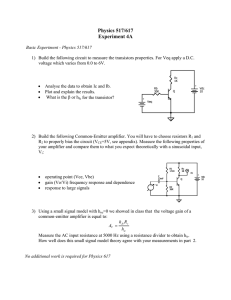
Physics 517/617 Experiment 4A
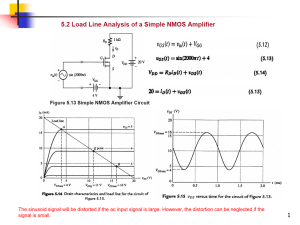
... 3) Using a small signal model with hoe=0 we showed in class that the voltage gain of a common-emitter amplifier is equal to: h fe Rc AV = hie Measure the AC input resistance at 5000 Hz using a resistance divider to obtain hie. How well does this small signal model theory agree with your measurements ...
... 3) Using a small signal model with hoe=0 we showed in class that the voltage gain of a common-emitter amplifier is equal to: h fe Rc AV = hie Measure the AC input resistance at 5000 Hz using a resistance divider to obtain hie. How well does this small signal model theory agree with your measurements ...
Data and Computer Communications
... electromagnetic interferences noncontinuous, consisting of irregular pulses or spikes short duration and high amplitude minor annoyance for analog signals but a major source of error in digital data ...
... electromagnetic interferences noncontinuous, consisting of irregular pulses or spikes short duration and high amplitude minor annoyance for analog signals but a major source of error in digital data ...
Chapter 10 - Electrical, Antenna and RF Safety
... determined by direct measurement, using calibrated instruments, or by calculations using either tables or computer software. • For analysis purposes, the area around an antenna is divided into the following regions: – Reactive near field • Considered to be within a half wavelength of antenna ...
... determined by direct measurement, using calibrated instruments, or by calculations using either tables or computer software. • For analysis purposes, the area around an antenna is divided into the following regions: – Reactive near field • Considered to be within a half wavelength of antenna ...
EE101L Laboratory 5
... signals in RC circuits. However, here you will deal with the steady-state response of an RC circuit to sinusoidally varying signals at various frequencies. You will represent these signals in the time and frequency domain and investigate the circuit’s frequency dependence. This frequency dependence ...
... signals in RC circuits. However, here you will deal with the steady-state response of an RC circuit to sinusoidally varying signals at various frequencies. You will represent these signals in the time and frequency domain and investigate the circuit’s frequency dependence. This frequency dependence ...
Chapter6 - UTK-EECS
... Advantages of Digital Transmission • Digital technology: low cost, can use low power • Long distance transmission: use digital repeaters • Capacity utilization: get rid of useless information and add useful redundancy for data protection • Security & privacy: encryption • Integration: treat analog ...
... Advantages of Digital Transmission • Digital technology: low cost, can use low power • Long distance transmission: use digital repeaters • Capacity utilization: get rid of useless information and add useful redundancy for data protection • Security & privacy: encryption • Integration: treat analog ...
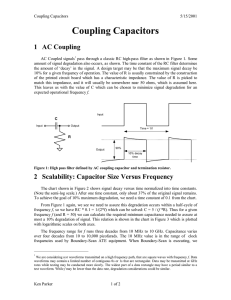
Coupling Capacitors (Updated 5-15
... 2 Scalability: Capacitor Size Versus Frequency The chart shown in Figure 2 shows signal decay versus time normalized into time constants. (Note the semi-log scale.) After one time constant, only about 37% of the original signal remains. To achieve the goal of 10% maximum degradation, we need a time ...
... 2 Scalability: Capacitor Size Versus Frequency The chart shown in Figure 2 shows signal decay versus time normalized into time constants. (Note the semi-log scale.) After one time constant, only about 37% of the original signal remains. To achieve the goal of 10% maximum degradation, we need a time ...
BSNL_Telecommodel2009 - 2 009
... terminated load resistance of 450 Ohm are given by (a) 57.3 mH; 0.283 μF (b) 28.66 μH; 0.14 μF (c) 114.64 mH; 0.566 mF (d) 50.23 mH; 0.632 mF Q.12 The driving point impedance with poles at ? = 0(zero) and ? = 8 (infinity) must have the (a) s term in the denominator and an excess term in the numerat ...
... terminated load resistance of 450 Ohm are given by (a) 57.3 mH; 0.283 μF (b) 28.66 μH; 0.14 μF (c) 114.64 mH; 0.566 mF (d) 50.23 mH; 0.632 mF Q.12 The driving point impedance with poles at ? = 0(zero) and ? = 8 (infinity) must have the (a) s term in the denominator and an excess term in the numerat ...
Document
... – Convert the source(s) to complex/phasor form (you can ignore the ωt component at this point) – Represent each circuit element by it's AC impedance. Impedances add like resistors. – Solve the resulting phasor circuit using standard circuit solving tools (equivalent impedances, voltage/ current divi ...
... – Convert the source(s) to complex/phasor form (you can ignore the ωt component at this point) – Represent each circuit element by it's AC impedance. Impedances add like resistors. – Solve the resulting phasor circuit using standard circuit solving tools (equivalent impedances, voltage/ current divi ...
Multi-functional Packaged Antennas for Next
... C1, C2 – Coupling capacitors short circuit for AC signals and open circuit for DC bias calculation ...
... C1, C2 – Coupling capacitors short circuit for AC signals and open circuit for DC bias calculation ...
Transmission of fast signals via optical fibres Richard White Michael Daniel for
... The linearity directly determines the usable dynamic range of the optical link – with the output pulse being linearly related to the input pulse. The lower limit of the dynamic range is related to the noise in the system, so the amount of noise introduced into a pulse at a given Ib and T is understo ...
... The linearity directly determines the usable dynamic range of the optical link – with the output pulse being linearly related to the input pulse. The lower limit of the dynamic range is related to the noise in the system, so the amount of noise introduced into a pulse at a given Ib and T is understo ...
PDF of the lab
... At the end of performing this experiment, learners would be able to: Describe the concept of Pulse Amplitude Modulation Understand the working of PAM under different sampling conditions Identify the concept of envelope detection Demodulate the PAM signal ...
... At the end of performing this experiment, learners would be able to: Describe the concept of Pulse Amplitude Modulation Understand the working of PAM under different sampling conditions Identify the concept of envelope detection Demodulate the PAM signal ...
Lec #10 ppt
... transformer turns ratio, electrical energy, electric power Coulomb, ampere, volt, ohm, farad, henry, joule, watt ...
... transformer turns ratio, electrical energy, electric power Coulomb, ampere, volt, ohm, farad, henry, joule, watt ...
Instrumental Chemistry
... signal consists of a series of pulses of energy produced as individuals atoms decay. These pulses can be converted to electrical pulses and counted. The resulting information can be expressed as an integer number of decays. ...
... signal consists of a series of pulses of energy produced as individuals atoms decay. These pulses can be converted to electrical pulses and counted. The resulting information can be expressed as an integer number of decays. ...