Ascensia® WinGLUCOFACTS® Professional Software Improves
... toward the disease. WinGLUCOFACTS was used solely on the HCP’s computer in this study. Although it can also be used at home on a patient’s personal computer, none of the subjects in this study downloaded their meters at home. Two primary care physicians managed 90 Test Group and 66 Control Group sub ...
... toward the disease. WinGLUCOFACTS was used solely on the HCP’s computer in this study. Although it can also be used at home on a patient’s personal computer, none of the subjects in this study downloaded their meters at home. Two primary care physicians managed 90 Test Group and 66 Control Group sub ...
Slide 1
... Currently 6 types of monogenic diabetes recognised Some types managed by diet and exercise alone Often initially misdiagnosed as type 1 or type 2 diabetes Diagnosing correctly can help • inform which treatments are most appropriate • give some idea of how the diabetes is likely to progress • affecte ...
... Currently 6 types of monogenic diabetes recognised Some types managed by diet and exercise alone Often initially misdiagnosed as type 1 or type 2 diabetes Diagnosing correctly can help • inform which treatments are most appropriate • give some idea of how the diabetes is likely to progress • affecte ...
Perioperative Hypoglycemia in Patients With Diabetes
... administered judiciously to minimize the risk of hypoglycemia. In patients with diabetes in whom preoperative blood glucose levels are on the low end of normal, hypoglycemia risk may be underestimated. This retrospective study enrolled subjects with presenting preoperative blood glucose values in th ...
... administered judiciously to minimize the risk of hypoglycemia. In patients with diabetes in whom preoperative blood glucose levels are on the low end of normal, hypoglycemia risk may be underestimated. This retrospective study enrolled subjects with presenting preoperative blood glucose values in th ...
Diabetic Ketoacidosis DKA
... Figure 6: How insulin and glucagon control blood glucose homeostasis. (90-100mg/dL is 4.9-5.5 mmol/L). ...
... Figure 6: How insulin and glucagon control blood glucose homeostasis. (90-100mg/dL is 4.9-5.5 mmol/L). ...
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
... Fasting Plasma Glucose FPG ≥126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L)* Fasting defined as no caloric intake for ≥8 hrs 2-hr PG ≥200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) during OGTT (75-g)* Performed as described by the WHO, using glucose load containing the equivalent of 75g anhydrous glucose dissolved in water. Oral glucose toler ...
... Fasting Plasma Glucose FPG ≥126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L)* Fasting defined as no caloric intake for ≥8 hrs 2-hr PG ≥200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) during OGTT (75-g)* Performed as described by the WHO, using glucose load containing the equivalent of 75g anhydrous glucose dissolved in water. Oral glucose toler ...
2012 SEMDSA Guideline for type 2 diabetes mellitus
... aSevere decompensation includes any of: FPG > 15mmol/L, HbA1C > 11%, marked polyuria & polydipsia, weight loss > 5% or ketoacidosis. Refer the patient for specialist care (Step 4). bRefer to Table I for expected HbA1C reductions. cRefer to text dIf at diagnosis, the patient’s HbA1C is >9% without fe ...
... aSevere decompensation includes any of: FPG > 15mmol/L, HbA1C > 11%, marked polyuria & polydipsia, weight loss > 5% or ketoacidosis. Refer the patient for specialist care (Step 4). bRefer to Table I for expected HbA1C reductions. cRefer to text dIf at diagnosis, the patient’s HbA1C is >9% without fe ...
Nurse Practitioner Clinical Guidelines Diabetes
... 7.1. Type 1 Diabetes Diabetes Mellitus is a metabolic disorder of multiple etiology, characterised by chronic hyperglycaemia. Type 1 diabetes is most often associated with a genetic predisposition, the presence of autoimmune markers, progressive beta cell destruction, severe insulin deficiency, and ...
... 7.1. Type 1 Diabetes Diabetes Mellitus is a metabolic disorder of multiple etiology, characterised by chronic hyperglycaemia. Type 1 diabetes is most often associated with a genetic predisposition, the presence of autoimmune markers, progressive beta cell destruction, severe insulin deficiency, and ...
Dynamics, Impact, and feasibility of self
... has revealed that the infrastructure necessary to remotely monitor patients who require a higher level of care also needed to be developed to improve glucose control in these patients. Separate investigations of our chronic disease activities in western Kenya have revealed that only 42% of patients ...
... has revealed that the infrastructure necessary to remotely monitor patients who require a higher level of care also needed to be developed to improve glucose control in these patients. Separate investigations of our chronic disease activities in western Kenya have revealed that only 42% of patients ...
