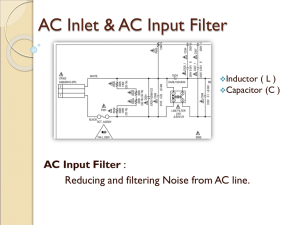
Bubba oscillator Summary References Related Web sites
... of R and RG. When low-distortion sine waves are required at all outputs, the gain should be distributed between all the op amps. The non-inverting input of the gain op amp is biased at 0.5 V to set the quiescent output voltage at 2.5 V. Gain distribution requires biasing of the other op amps, but it ...
... of R and RG. When low-distortion sine waves are required at all outputs, the gain should be distributed between all the op amps. The non-inverting input of the gain op amp is biased at 0.5 V to set the quiescent output voltage at 2.5 V. Gain distribution requires biasing of the other op amps, but it ...
EN34855860
... difference into an analog control voltage which is same as the average output of phase detector. The filter converts rapid variations of the phase detector output into a slow varying signal, which will later control the voltage controlled oscillator. The most important part of PLL is VCO which is us ...
... difference into an analog control voltage which is same as the average output of phase detector. The filter converts rapid variations of the phase detector output into a slow varying signal, which will later control the voltage controlled oscillator. The most important part of PLL is VCO which is us ...
Integer N Frequency Synthesizer using Phase Lock Loop
... Synthesizer is that it can generate frequencies of 100200MHz comparable to the accuracy of a crystal oscillator. This paper gives a brief introduction to the basics of Phase Locked loops. Keywords — Phase locked loop, Phase frequency detector, Charge pump, Loop filter, Voltage controlled oscillator, ...
... Synthesizer is that it can generate frequencies of 100200MHz comparable to the accuracy of a crystal oscillator. This paper gives a brief introduction to the basics of Phase Locked loops. Keywords — Phase locked loop, Phase frequency detector, Charge pump, Loop filter, Voltage controlled oscillator, ...
Angle Modulation Part 2
... The phase detector produces an average output voltage that is linear function of the phase difference between the two input signals. This low frequency component is selected by LPF. ...
... The phase detector produces an average output voltage that is linear function of the phase difference between the two input signals. This low frequency component is selected by LPF. ...
Low Phase Noise Rubidium Atomic Oscillator Module
... and -158dBc/Hz at 10kHz. It is housed in a 95.5 x 62.5 x 44.3mm module so can be used in a 1U rack. The electrical connections include an SMA connector for RF output, RS232 connectors RX & TX, a voltage control input and a frequency locked monitor. With a short term stability 100 times better than a ...
... and -158dBc/Hz at 10kHz. It is housed in a 95.5 x 62.5 x 44.3mm module so can be used in a 1U rack. The electrical connections include an SMA connector for RF output, RS232 connectors RX & TX, a voltage control input and a frequency locked monitor. With a short term stability 100 times better than a ...
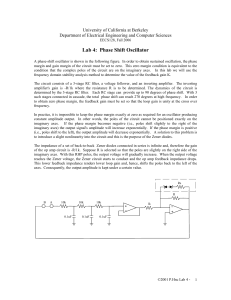
Lab 4: Phase Shift Oscillator - EECS: www
... The circuit consists of a 3-stage RC filter, a voltage follower, and an inverting amplifier. The inverting amplifier's gain is -R/1k where the resistance R is to be determined. The dynamics of the circuit is determined by the 3-stage RC filter. Each RC stage can provide up to 90 degrees of phase shi ...
... The circuit consists of a 3-stage RC filter, a voltage follower, and an inverting amplifier. The inverting amplifier's gain is -R/1k where the resistance R is to be determined. The dynamics of the circuit is determined by the 3-stage RC filter. Each RC stage can provide up to 90 degrees of phase shi ...
Systematic Design of Space-Time Trellis Codes for Wireless
... Superheterodyne receiver – Heterodyne: mixing two signals for new frequency – Superheterodyne receiver: heterodyne RF signals with local tuner, convert to common IF ...
... Superheterodyne receiver – Heterodyne: mixing two signals for new frequency – Superheterodyne receiver: heterodyne RF signals with local tuner, convert to common IF ...
In this method cross correlation is used to find the impedance of the
... oscillate via an Op-amp. Using the Op-amp here will be beneficial in allowing low output impedance, and flat frequency response. The crystal’s output signal will then be fed into an Op-amp of the same type as the input. The signal will then be converted back to digital using an A/D converter, which ...
... oscillate via an Op-amp. Using the Op-amp here will be beneficial in allowing low output impedance, and flat frequency response. The crystal’s output signal will then be fed into an Op-amp of the same type as the input. The signal will then be converted back to digital using an A/D converter, which ...
Document
... ◦ Squarewave - easier to work with ◦ Four Phases for the Channel Select ◦ Frequency error also divided down ...
... ◦ Squarewave - easier to work with ◦ Four Phases for the Channel Select ◦ Frequency error also divided down ...
Synchronized, easily adjustable, 3 Frequency PWM
... Needless to say that since the phase shift is naturally frequency dependent, altering the frequency will (slightly) alter the phase shift. The ‘Q’ output of IC5A (pin 6) is connected to the second non-retriggerable monostable’s (IC5B) “B” input (pin 11, falling edge trigger). IC5B is the sync pulse ...
