Analog Communication
... sometimes heard by cell phone users at the edge of a cell's coverage area, or (more likely) by the landline user to whom the cell phone is connected. • "Picket fencing" refers to the way portions of speech are stripped from the conversation, as if the listener was walking by a picket fence, and hear ...
... sometimes heard by cell phone users at the edge of a cell's coverage area, or (more likely) by the landline user to whom the cell phone is connected. • "Picket fencing" refers to the way portions of speech are stripped from the conversation, as if the listener was walking by a picket fence, and hear ...
How to make Frequency plots with Pspice
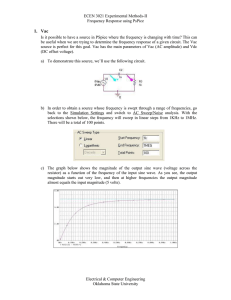
... ECEN 3021 Experimental Methods-II Frequency Response using PsPice ...
... ECEN 3021 Experimental Methods-II Frequency Response using PsPice ...
DT3: RF On/Off Remote Control Technology
... Information sent using analog tones within the voice band (20 Hz – 20 kHz) Tones detected or not detected, corresponding to binary ‘1’ or ‘0’ Tones of frequency ‘a’ corresponds to ‘1’, frequency ‘b’ corresponds to ‘0’ (AFSK) ...
... Information sent using analog tones within the voice band (20 Hz – 20 kHz) Tones detected or not detected, corresponding to binary ‘1’ or ‘0’ Tones of frequency ‘a’ corresponds to ‘1’, frequency ‘b’ corresponds to ‘0’ (AFSK) ...
Exp-7 - WordPress.com
... audio applications. Figure 1 shows the basic Wien Bridge circuit configuration. On the positive side, this circuit has only a few components and good frequency stability. Because of its simplicity and stability, it is the most commonly used audio-frequency oscillator. In the figure shown the Wien Br ...
... audio applications. Figure 1 shows the basic Wien Bridge circuit configuration. On the positive side, this circuit has only a few components and good frequency stability. Because of its simplicity and stability, it is the most commonly used audio-frequency oscillator. In the figure shown the Wien Br ...
university of oslo faculty of mathematics and natural sciences
... 4a) Sketch the Thevenin-equivalent of the forward biasing of the base, and calculate the Thevenin-voltage (VTH) and the Thevenin-resistance (RTH) 4b) Calculate the base current IB. 4c) Calculate the collector current IC. 4d) Calculate the transconductance gm of the transistor. 4e) Draw the small sig ...
... 4a) Sketch the Thevenin-equivalent of the forward biasing of the base, and calculate the Thevenin-voltage (VTH) and the Thevenin-resistance (RTH) 4b) Calculate the base current IB. 4c) Calculate the collector current IC. 4d) Calculate the transconductance gm of the transistor. 4e) Draw the small sig ...
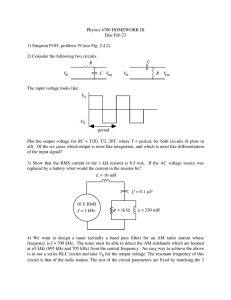
Physics 4700 HOMEWORK III Due Feb 23
... 3) Show that the RMS current in the 1 kΩ resistor is 6.5 mA. If the AC voltage source was replaced by a battery what would the current in the resistor be? ...
... 3) Show that the RMS current in the 1 kΩ resistor is 6.5 mA. If the AC voltage source was replaced by a battery what would the current in the resistor be? ...
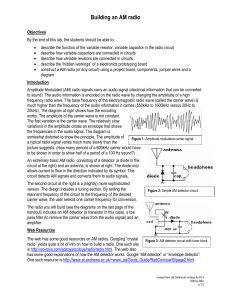
Study of Amplitude Modulation Transmitter
... the strength (amplitude) of the carrier in proportion to the waveform being sent. That waveform may, for instance, correspond to the sounds to be reproduced by a loudspeaker. This contrasts with frequency modulation, in which the frequency of the carrier signal is varied, and phase modulation, in wh ...
... the strength (amplitude) of the carrier in proportion to the waveform being sent. That waveform may, for instance, correspond to the sounds to be reproduced by a loudspeaker. This contrasts with frequency modulation, in which the frequency of the carrier signal is varied, and phase modulation, in wh ...
Electronic Music
... AM carrier waves have much longer wavelengths than FM carrier waves, and as a result, they can bend around obstacles like mountains and buildings better than FM waves and can travel greater distances before the signal fades. ...
... AM carrier waves have much longer wavelengths than FM carrier waves, and as a result, they can bend around obstacles like mountains and buildings better than FM waves and can travel greater distances before the signal fades. ...
Radio Communications Principles
... data can be transmitted • Bandwidth – the bandwidth of the transmitted signal as constrained by the transmitter and the nature of the transmission medium, in cycles per second, hertz • Noise – the average white/thermal level of noise over the communications path • Error Rate – the rate at which erro ...
... data can be transmitted • Bandwidth – the bandwidth of the transmitted signal as constrained by the transmitter and the nature of the transmission medium, in cycles per second, hertz • Noise – the average white/thermal level of noise over the communications path • Error Rate – the rate at which erro ...