Full Text - Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology
... toward the disease. WinGLUCOFACTS was used solely on the HCP’s computer in this study. Although it can also be used at home on a patient’s personal computer, none of the subjects in this study downloaded their meters at home. Two primary care physicians managed 90 Test Group and 66 Control Group sub ...
... toward the disease. WinGLUCOFACTS was used solely on the HCP’s computer in this study. Although it can also be used at home on a patient’s personal computer, none of the subjects in this study downloaded their meters at home. Two primary care physicians managed 90 Test Group and 66 Control Group sub ...
diabetes in cats
... In human diabetes, Type 1 refers to a condition of insulin dependency seen in people who are generally lean, young and prone to ketogenesis. It is caused by immune-‐mediated beta cell depletion, causing ...
... In human diabetes, Type 1 refers to a condition of insulin dependency seen in people who are generally lean, young and prone to ketogenesis. It is caused by immune-‐mediated beta cell depletion, causing ...
Glucagon Administration for Unlicensed Personnel
... hypoglycemia may vary from person to person; a given individual may not experience all of these symptoms in the order they are listed. ...
... hypoglycemia may vary from person to person; a given individual may not experience all of these symptoms in the order they are listed. ...
Glucagon Injections
... hypoglycemia may vary from person to person; a given individual may not experience all of these symptoms in the order they are listed. ...
... hypoglycemia may vary from person to person; a given individual may not experience all of these symptoms in the order they are listed. ...
Management of Hyperglycemia in the Critical Care Setting
... Calculate the initial insulin glargine dose at 80% of the 24-h basal insulin requirement during the previous time interval Stop IV infusion of insulin 2 h after first insulin glargine dose Monitor blood glucose preprandially, at bedtime, and at 3:00 a.m. Order a correction dose algorithm for use of ...
... Calculate the initial insulin glargine dose at 80% of the 24-h basal insulin requirement during the previous time interval Stop IV infusion of insulin 2 h after first insulin glargine dose Monitor blood glucose preprandially, at bedtime, and at 3:00 a.m. Order a correction dose algorithm for use of ...
View PDF - The Journal of Precision Medicine
... Diabetes manifests ultimately as elevated blood glucose levels with concomitant excessive thirst, frequent urination and blurred vision. However, causal onset can be due to a number of factors and this has resulted in the definition of three main types of diabetes as summarized in Figure 1. Type 1 d ...
... Diabetes manifests ultimately as elevated blood glucose levels with concomitant excessive thirst, frequent urination and blurred vision. However, causal onset can be due to a number of factors and this has resulted in the definition of three main types of diabetes as summarized in Figure 1. Type 1 d ...
Almost every one of us knows someone who has diabetes
... do not know exactly what causes the body's immune system to attack the beta cells, but they believe that both genetic factors and viruses are involved. Type 1 diabetes accounts for about 5 to 10 percent of diagnosed diabetes in the United States. Type 1 diabetes develops most often in children and y ...
... do not know exactly what causes the body's immune system to attack the beta cells, but they believe that both genetic factors and viruses are involved. Type 1 diabetes accounts for about 5 to 10 percent of diagnosed diabetes in the United States. Type 1 diabetes develops most often in children and y ...
Diabetes - Introduction - Patient Education Institute
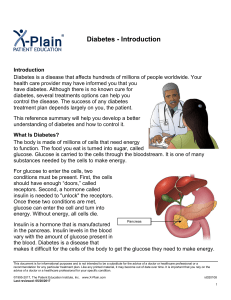
... Type 1 diabetes happens when the pancreas does not make insulin. Because insulin is needed to “unlock" the receptors, glucose cannot enter the cells. Glucose stays in the bloodstream, causing blood glucose levels to rise. Type 2 diabetes happens when enough insulin is present in the blood, but ther ...
... Type 1 diabetes happens when the pancreas does not make insulin. Because insulin is needed to “unlock" the receptors, glucose cannot enter the cells. Glucose stays in the bloodstream, causing blood glucose levels to rise. Type 2 diabetes happens when enough insulin is present in the blood, but ther ...
Almost every one of us knows someone who has diabetes
... do not know exactly what causes the body's immune system to attack the beta cells, but they believe that both genetic factors and viruses are involved. Type 1 diabetes accounts for about 5 to 10 percent of diagnosed diabetes in the United States. Type 1 diabetes develops most often in children and y ...
