frequency of SIGIN is higher than that of COMPIN, the p-type output driver is held “ON” for most of the input signal cycle time, and for the remainder of the cycle both n and p- type drivers are ”OFF” (3-state). If the SIGIN frequency is lower than the COMPIN frequency, then it is the n-typ ...
... When the frequency of SIGIN is higher than that of COMPIN, the p-type output driver is held “ON” for most of the input signal cycle time, and for the remainder of the cycle both n and p- type drivers are ”OFF” (3-state). If the SIGIN frequency is lower than the COMPIN frequency, then it is the n-typ ...
SG6842
... The proprietary Green-mode function provides off-time modulation to linearly decrease the switching frequency under light-load conditions. On-time is limited to provide protection against abnormal conditions and brownouts. To further reduce power consumption under zero-load conditions, PWM output wi ...
... The proprietary Green-mode function provides off-time modulation to linearly decrease the switching frequency under light-load conditions. On-time is limited to provide protection against abnormal conditions and brownouts. To further reduce power consumption under zero-load conditions, PWM output wi ...
MAX5098A Dual, 2.2MHz, Automotive Buck or Boost Converter with 80V Load-Dump Protection
... Dual, 2.2MHz, Automotive Buck or Boost Converter with 80V Load-Dump Protection The MAX5098A is a dual-output, high-switching-frequency DC-DC converter with integrated n-channel switches that can be used either in high-side or low-side configuration. Each output can be configured either as a buck con ...
... Dual, 2.2MHz, Automotive Buck or Boost Converter with 80V Load-Dump Protection The MAX5098A is a dual-output, high-switching-frequency DC-DC converter with integrated n-channel switches that can be used either in high-side or low-side configuration. Each output can be configured either as a buck con ...
The DatasheetArchive - Datasheet Search Engine
... ■ 2.3V to 3.6V VCC specifications provided ■ 7.0 ns tPD max (VCC = 3.3V), 10 µA ICC max ■ Power down high impedance inputs and outputs ■ Supports live insertion/withdrawal (Note 1) ■ ±24 mA output drive (VCC = 3.0V) ■ Implements patented noise/EMI reduction circuitry ■ Latch-up performance exceeds 5 ...
... ■ 2.3V to 3.6V VCC specifications provided ■ 7.0 ns tPD max (VCC = 3.3V), 10 µA ICC max ■ Power down high impedance inputs and outputs ■ Supports live insertion/withdrawal (Note 1) ■ ±24 mA output drive (VCC = 3.0V) ■ Implements patented noise/EMI reduction circuitry ■ Latch-up performance exceeds 5 ...
PTH05T210W
... The PTH05T210W is a high-performance 30-A rated, non-isolated power module which utilizes a multi-phase, switch-mode topology. This module represents the 2nd generation of the PTH series power modules which includes a reduced footprint and improved features. Operating from an input voltage range of ...
... The PTH05T210W is a high-performance 30-A rated, non-isolated power module which utilizes a multi-phase, switch-mode topology. This module represents the 2nd generation of the PTH series power modules which includes a reduced footprint and improved features. Operating from an input voltage range of ...
NCP1631 - Power Factor Controller, 2-Phase
... stages in lieu of a bigger one, more difficult to design. This approach has several merits like the ease of implementation, the use of smaller components or a better distribution of the heating. Also, Interleaving extends the power range of Critical Conduction Mode that is an efficient and cost−effe ...
... stages in lieu of a bigger one, more difficult to design. This approach has several merits like the ease of implementation, the use of smaller components or a better distribution of the heating. Also, Interleaving extends the power range of Critical Conduction Mode that is an efficient and cost−effe ...
AD5310 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... The write sequence begins by bringing the SYNC line low. Data from the DIN line is clocked into the 16-bit shift register on the falling edge of SCLK. The serial clock frequency can be as high as 30 MHz making the AD5310 compatible with high speed DSPs. On the sixteenth falling clock edge, the last ...
... The write sequence begins by bringing the SYNC line low. Data from the DIN line is clocked into the 16-bit shift register on the falling edge of SCLK. The serial clock frequency can be as high as 30 MHz making the AD5310 compatible with high speed DSPs. On the sixteenth falling clock edge, the last ...
Single-Supply, 10MHz, Rail-to-Rail Output, Low-Noise, JFET Amplifier OPA141 OPA2141
... Junction Temperature, TJ ...
... Junction Temperature, TJ ...
ADP1147 High Efficiency Step-Down Switching Regulator
... When load currents are low, comparator B sets the R-S flip-flop #2 and asserts the power savings mode of operation. Comparator B monitors the voltage developed across RSENSE. As the load current decreases to 50% of the designed inductor ripple current, the voltage reverses polarity. This reversal ca ...
... When load currents are low, comparator B sets the R-S flip-flop #2 and asserts the power savings mode of operation. Comparator B monitors the voltage developed across RSENSE. As the load current decreases to 50% of the designed inductor ripple current, the voltage reverses polarity. This reversal ca ...
FEATURES APPLICATIONS DESCRIPTION
... filter inductors or current sense resistors installed in series with output. The first method involves generation of a current signal with an R-C circuit (shown in the applications diagram). The R-C values are selected by matching time constants of the RC circuit and the inductor time constant, R×C ...
... filter inductors or current sense resistors installed in series with output. The first method involves generation of a current signal with an R-C circuit (shown in the applications diagram). The R-C values are selected by matching time constants of the RC circuit and the inductor time constant, R×C ...
Lecture 13: Amplifier Noise Calculations - RFIC
... If the LNA input is not matched, the impedance seen by the antenna depends on the length of this transmission line (EECS 117). This is a bad situation because we cannot predict how much power will reach the LNA ! But if we match, then you’re certain that regardless of the length of the T-line, the i ...
... If the LNA input is not matched, the impedance seen by the antenna depends on the length of this transmission line (EECS 117). This is a bad situation because we cannot predict how much power will reach the LNA ! But if we match, then you’re certain that regardless of the length of the T-line, the i ...
General Description Features
... The MAX16821A, MAX16821B, and MAX16821C are high-performance average current-mode PWM controllers for high-power and high-brightness LEDs (HB LEDs). The average current-mode control technique offers inherently stable operation, reduces component derating and size by accurately controlling the induct ...
... The MAX16821A, MAX16821B, and MAX16821C are high-performance average current-mode PWM controllers for high-power and high-brightness LEDs (HB LEDs). The average current-mode control technique offers inherently stable operation, reduces component derating and size by accurately controlling the induct ...
Performance Verification of Low Noise, Low Dropout Regulators
... low dropout while minimizing base drive loss. This is particularly the case at higher pass currents. Considerable effort was expended in this direction in the LT176X through LT196X designs. Common source connected P-channel MOSFETs are also candidates. The do not suffer the drive losses of bipolars, ...
... low dropout while minimizing base drive loss. This is particularly the case at higher pass currents. Considerable effort was expended in this direction in the LT176X through LT196X designs. Common source connected P-channel MOSFETs are also candidates. The do not suffer the drive losses of bipolars, ...
Exp_8_FFT_Spring13b
... As we discussed in Experiment 7, transistors are devices used to amplify electrical signals. They come in two general types, bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and field effect transistors (FETs). The input to a FET is called the gate. (Remember from Experiment 7: the input to a BJT is called the b ...
... As we discussed in Experiment 7, transistors are devices used to amplify electrical signals. They come in two general types, bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and field effect transistors (FETs). The input to a FET is called the gate. (Remember from Experiment 7: the input to a BJT is called the b ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).