ISD2560/75/90/120 - Experimentalists Anonymous
... The ISD2500 series is designed with several built-in Operational Modes that provide maximum functionality with minimum external components. These modes are described in details as below. The Operational Modes are accessed via the address pins and mapped beyond the normal message address range. When ...
... The ISD2500 series is designed with several built-in Operational Modes that provide maximum functionality with minimum external components. These modes are described in details as below. The Operational Modes are accessed via the address pins and mapped beyond the normal message address range. When ...
real-time monitoring and assessment of circuit breaker operations
... A solution called Circuit Breaker Monitoring and Analysis (CBMA) developed at Texas A&M University, intends to solve described problems by integrating customized software and hardware solutions into a single, real-time monitoring and analysis system. The system for real-time monitoring and analysis ...
... A solution called Circuit Breaker Monitoring and Analysis (CBMA) developed at Texas A&M University, intends to solve described problems by integrating customized software and hardware solutions into a single, real-time monitoring and analysis system. The system for real-time monitoring and analysis ...
AN4130
... over time. Since the voltage on this pin, divided by 2, directly sets the current at which the FET switch turns off, the output current is regulated. In DC-input flyback power supplies very small capacitors are used on the ILED pin for quick response to changing loads or input voltage. The capacitor ...
... over time. Since the voltage on this pin, divided by 2, directly sets the current at which the FET switch turns off, the output current is regulated. In DC-input flyback power supplies very small capacitors are used on the ILED pin for quick response to changing loads or input voltage. The capacitor ...
MAX1705/MAX1706 1- to 3-Cell, High-Current, Low-Noise, Step-Up DC-DC Converters with Linear Regulator
... The MAX1705/MAX1706 are high-efficiency, low-noise, step-up DC-DC converters with an auxiliary linearregulator output. These devices are intended for use in battery-powered wireless applications. They use a synchronous rectifier pulse-width-modulation (PWM) boost topology to generate 2.5V to 5.5V ou ...
... The MAX1705/MAX1706 are high-efficiency, low-noise, step-up DC-DC converters with an auxiliary linearregulator output. These devices are intended for use in battery-powered wireless applications. They use a synchronous rectifier pulse-width-modulation (PWM) boost topology to generate 2.5V to 5.5V ou ...
bq76925 Analog Front End for 3 to 6 Series Lithium
... The bq76925 device integrates cell balancing FETs that are fully controlled by the Host. The balancing current is set by external resistors up to a maximum value of 50 mA. These same FETs may be utilized in conjunction with cell voltage measurements to detect an open wire on a cell sense-line. The H ...
... The bq76925 device integrates cell balancing FETs that are fully controlled by the Host. The balancing current is set by external resistors up to a maximum value of 50 mA. These same FETs may be utilized in conjunction with cell voltage measurements to detect an open wire on a cell sense-line. The H ...
THS4504 THS4505
... Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet. PowerPAD is a trademark of Texas Instruments, Incorporated. All other trade ...
... Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet. PowerPAD is a trademark of Texas Instruments, Incorporated. All other trade ...
MAX5088/MAX5089 2.2MHz, 2A Buck Converters with an Integrated High-Side Switch General Description
... The MAX5088/MAX5089 use a pulse-width modulation (PWM) voltage-mode control scheme. The MAX5088 is a nonsynchronous converter and uses an external lowforward-drop Schottky diode for rectification. The MAX5089 is a synchronous converter and drives a lowside, low-gate-charge MOSFET for higher efficien ...
... The MAX5088/MAX5089 use a pulse-width modulation (PWM) voltage-mode control scheme. The MAX5088 is a nonsynchronous converter and uses an external lowforward-drop Schottky diode for rectification. The MAX5089 is a synchronous converter and drives a lowside, low-gate-charge MOSFET for higher efficien ...
EcoSpeedTM Step-down Controller with I2C Interface
... controller. Additionally, a status register provides information on device state and faults. The controller is capable of operating with all ceramic solutions and switching frequencies up to 1MHz. The programmable frequency and selectable power save mode offer the flexibility to optimize the control ...
... controller. Additionally, a status register provides information on device state and faults. The controller is capable of operating with all ceramic solutions and switching frequencies up to 1MHz. The programmable frequency and selectable power save mode offer the flexibility to optimize the control ...
Aalborg Universitet Zero sequence blocking transformers for multi-pulse rectifier in aerospace applications
... power into different voltages from the generator. Thus, ACDC converters are widely used in MEA. There are mainly two types of AC-DC conversion systems on board – Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) converter and Auto-Transformer Rectifier Unit (ATRU). The later one has been widely adopted in military and c ...
... power into different voltages from the generator. Thus, ACDC converters are widely used in MEA. There are mainly two types of AC-DC conversion systems on board – Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) converter and Auto-Transformer Rectifier Unit (ATRU). The later one has been widely adopted in military and c ...
E4OD Quick 1 Manual - The US Shift Transmission Control System
... will use the secondary calibration tables, allowing a completely different calibration to be selected for the transmission at any time. The Table Selection input may also be connected to a nitrous oxide system to provide an alternate calibration for use when the nitrous system is engaged. Other uses ...
... will use the secondary calibration tables, allowing a completely different calibration to be selected for the transmission at any time. The Table Selection input may also be connected to a nitrous oxide system to provide an alternate calibration for use when the nitrous system is engaged. Other uses ...
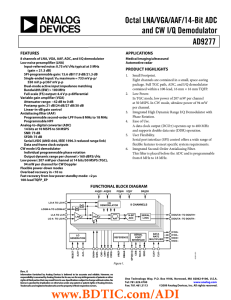
Octal LNA/VGA/AAF/14-Bit ADC and CW I/Q Demodulator AD9277
... amplifier (VGA) with a low noise preamplifier (LNA); an antialiasing filter (AAF); a 14-bit, 10 MSPS to 50 MSPS analog-todigital converter (ADC); and an I/Q demodulator with programmable phase rotation. Each channel features a variable gain range of 42 dB, a fully differential signal path, an active ...
... amplifier (VGA) with a low noise preamplifier (LNA); an antialiasing filter (AAF); a 14-bit, 10 MSPS to 50 MSPS analog-todigital converter (ADC); and an I/Q demodulator with programmable phase rotation. Each channel features a variable gain range of 42 dB, a fully differential signal path, an active ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).