analysis of pwm strategies for a three phase quasi z
... and is very low and it cannot be connected to the grid directly. Conventional configuration of connecting photovoltaic array to the grid is a combination of dc/dc converter and an inverter. DC to DC converter can act as a buck boost converter and the function of inverter is to deliver power to the g ...
... and is very low and it cannot be connected to the grid directly. Conventional configuration of connecting photovoltaic array to the grid is a combination of dc/dc converter and an inverter. DC to DC converter can act as a buck boost converter and the function of inverter is to deliver power to the g ...
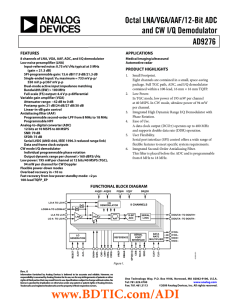
Octal LNA/VGA/AAF/12-Bit ADC and CW I/Q Demodulator AD9276
... amplifier (VGA) with a low noise preamplifier (LNA); an antialiasing filter (AAF); a 12-bit, 10 MSPS to 80 MSPS analog-todigital converter (ADC); and an I/Q demodulator with programmable phase rotation. Each channel features a variable gain range of 42 dB, a fully differential signal path, an active ...
... amplifier (VGA) with a low noise preamplifier (LNA); an antialiasing filter (AAF); a 12-bit, 10 MSPS to 80 MSPS analog-todigital converter (ADC); and an I/Q demodulator with programmable phase rotation. Each channel features a variable gain range of 42 dB, a fully differential signal path, an active ...
TL783 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... The TL783 is an adjustable three-terminal high-voltage regulator with an output range of 1.25 V to 125 V and a DMOS output transistor capable of sourcing more than 700 mA. It is designed for use in high-voltage applications where standard bipolar regulators cannot be used. Excellent performance spec ...
... The TL783 is an adjustable three-terminal high-voltage regulator with an output range of 1.25 V to 125 V and a DMOS output transistor capable of sourcing more than 700 mA. It is designed for use in high-voltage applications where standard bipolar regulators cannot be used. Excellent performance spec ...
Chapter 6: Voltage Regulator
... resistance, the decrease is sensed by R1 and R2. A feedback voltage obtained from voltage divider R1 and R2 is applied to the op-amp’s non-inverting input and compared to the Zener voltage to control the drive current to the transistor. The current through resistor RS is thus controlled to drop ...
... resistance, the decrease is sensed by R1 and R2. A feedback voltage obtained from voltage divider R1 and R2 is applied to the op-amp’s non-inverting input and compared to the Zener voltage to control the drive current to the transistor. The current through resistor RS is thus controlled to drop ...
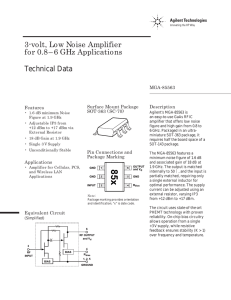
Detection of optical radiation
... types of discrete devices or integrated circuits (ICs) are suitable for the active element in preamplifiers: bipolar (BJT) or field-effect transistor (FET) or an integrated circuit with an input bipolar, FET or MOSFET transistor can be used. The most important parameter of each receiving device is its ...
... types of discrete devices or integrated circuits (ICs) are suitable for the active element in preamplifiers: bipolar (BJT) or field-effect transistor (FET) or an integrated circuit with an input bipolar, FET or MOSFET transistor can be used. The most important parameter of each receiving device is its ...
NIR-10 - scootworks
... data, etc.) within the audio passband. It rejects the non-coherent frequencies of white noise and similar noise types. This provides a second means of noise reduction for the user. With CW signals, if a CW tone can be separated with the receiver filter, it can be further peaked and noise-reduced usi ...
... data, etc.) within the audio passband. It rejects the non-coherent frequencies of white noise and similar noise types. This provides a second means of noise reduction for the user. With CW signals, if a CW tone can be separated with the receiver filter, it can be further peaked and noise-reduced usi ...
Chapter 6: Voltage Regulator
... resistance, the decrease is sensed by R1 and R2. A feedback voltage obtained from voltage divider R1 and R2 is applied to the op-amp’s non-inverting input and compared to the Zener voltage to control the drive current to the transistor. The current through resistor RS is thus controlled to drop ...
... resistance, the decrease is sensed by R1 and R2. A feedback voltage obtained from voltage divider R1 and R2 is applied to the op-amp’s non-inverting input and compared to the Zener voltage to control the drive current to the transistor. The current through resistor RS is thus controlled to drop ...
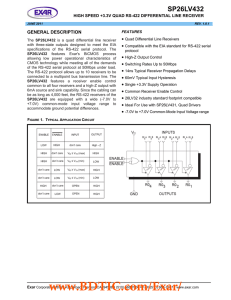
SP26LV432 数据资料DataSheet下载
... protocol allows up to 10 receivers to be connected to a data bus, making it an ideal choice for multi-drop applications. Since the cabling can be as long as 4,000 feet, RS-422 Receivers have an input sensitivity of 200mV over the wide (-7.0V to +7.0V) common mode range to accommodate ground potentia ...
