Purposes Of Apoptosis
... • Amplifying cascade involving initiator and executioner caspases • Executioner caspases cleave substrates responsible for cell death ...
... • Amplifying cascade involving initiator and executioner caspases • Executioner caspases cleave substrates responsible for cell death ...
Human Reproduction Notes
... epididymus, where they complete maturation. Passage takes about 20 days. ...
... epididymus, where they complete maturation. Passage takes about 20 days. ...
BIO EXAM NOTES
... MEIOSIS II Identical to meiosis, but haploid karyotype chart: a photograph of pairs of homologous chromosomes in a cell - cell sample is collected and treated to stop cell division during metaphase - sample is stained to produce a banding pattern on the chromosomes - chromosomes are sorted and pair ...
... MEIOSIS II Identical to meiosis, but haploid karyotype chart: a photograph of pairs of homologous chromosomes in a cell - cell sample is collected and treated to stop cell division during metaphase - sample is stained to produce a banding pattern on the chromosomes - chromosomes are sorted and pair ...
A Closer Look at Conception presentation
... In Vitro Fertilization- Doctor combines a mature ovum from the woman with sperm from her husband. If the ovum becomes fertilized then the doctor places it in the uterus. Ovum Transfer- Similar to In Vitro, except that the ovum is donated by another woman. It is fertilized in the laboratory and p ...
... In Vitro Fertilization- Doctor combines a mature ovum from the woman with sperm from her husband. If the ovum becomes fertilized then the doctor places it in the uterus. Ovum Transfer- Similar to In Vitro, except that the ovum is donated by another woman. It is fertilized in the laboratory and p ...
Exam 1 Review - Iowa State University
... A) each cell will develop into a full-sized, normal embryo B) each cell may develop into a smaller than average, but normal embryo C) each cell may continue to develop, but only into an embryo that lacks many parts D) all 4 cells will die 34. If you separate 4 cells that are indeterminate, what will ...
... A) each cell will develop into a full-sized, normal embryo B) each cell may develop into a smaller than average, but normal embryo C) each cell may continue to develop, but only into an embryo that lacks many parts D) all 4 cells will die 34. If you separate 4 cells that are indeterminate, what will ...
Mitosis Nuclear division M Phase
... Autosomes are the other 44 chromosomes One from your mom one from your dad, same size, shape and banding pattern, code for the same traits Identical due to DNA replication in the S phase of interphase Diploid contains both chromosomes of a homologous pair. Haploid cells only contain one chromosom ...
... Autosomes are the other 44 chromosomes One from your mom one from your dad, same size, shape and banding pattern, code for the same traits Identical due to DNA replication in the S phase of interphase Diploid contains both chromosomes of a homologous pair. Haploid cells only contain one chromosom ...
Chapter 6 notes
... Sexual reproduction – requires two parents and produces offspring that are genetically different from each other ...
... Sexual reproduction – requires two parents and produces offspring that are genetically different from each other ...
Cells and human reproduction
... Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) can be passed from one person to another through sexual activities or blood contact. ...
... Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) can be passed from one person to another through sexual activities or blood contact. ...
File
... The zygote splits through a process called ___________________________ and more cells are made Continued cell division creates a multi-cellular life form called an ________________________________ This ____________________________ develops inside the female (in most mammals) or outside (like an egg) ...
... The zygote splits through a process called ___________________________ and more cells are made Continued cell division creates a multi-cellular life form called an ________________________________ This ____________________________ develops inside the female (in most mammals) or outside (like an egg) ...
Chapter 20 - Dr. Jennifer Capers
... ○ Inbred strains reduce variation caused by differences in genetic backgrounds - 20 or more generations of brother-sister mating ...
... ○ Inbred strains reduce variation caused by differences in genetic backgrounds - 20 or more generations of brother-sister mating ...
What we`ve already established
... • Lethal dominant genes are rare – why? – People can’t “carry” the gene ...
... • Lethal dominant genes are rare – why? – People can’t “carry” the gene ...
Human Development
... product thereof) that results in maleness in humans and some other species. ...
... product thereof) that results in maleness in humans and some other species. ...
Mechtcheriakova D et al Symbol Synonym Accession number Short
... B-cell lineage specific activator protein/transcription factor that is expressed at early, but not late stages of B-cell differentiation. Deregulation of transcription of this gene contributes to the pathogenesis of lymphomas. Interferon consensus sequence-binding protein (ICSBP) is a transcription ...
... B-cell lineage specific activator protein/transcription factor that is expressed at early, but not late stages of B-cell differentiation. Deregulation of transcription of this gene contributes to the pathogenesis of lymphomas. Interferon consensus sequence-binding protein (ICSBP) is a transcription ...
11 Big Fish, Little Fish
... fishes either had totally independent or completely fused males, then how could we even imagine an evolutionary transition to the peculiar sexual system of the anglerfish? But the abundance of structurally intermediate stages temporary attachment or fusion of some males only-con veys an evolutiona ...
... fishes either had totally independent or completely fused males, then how could we even imagine an evolutionary transition to the peculiar sexual system of the anglerfish? But the abundance of structurally intermediate stages temporary attachment or fusion of some males only-con veys an evolutiona ...