... Needless to say that since the phase shift is naturally frequency dependent, altering the frequency will (slightly) alter the phase shift. The ‘Q’ output of IC5A (pin 6) is connected to the second non-retriggerable monostable’s (IC5B) “B” input (pin 11, falling edge trigger). IC5B is the sync pulse ...
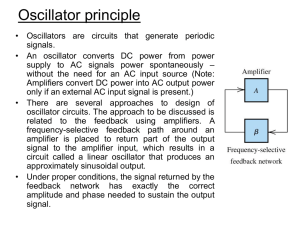
Frequency response of feedback amplifiers
... a slight reduction in gain would result in oscillations that decays to zero. • One important thing to note is that the initial input Xin is not needed, as in real circuits noise and transient signals associated with circuit turning on can always provide an initial signal that grows in amplitude as i ...
... a slight reduction in gain would result in oscillations that decays to zero. • One important thing to note is that the initial input Xin is not needed, as in real circuits noise and transient signals associated with circuit turning on can always provide an initial signal that grows in amplitude as i ...
B++--The Design of A Low-Power Low-Noise Phase Lock
... the phase of the output signal to the phase of the reference or the input signal. Hence the name, “Phase-locked loop”. It is important here to note that, the PLL not only sets a fixed relationship between its output clock phase and the input or reference clock phase but also tracks the subsequent ph ...
... the phase of the output signal to the phase of the reference or the input signal. Hence the name, “Phase-locked loop”. It is important here to note that, the PLL not only sets a fixed relationship between its output clock phase and the input or reference clock phase but also tracks the subsequent ph ...
Lecture Notes - Bandpass Circuits File
... e(t) is called the Phase Error. The Phase Error voltage characteristics is SINUSOIDAL. A PLL can track the incoming frequency only over a finite range Lock/hold-in range The frequency range over which the input will cause the loop to lock pull-in/capture range Eeng 360 22 ...
... e(t) is called the Phase Error. The Phase Error voltage characteristics is SINUSOIDAL. A PLL can track the incoming frequency only over a finite range Lock/hold-in range The frequency range over which the input will cause the loop to lock pull-in/capture range Eeng 360 22 ...
ISSCC 2015 / SESSION 25 / RF FREQUENCY GENERATION FROM
... This paper presents an all-digital phase-locked loop (PLL) using a voltage-domain digitization realized by an analog-to-digital converter (ADC). It consists of an 18b Class-C digitally-controlled oscillator (DCO), 4b comparator, digital loop filter (DLF), and frequency-locked loop (FLL). Implemented ...
... This paper presents an all-digital phase-locked loop (PLL) using a voltage-domain digitization realized by an analog-to-digital converter (ADC). It consists of an 18b Class-C digitally-controlled oscillator (DCO), 4b comparator, digital loop filter (DLF), and frequency-locked loop (FLL). Implemented ...
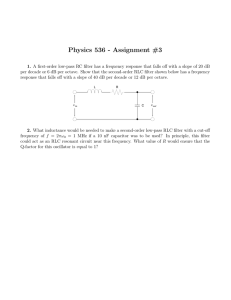
Physics 536 - Assignment #3
... per decade or 6 dB per octave. Show that the second-order RLC filter shown below has a frequency response that falls off with a slope of 40 dB per decade or 12 dB per octave. L ...
... per decade or 6 dB per octave. Show that the second-order RLC filter shown below has a frequency response that falls off with a slope of 40 dB per decade or 12 dB per octave. L ...
Exp-7 - WordPress.com
... To build op-amp based Weign bridge oscillator circuit, and measure and verify its frequency of operation. APPARATUS: Analog board, AB70. DC power supplies Oscilloscope and probes 2mm patch cords. THEORY: Oscillators are circuits that produce periodic waveforms without input other than perhaps a trig ...
... To build op-amp based Weign bridge oscillator circuit, and measure and verify its frequency of operation. APPARATUS: Analog board, AB70. DC power supplies Oscilloscope and probes 2mm patch cords. THEORY: Oscillators are circuits that produce periodic waveforms without input other than perhaps a trig ...
Lecture 11
... This is rarely the case with FM receivers, however, except for frequencies in excess of 1GHz when it becomes preferable to omit it. The essence of the problem is that FM receivers can function with smaller received signals than AM or SSB receivers because of their inherent noise reduction capability ...
... This is rarely the case with FM receivers, however, except for frequencies in excess of 1GHz when it becomes preferable to omit it. The essence of the problem is that FM receivers can function with smaller received signals than AM or SSB receivers because of their inherent noise reduction capability ...
fpga implementation of phase locked loop (pll) with
... A counter is used in the simulation code to generate a clock input to the PLL. The counter is a down counter. The output clock frequency is caused to change by changing the upper limit of the counter. By observing for a low value of the output clock on the previous cycle and a high value on the curr ...
... A counter is used in the simulation code to generate a clock input to the PLL. The counter is a down counter. The output clock frequency is caused to change by changing the upper limit of the counter. By observing for a low value of the output clock on the previous cycle and a high value on the curr ...
What is a Phase Locked Loop
... This curve depicts the behavior of the PFD in the unlocked state of DPLL. b.2 Voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO). ...
... This curve depicts the behavior of the PFD in the unlocked state of DPLL. b.2 Voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO). ...