... do not know exactly what causes the body's immune system to attack the beta cells, but they believe that both genetic factors and viruses are involved. Type 1 diabetes accounts for about 5 to 10 percent of diagnosed diabetes in the United States. Type 1 diabetes develops most often in children and y ...
What is diabetes? - Key Medical Resources
... do not know exactly what causes the body's immune system to attack the beta cells, but they believe that both genetic factors and viruses are involved. Type 1 diabetes accounts for about 5 to 10 percent of diagnosed diabetes in the United States. Type 1 diabetes develops most often in children and y ...
... do not know exactly what causes the body's immune system to attack the beta cells, but they believe that both genetic factors and viruses are involved. Type 1 diabetes accounts for about 5 to 10 percent of diagnosed diabetes in the United States. Type 1 diabetes develops most often in children and y ...
Inpatient Glycemic Management in Non Critically Ill patients
... –initiated treatment, including glucagon for severe hypoglycemia when IV access is not readily available [Grade D, consensus] ...
... –initiated treatment, including glucagon for severe hypoglycemia when IV access is not readily available [Grade D, consensus] ...
Diabetes
... in type 2 diabetes: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy. Diabetes Care 2008;31(12):1–11. Nathan DM, Buse JB, Davidson MB, et al. Medical management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy. Diabetes Care 20 ...
... in type 2 diabetes: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy. Diabetes Care 2008;31(12):1–11. Nathan DM, Buse JB, Davidson MB, et al. Medical management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy. Diabetes Care 20 ...
Document
... It is made in the pancreas, and is released into the bloodstream when glucose levels increase, such as after eating The release of insulin into the system helps glucose to enter the body’s cells, where it is either used immediately for energy, or stored for future use ...
... It is made in the pancreas, and is released into the bloodstream when glucose levels increase, such as after eating The release of insulin into the system helps glucose to enter the body’s cells, where it is either used immediately for energy, or stored for future use ...
observations - Diabetes Care - American Diabetes Association
... significant cardiac history based on clinical examination, electrocardiograph recording, and chest radiography. Four blood samples were collected before and 1, 2, and 3 h (T0 to T3) after a standardized meal (72 g carbohydrates, 21 g lipids, and 32 g proteins) to measure plasma BNP concentrations (I ...
... significant cardiac history based on clinical examination, electrocardiograph recording, and chest radiography. Four blood samples were collected before and 1, 2, and 3 h (T0 to T3) after a standardized meal (72 g carbohydrates, 21 g lipids, and 32 g proteins) to measure plasma BNP concentrations (I ...
Endocrine Drugs - My Illinois State
... intake and help with weight control) Available in liquid form (Riomet) Also available in extended-release tablets (Fortamet, Glucophage XR)—Dose is taken once daily, best with the evening meal Not metabolized; must be excreted by the kidney High levels of metformin can cause fatal lactic aci ...
... intake and help with weight control) Available in liquid form (Riomet) Also available in extended-release tablets (Fortamet, Glucophage XR)—Dose is taken once daily, best with the evening meal Not metabolized; must be excreted by the kidney High levels of metformin can cause fatal lactic aci ...
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes (or gestational diabetes mellitus, GDM) is a condition in which women without previously diagnosed diabetes exhibit high blood glucose (blood sugar) levels during pregnancy (especially during their third trimester). Gestational diabetes is caused when insulin receptors do not function properly. This is likely due to pregnancy-related factors such as the presence of human placental lactogen that interferes with susceptible insulin receptors. This in turn causes inappropriately elevated blood sugar levels.Gestational diabetes generally has few symptoms and it is most commonly diagnosed by screening during pregnancy. Diagnostic tests detect inappropriately high levels of glucose in blood samples. Gestational diabetes affects 3-10% of pregnancies, depending on the population studied.As with diabetes mellitus in pregnancy in general, babies born to mothers with untreated gestational diabetes are typically at increased risk of problems such as being large for gestational age (which may lead to delivery complications), low blood sugar, and jaundice. If untreated, it can also cause seizures or stillbirth. Gestational diabetes is a treatable condition and women who have adequate control of glucose levels can effectively decrease these risks. The food plan is often the first recommended target for strategic management of GDM.Women with unmanaged gestational diabetes are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus (or, very rarely, latent autoimmune diabetes or Type 1) after pregnancy, as well as having a higher incidence of pre-eclampsia and Caesarean section; their offspring are prone to developing childhood obesity, with type 2 diabetes later in life. Most women are able to manage their blood glucose levels with a modified diet and the introduction of moderate exercise, but some require antidiabetic drugs, including insulin.