Chlamydia pneumoniae - DigitalCommons@PCOM
... Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is considered to be the most common form of late-life dementia affecting memory, cognition, personality, and behavior (1). The cause(s) of AD are thought to involve both environmental and genetic factors. There are two main forms of the disease: familial or early-onset that ...
... Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is considered to be the most common form of late-life dementia affecting memory, cognition, personality, and behavior (1). The cause(s) of AD are thought to involve both environmental and genetic factors. There are two main forms of the disease: familial or early-onset that ...
Back to Reality: Reproduction Quiz Name: score : /40 1. The ovaries
... 1. The ovaries of the female reproductive system produce hormones and _______________. A) cilia B) estrogens C) sperm D) eggs 2. An embryo develops inside the ___________________. A) vagina B) uterus C) cervix D) ovary 3. The vagina is the passageway through which a baby moves during _______________ ...
... 1. The ovaries of the female reproductive system produce hormones and _______________. A) cilia B) estrogens C) sperm D) eggs 2. An embryo develops inside the ___________________. A) vagina B) uterus C) cervix D) ovary 3. The vagina is the passageway through which a baby moves during _______________ ...
RhoGTPases — NODes for effector-triggered immunity in
... mechanism has now been provided in Drosophila melanogaster, Caenorabditis elegans and mammals [3]. The ETI model is of particular relevance when considering that most major pathogenic bacteria have evolved many protein effectors commonly referred to as virulence factors. These effectors are either d ...
... mechanism has now been provided in Drosophila melanogaster, Caenorabditis elegans and mammals [3]. The ETI model is of particular relevance when considering that most major pathogenic bacteria have evolved many protein effectors commonly referred to as virulence factors. These effectors are either d ...
Structure of mating systems
... much of a contribution to parental fitness. That difference in genetic contribution between sexual and asexual reproduction is called the cost of meiosis. There have been numerous attempts to study species that can reproduce both asexually and sexually. The object has been to show that females repro ...
... much of a contribution to parental fitness. That difference in genetic contribution between sexual and asexual reproduction is called the cost of meiosis. There have been numerous attempts to study species that can reproduce both asexually and sexually. The object has been to show that females repro ...
Female Reproductive System
... – In humans and many animals, sperm require temp lower than body temperature. – This is why testes are found outside the body. • Ejaculated semen can reach the speed of 200” per second. • Sperm can survive in a females body for up to 3 days. • 25% of sperm are deformed from beginning. ...
... – In humans and many animals, sperm require temp lower than body temperature. – This is why testes are found outside the body. • Ejaculated semen can reach the speed of 200” per second. • Sperm can survive in a females body for up to 3 days. • 25% of sperm are deformed from beginning. ...
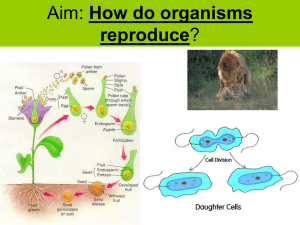
How do organisms reproduce
... asexual reproduction? Yes When do the cells of our body undergo Asexual Reproduction? Growth ...
... asexual reproduction? Yes When do the cells of our body undergo Asexual Reproduction? Growth ...
Noncoelomate Invertebrates Power Point
... colony, they can all be attached to common tissue • Medusa: umbrella-shaped, mouth on underside surrounded by tentacles, live free in the water • Some can alternate between the two in their reproductive cycle ...
... colony, they can all be attached to common tissue • Medusa: umbrella-shaped, mouth on underside surrounded by tentacles, live free in the water • Some can alternate between the two in their reproductive cycle ...
tools in develoomental biology
... Questions to be answered in Dev. Bio.: -aging - germ cell development, fertilization - stem cells (what are they (multipotency, ability to selfrenew), why did they become so ‘trendy’ (Dolly the sheep, 1997, showed that cloning was possible; development of human ES cells, 1998) - regeneration - How ...
... Questions to be answered in Dev. Bio.: -aging - germ cell development, fertilization - stem cells (what are they (multipotency, ability to selfrenew), why did they become so ‘trendy’ (Dolly the sheep, 1997, showed that cloning was possible; development of human ES cells, 1998) - regeneration - How ...
Drosophila melanogaster
.jpg?width=300)
Drosophila melanogaster is a species of fly (the taxonomic order Diptera) in the family Drosophilidae. The species is known generally as the common fruit fly or vinegar fly. Starting with Charles W. Woodworth's proposal of the use of this species as a model organism, D. melanogaster continues to be widely used for biological research in studies of genetics, physiology, microbial pathogenesis, and life history evolution. It is typically used because it is an animal species that is easy to care for, has four pairs of chromosomes, breeds quickly, and lays many eggs. D. melanogaster is a common pest in homes, restaurants, and other occupied places where food is served.Flies belonging to the family Tephritidae are also called ""fruit flies"". This can cause confusion, especially in Australia and South Africa, where the Mediterranean fruit fly Ceratitis capitata is an economic pest.