MAX15026 Low-Cost, Small, 4.5V to 28V Wide Operating General Description
... The MAX15026 synchronous step-down controller operates from a 4.5V to 28V input voltage range and generates an adjustable output voltage from 85% of the input voltage down to 0.6V while supporting loads up to 25A. As long as the device supply voltage is within 5.0V to 5.5V, the input power bus (VIN) ...
... The MAX15026 synchronous step-down controller operates from a 4.5V to 28V input voltage range and generates an adjustable output voltage from 85% of the input voltage down to 0.6V while supporting loads up to 25A. As long as the device supply voltage is within 5.0V to 5.5V, the input power bus (VIN) ...
TPS40054 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... used as a second non-inverting input to the error amplifier. The output voltage begins to rise when VSS/SD is approximately 0.85 V. The output continues to rise and reaches regulation when VSS/SD is approximately 1.55 V. The controller is considered shut down when VSS/SD is 125 mV or less. The inter ...
... used as a second non-inverting input to the error amplifier. The output voltage begins to rise when VSS/SD is approximately 0.85 V. The output continues to rise and reaches regulation when VSS/SD is approximately 1.55 V. The controller is considered shut down when VSS/SD is 125 mV or less. The inter ...
MAX9814 - Part Number Search
... time. When the output signal subsequently lowers in amplitude, the gain is held at the reduced state for a short period before slowly increasing to the normal value. This process is known as the hold and release time. The speed at which the amplifiers adjust to changing input signals is set by the e ...
... time. When the output signal subsequently lowers in amplitude, the gain is held at the reduced state for a short period before slowly increasing to the normal value. This process is known as the hold and release time. The speed at which the amplifiers adjust to changing input signals is set by the e ...
Op_amps.pdf
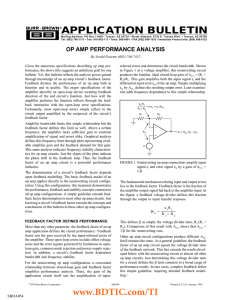
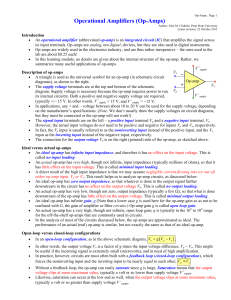
... The signal input terminals are on the left – a positive input terminal Vp and a negative input terminal, Vn. However, the actual input voltages do not need to be positive and negative for inputs Vp and Vn, respectively. In fact, the Vp input is usually referred to as the noninverting input inste ...
... The signal input terminals are on the left – a positive input terminal Vp and a negative input terminal, Vn. However, the actual input voltages do not need to be positive and negative for inputs Vp and Vn, respectively. In fact, the Vp input is usually referred to as the noninverting input inste ...
Section 5 High Speed PCB Layout Techniques
... made even worse by the break in the ground plane. The obvious issue with this is the ground plane is often used as a reference point for other parts of the system. If the current flow density is high near one of these reference points, this can (and often does) cause noise to occur in the circuit an ...
... made even worse by the break in the ground plane. The obvious issue with this is the ground plane is often used as a reference point for other parts of the system. If the current flow density is high near one of these reference points, this can (and often does) cause noise to occur in the circuit an ...
LT5554
... of input coupling capacitor sets the low frequency corner (LF) at input. The output coupling capacitors or the transformer sets the low frequency corner (LF) at the output. The LT5554 operates internally down to DC. ...
... of input coupling capacitor sets the low frequency corner (LF) at input. The output coupling capacitors or the transformer sets the low frequency corner (LF) at the output. The LT5554 operates internally down to DC. ...
LF412-N 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... The LF412 series of JFET input dual op amps are internally trimmed (BI-FET II™) providing very low input offset voltages and guaranteed input offset voltage drift. These JFETs have large reverse breakdown voltages from gate to source and drain eliminating the need for clamps across the inputs. There ...
... The LF412 series of JFET input dual op amps are internally trimmed (BI-FET II™) providing very low input offset voltages and guaranteed input offset voltage drift. These JFETs have large reverse breakdown voltages from gate to source and drain eliminating the need for clamps across the inputs. There ...
An Si–SiGe BiCMOS Direct-Conversion Mixer With Second-Order and Third-Order Nonlinearity
... to 14-dB linearity improvement can be achieved with proper choice of source harmonic termination. In Section II, we directly compute the nonlinear response of a differential CE circuit. The direct nonlinear response is solved, then a relatively straightforward expression for third-order nonlinearity ...
... to 14-dB linearity improvement can be achieved with proper choice of source harmonic termination. In Section II, we directly compute the nonlinear response of a differential CE circuit. The direct nonlinear response is solved, then a relatively straightforward expression for third-order nonlinearity ...
Simulation and Experimental Demonstration ofLow-/High
... Memristor was first postulated by Prof. Leon Chua in the year 1971, as the missing non-linear two terminal passive device relating magnetic flux and electric charge. The memristor behaves like a non-linear resistor having ‘memory’, as its present state is dependent upon the history of the current th ...
... Memristor was first postulated by Prof. Leon Chua in the year 1971, as the missing non-linear two terminal passive device relating magnetic flux and electric charge. The memristor behaves like a non-linear resistor having ‘memory’, as its present state is dependent upon the history of the current th ...
MAX536/MAX537 Calibrated, Quad, 12-Bit Voltage-Output DACs with Serial Interface _______________General Description
... Crosstalk is defined as the glitch energy at any DAC output in response to a full-scale step change on any other DAC. Digital inputs at 2.4V; with digital inputs at CMOS levels, IDD decreases slightly. All input signals are specified with tR = tF ≤ 5ns. Logic input swing is 0V to 5V. Serial data clo ...
... Crosstalk is defined as the glitch energy at any DAC output in response to a full-scale step change on any other DAC. Digital inputs at 2.4V; with digital inputs at CMOS levels, IDD decreases slightly. All input signals are specified with tR = tF ≤ 5ns. Logic input swing is 0V to 5V. Serial data clo ...
FAN2306 / FAN2306M TinyBuck™ 6 A Integrated Synchronous Buck Regulator F A
... Typical Performance Characteristics ...
... Typical Performance Characteristics ...
Evaluation Board User Guide UG-224
... This button allows the user to have a fixed x-axis or a dynamic x-axis. When the x-axis is fixed, the number of samples to display is entered in the X-scale Samples text box. ...
... This button allows the user to have a fixed x-axis or a dynamic x-axis. When the x-axis is fixed, the number of samples to display is entered in the X-scale Samples text box. ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).