... protocol allows up to 10 receivers to be connected to a data bus, making it an ideal choice for multi-drop applications. Since the cabling can be as long as 4,000 feet, RS-422 Receivers have an input sensitivity of 200mV over the wide (-7.0V to +7.0V) common mode range to accommodate ground potentia ...
III. Dual -band energy harvester - Ece.umd.edu
... same frequency. Simultaneous power matching and boosting can be achieved by the co-design of the antenna and RF energy harvester. The matching impedance of the antenna and the energy harvester is generally designed to be 50 Ohm [4]. Since the antenna can connect to the energy harvester directly, max ...
... same frequency. Simultaneous power matching and boosting can be achieved by the co-design of the antenna and RF energy harvester. The matching impedance of the antenna and the energy harvester is generally designed to be 50 Ohm [4]. Since the antenna can connect to the energy harvester directly, max ...
TPA3002D2 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... applied to the volume control terminal offering a range of gain from –40 dB to 36 dB. Line outputs, for driving external headphone amplifier inputs, are also dc voltage controlled with a range of gain from –56 dB to 20 dB. An integrated 5-V regulated supply is provided for ...
... applied to the volume control terminal offering a range of gain from –40 dB to 36 dB. Line outputs, for driving external headphone amplifier inputs, are also dc voltage controlled with a range of gain from –56 dB to 20 dB. An integrated 5-V regulated supply is provided for ...
TS555
... pulse simultaneously to the Reset terminal (pin 4) and the Trigger terminal (pin 2) during the timing cycle discharges the external capacitor and causes the cycle to start over. The timing cycle then starts on the positive edge of the reset pulse. While the reset pulse is applied, the output is driv ...
... pulse simultaneously to the Reset terminal (pin 4) and the Trigger terminal (pin 2) during the timing cycle discharges the external capacitor and causes the cycle to start over. The timing cycle then starts on the positive edge of the reset pulse. While the reset pulse is applied, the output is driv ...
Soundmate 2 - Pro Lighting
... Never let the power-cord come into contact with other cables! Handle the power-cord and all connections with the mains with particular caution! Never remove warning or informative labels from the unit. Never use anything to cover the ground contact. Do not insert objects into air vents. Do not conne ...
... Never let the power-cord come into contact with other cables! Handle the power-cord and all connections with the mains with particular caution! Never remove warning or informative labels from the unit. Never use anything to cover the ground contact. Do not insert objects into air vents. Do not conne ...
Chapt9_1.pps
... – Common mode noise is the voltage picked up on the leads connecting the sensor to the amplifier may be 100 to 1000 times greater than the magnitude of the sensor signal itself; – The CMRR of the OA ensures that any signal appearing on both inputs at the same time will be attenuated considerably at ...
... – Common mode noise is the voltage picked up on the leads connecting the sensor to the amplifier may be 100 to 1000 times greater than the magnitude of the sensor signal itself; – The CMRR of the OA ensures that any signal appearing on both inputs at the same time will be attenuated considerably at ...
ANTARIS® 4 GPS Modules Data Sheet
... National Semiconductors, Linear Technology, LTC1860, 12-bit A/D converter LM70, precision: 10 bits plus sign Table 9: Supported peripheral components ...
... National Semiconductors, Linear Technology, LTC1860, 12-bit A/D converter LM70, precision: 10 bits plus sign Table 9: Supported peripheral components ...
Low-Noise, Low Quiescent Current, Precision Operational Amplifier e-trim™ OPA376
... significantly reduces ringing while maintaining dc performance for purely capacitive loads. However, if there is a resistive load in parallel with the capacitive ...
... significantly reduces ringing while maintaining dc performance for purely capacitive loads. However, if there is a resistive load in parallel with the capacitive ...
Diapositivo 1
... – Common mode noise is the voltage picked up on the leads connecting the sensor to the amplifier may be 100 to 1000 times greater than the magnitude of the sensor signal itself; – The CMRR of the OA ensures that any signal appearing on both inputs at the same time will be attenuated considerably at ...
... – Common mode noise is the voltage picked up on the leads connecting the sensor to the amplifier may be 100 to 1000 times greater than the magnitude of the sensor signal itself; – The CMRR of the OA ensures that any signal appearing on both inputs at the same time will be attenuated considerably at ...
BUF602 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... (1000MHz) and high slew rate (8000V/µs) make it ideal for buffering very high-frequency signals. For AC-coupled applications, an optional mid-point reference (VREF) is provided, reducing the number of external components required and the necessary supply current to provide that reference. ...
... (1000MHz) and high slew rate (8000V/µs) make it ideal for buffering very high-frequency signals. For AC-coupled applications, an optional mid-point reference (VREF) is provided, reducing the number of external components required and the necessary supply current to provide that reference. ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).