SN74LV4046A High-Speed CMOS Logic Phase
... and three different phase comparators (PC1, PC2, and PC3) as explained in the Features section. A signal input and a comparator input are common to each comparator as shown in the Functional Block Diagram. The signal input can be directly coupled to large voltage signals, or indirectly coupled (with ...
... and three different phase comparators (PC1, PC2, and PC3) as explained in the Features section. A signal input and a comparator input are common to each comparator as shown in the Functional Block Diagram. The signal input can be directly coupled to large voltage signals, or indirectly coupled (with ...
using only two transistors
... output will consist of noise. The frequency can now be adjusted using a screwdriver: when an FM station is encountered the noise will reduce in volume or disappear altogether. The tuning must be adjusted so that it is just on the edge of the band occupied by the transmitted signal: this requires a l ...
... output will consist of noise. The frequency can now be adjusted using a screwdriver: when an FM station is encountered the noise will reduce in volume or disappear altogether. The tuning must be adjusted so that it is just on the edge of the band occupied by the transmitted signal: this requires a l ...
Lecture 4 Power Point Presentation
... arithmetic to be performed as well as many more useful applications. - they are essential components of modern-day equipment including your POTENTIOSTAT / GALVANOSTAT !! ...
... arithmetic to be performed as well as many more useful applications. - they are essential components of modern-day equipment including your POTENTIOSTAT / GALVANOSTAT !! ...
Radar Signal Processing
... Signal convolution (impulse response) Example Many radar convolution applications involve impulses. An impulse in the continuous world is a rectangular pulse, having width of zero, infinite amplitude, and an area of one. Continuous convolution with impulses is quite simple. The function being convo ...
... Signal convolution (impulse response) Example Many radar convolution applications involve impulses. An impulse in the continuous world is a rectangular pulse, having width of zero, infinite amplitude, and an area of one. Continuous convolution with impulses is quite simple. The function being convo ...
BDTIC www.BDTIC.com/infineon Application Note No. 061
... frequencies, it becomes difficult to construct a feedback circuit without introducing excess phase shift. Therefore almost all oscillators in this frequency range are classified as a negative resistance oscillator. Figure 3 shows a block diagram of a negative resistance oscillator. In the negative r ...
... frequencies, it becomes difficult to construct a feedback circuit without introducing excess phase shift. Therefore almost all oscillators in this frequency range are classified as a negative resistance oscillator. Figure 3 shows a block diagram of a negative resistance oscillator. In the negative r ...
quick reference
... This input is used to change the direction of the motor. Physical direction also depends upon the connection of the motor windings. ...
... This input is used to change the direction of the motor. Physical direction also depends upon the connection of the motor windings. ...
Current Mode Compensation Article
... compensation. Notable advantages of PCMC include automatic input line feedforward, inherent cycle-by-cycle overload protection, and current sharing capability in multiphase converters. Acute shortcomings are current loop noise sensitivity and switch minimum on-time limitations, particularly in high ...
... compensation. Notable advantages of PCMC include automatic input line feedforward, inherent cycle-by-cycle overload protection, and current sharing capability in multiphase converters. Acute shortcomings are current loop noise sensitivity and switch minimum on-time limitations, particularly in high ...
Electronics Letters
... where fMHzis the frequency in MHz, R is the distance, d is the diameter of the collimated region, and CF is a correction factor for the field distribution in the collimated region. The distance R is required as the response of the CAR is independent of distance along its radiation axis within the co ...
... where fMHzis the frequency in MHz, R is the distance, d is the diameter of the collimated region, and CF is a correction factor for the field distribution in the collimated region. The distance R is required as the response of the CAR is independent of distance along its radiation axis within the co ...
High-frequency two-input CMOS OTA for continuous
... to increase the output resistance of the amplifier. SPICE simulations show that DC-gain enhancement can be obtained without significant bandwidth limitation. The two-input OTA developed is used in hgh-frequency tuneable filter design based on IFLF and LC ladder simulation structures. Simulated resul ...
... to increase the output resistance of the amplifier. SPICE simulations show that DC-gain enhancement can be obtained without significant bandwidth limitation. The two-input OTA developed is used in hgh-frequency tuneable filter design based on IFLF and LC ladder simulation structures. Simulated resul ...
Picosecond Wireless Synchronization Using an Optically Locked 77005,
... a wireless microwave signal may be used to synchronize the array elements. While wireless synchronization improves the flexibility and reconfigurability of an array, it suffers from the multi-path problem [1]. In a multi-path environment, both the amplitude and phase of the synchronization signal be ...
... a wireless microwave signal may be used to synchronize the array elements. While wireless synchronization improves the flexibility and reconfigurability of an array, it suffers from the multi-path problem [1]. In a multi-path environment, both the amplitude and phase of the synchronization signal be ...
MAX7031 Low-Cost, 308MHz, 315MHz, and 433.92MHz FSK Transceiver with Fractional-N PLL General Description
... receiver’s local oscillator (LO) is generated by an integer-N PLL. This hybrid architecture eliminates the need for separate transmit and receive crystal reference oscillators because the fractional-N PLL is preset to be 10.7MHz above the receive LO. Retaining the fixed-N PLL for the receiver avoids ...
... receiver’s local oscillator (LO) is generated by an integer-N PLL. This hybrid architecture eliminates the need for separate transmit and receive crystal reference oscillators because the fractional-N PLL is preset to be 10.7MHz above the receive LO. Retaining the fixed-N PLL for the receiver avoids ...
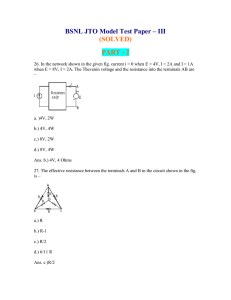
BSNL JTO Model Test Paper – III
... 29. If for the network shown in the following fig. the value of Z(s) is value of C and R are respectively – ...
... 29. If for the network shown in the following fig. the value of Z(s) is value of C and R are respectively – ...
Chapter 5 Low-Noise Design Methodology
... • so the conversion gain is proportional to the magnitude of the local oscillator voltage. For maximum conversion gain, the local oscillator amplitude should be selected so that it drives the gate just to the point of transistor saturation. • The input signal is normally connected to the lower (clo ...
... • so the conversion gain is proportional to the magnitude of the local oscillator voltage. For maximum conversion gain, the local oscillator amplitude should be selected so that it drives the gate just to the point of transistor saturation. • The input signal is normally connected to the lower (clo ...
Bandwidth
... signal levels are on one side of the time axis - either above or below NRZ - Non Return to Zero scheme is an example of this code. The signal level does not return to zero during a symbol transmission. Scheme is prone to baseline wandering and DC components. It has no synchronization or any erro ...
... signal levels are on one side of the time axis - either above or below NRZ - Non Return to Zero scheme is an example of this code. The signal level does not return to zero during a symbol transmission. Scheme is prone to baseline wandering and DC components. It has no synchronization or any erro ...
EET 2351 Lecture 2 - MDC Faculty Home Pages
... Multiply the square the positive voltage, Vp2, by the duty cycle, D. Multiply the square the negative voltage, Vn2, by one minus the duty cycle, (1-D). Add these two quantities. This is the mean or average of the squares. ...
... Multiply the square the positive voltage, Vp2, by the duty cycle, D. Multiply the square the negative voltage, Vn2, by one minus the duty cycle, (1-D). Add these two quantities. This is the mean or average of the squares. ...