1.8 V, 6 LVDS/12 CMOS Outputs Low Power Clock Fanout Buffer ADCLK846
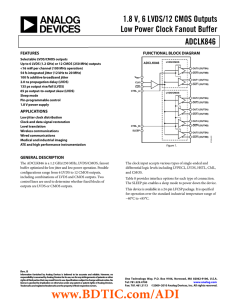
... The clock input accepts various types of single-ended and differential logic levels including LVPECL, LVDS, HSTL, CML, and CMOS. Table 8 provides interface options for each type of connection. The SLEEP pin enables a sleep mode to power down the device. This device is available in a 24-pin LFCSP pac ...
... The clock input accepts various types of single-ended and differential logic levels including LVPECL, LVDS, HSTL, CML, and CMOS. Table 8 provides interface options for each type of connection. The SLEEP pin enables a sleep mode to power down the device. This device is available in a 24-pin LFCSP pac ...
ADP5024 英文数据手册DataSheet 下载
... When the MODE pin is set high, the buck regulators operate in forced PWM mode. When the MODE pin is set low, the buck regulators operate in PWM mode when the load current is above a predefined threshold. When the load current falls below a predefined threshold, the regulator operates in power save m ...
... When the MODE pin is set high, the buck regulators operate in forced PWM mode. When the MODE pin is set low, the buck regulators operate in PWM mode when the load current is above a predefined threshold. When the load current falls below a predefined threshold, the regulator operates in power save m ...
TPS2331 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... transients on the voltage rail, the voltage sense circuit incorporates a 20-µs deglitch filter. When VSENSE is lower than the reference voltage (about 1.23 V), PWRGD is active-low to indicate an undervoltage condition on the power-rail voltage. PWRGD may not correctly report power conditions when th ...
... transients on the voltage rail, the voltage sense circuit incorporates a 20-µs deglitch filter. When VSENSE is lower than the reference voltage (about 1.23 V), PWRGD is active-low to indicate an undervoltage condition on the power-rail voltage. PWRGD may not correctly report power conditions when th ...
JFG_Lyon_10_15_08-1 - Indico
... • 3 cyclic phase coordinates • Cyclically varying electrodes allow – Determination of a coarse position using a Vernier type technique – Spatial resolution greater than charge measurement accuracy – The full unique range of the pattern can be utilized ...
... • 3 cyclic phase coordinates • Cyclically varying electrodes allow – Determination of a coarse position using a Vernier type technique – Spatial resolution greater than charge measurement accuracy – The full unique range of the pattern can be utilized ...
Radio Receivers
... The closure the input frequency is to the resonant circuit the greater the output voltage. The IF frequency falls exactly half way between the output voltage from the two tuned circuits. The rectified output voltage across R1 and R2 when added produce a differential output voltage Vout = 0. When the ...
... The closure the input frequency is to the resonant circuit the greater the output voltage. The IF frequency falls exactly half way between the output voltage from the two tuned circuits. The rectified output voltage across R1 and R2 when added produce a differential output voltage Vout = 0. When the ...
AD587 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... The AD587 is designed for precision reference applications where temperature performance is critical. Extensive temperature testing ensures that the device’s high level of performance is maintained over the operating temperature range. Some confusion exists in the area of defining and specifying ref ...
... The AD587 is designed for precision reference applications where temperature performance is critical. Extensive temperature testing ensures that the device’s high level of performance is maintained over the operating temperature range. Some confusion exists in the area of defining and specifying ref ...
AD5066 数据手册DataSheet 下载
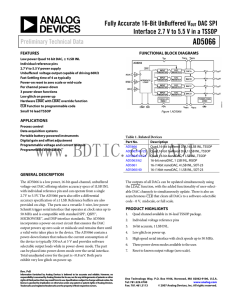
... the LDAC function, with the added functionality of user-selectable DAC channels to simultaneously update. There is also an asynchronous CLR that clears all DACs to a software-selectable code - 0 V, midscale, or full scale. ...
... the LDAC function, with the added functionality of user-selectable DAC channels to simultaneously update. There is also an asynchronous CLR that clears all DACs to a software-selectable code - 0 V, midscale, or full scale. ...
document
... on the performance and non-linearity. To test this, an the implementation with just a single TDC and one ring of logic-free slices around the delay line was implemented. A second implementation without such a guard ring was also tested; this implementation consisted of three consecutive TDCs with th ...
... on the performance and non-linearity. To test this, an the implementation with just a single TDC and one ring of logic-free slices around the delay line was implemented. A second implementation without such a guard ring was also tested; this implementation consisted of three consecutive TDCs with th ...
302 User Guide and Technical Information
... wide gain range to accommodate nearly all signal types. The 302 easily accepts signals from lowsensitivity ribbon and dynamic microphones, medium level wireless and condenser mic outputs, and “hot” line-level signals. 302 inputs are transformer-balanced. The isolation characteristics of transformers ...
... wide gain range to accommodate nearly all signal types. The 302 easily accepts signals from lowsensitivity ribbon and dynamic microphones, medium level wireless and condenser mic outputs, and “hot” line-level signals. 302 inputs are transformer-balanced. The isolation characteristics of transformers ...
MAX17129/MAX17149 Low-Cost, 6-String WLED Drivers with Quick-PWM Step-Up Converter General Description
... frequency ranges from 100Hz to 25kHz with 400ns minimum on-time. In hybrid dimming mode, the LED current amplitude can be adjusted to 25% of full-scale LED current to improve system efficiency when brightness is low. The devices have multiple features to protect the controller from fault conditions. ...
... frequency ranges from 100Hz to 25kHz with 400ns minimum on-time. In hybrid dimming mode, the LED current amplitude can be adjusted to 25% of full-scale LED current to improve system efficiency when brightness is low. The devices have multiple features to protect the controller from fault conditions. ...
ADG711 数据手册DataSheet下载
... input and the output switching off. “OFF” time or “ON” time measured between the 90% points of both switches, when switching from one address state to another. (ADG713 only). A measure of unwanted signal that is coupled through from one channel to another as a result of parasitic capacitance. A meas ...
... input and the output switching off. “OFF” time or “ON” time measured between the 90% points of both switches, when switching from one address state to another. (ADG713 only). A measure of unwanted signal that is coupled through from one channel to another as a result of parasitic capacitance. A meas ...
ABCs of DMMs
... age is usually the first step when wave, but is often much higher for a rectifier current pulse, for troubleshooting a circuit. If there example. As a result, an average is no voltage present, or if it is responding meter will often read too high or too low, the voltage problem should be corrected m ...
... age is usually the first step when wave, but is often much higher for a rectifier current pulse, for troubleshooting a circuit. If there example. As a result, an average is no voltage present, or if it is responding meter will often read too high or too low, the voltage problem should be corrected m ...
Power Monitor - Cypress Semiconductor
... VType[x] – This parameter determines type of voltage measurement for the power converter. The options are Single Ended or Differential. If Differential option is selected, then that power converter forfeits the current measurement. In this case, the symbol will display a terminal with name “rtn” whi ...
... VType[x] – This parameter determines type of voltage measurement for the power converter. The options are Single Ended or Differential. If Differential option is selected, then that power converter forfeits the current measurement. In this case, the symbol will display a terminal with name “rtn” whi ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).