AH summary Unit 1
... Receptor molecules of target cells are proteins with a binding site for a specific signal molecule. Binding changes the conformation of the receptor and this can alter the response of the cell. Different cell types produce specific signals which can only be detected and responded to by cells with th ...
... Receptor molecules of target cells are proteins with a binding site for a specific signal molecule. Binding changes the conformation of the receptor and this can alter the response of the cell. Different cell types produce specific signals which can only be detected and responded to by cells with th ...
a zebrafish model of myotubular myopathy
... disorders of childhood. It is caused by mutations in the myotubularin (MTM1) gene. In vitro, MTM1 functions as a lipid phosphatase that dephosphorylates specific phosphoinositides (PIs). Via its ability to modify PIs, MTM1 serves as a critical regulator of several processes, most notably endocytosis ...
... disorders of childhood. It is caused by mutations in the myotubularin (MTM1) gene. In vitro, MTM1 functions as a lipid phosphatase that dephosphorylates specific phosphoinositides (PIs). Via its ability to modify PIs, MTM1 serves as a critical regulator of several processes, most notably endocytosis ...
Proteins - Magrin Science
... It’s SHAPE that matters! __________________________________ __________________________________ Unfolding a protein destroys its shape ...
... It’s SHAPE that matters! __________________________________ __________________________________ Unfolding a protein destroys its shape ...
Carbon Compounds
... molecule combines with compounds called fatty acids. • If each carbon atom in a lipid’s fatty acid chains is joined to another carbon atom by a single bond, the lipid is said to be ...
... molecule combines with compounds called fatty acids. • If each carbon atom in a lipid’s fatty acid chains is joined to another carbon atom by a single bond, the lipid is said to be ...
HTRA1 (S328A) Protein HTRA1 (S328A) Protein
... Scientific Background HTRA1 is a serine protease. HTRA1 targets a variety of proteins (1 & 2), including fibronectin (induce synovial cells to up-regulate MMP1 and MMP3 production), proteoglycans (release soluble FGF-glycosaminoglycan complexes that promote the range and intensity of FGF signals in ...
... Scientific Background HTRA1 is a serine protease. HTRA1 targets a variety of proteins (1 & 2), including fibronectin (induce synovial cells to up-regulate MMP1 and MMP3 production), proteoglycans (release soluble FGF-glycosaminoglycan complexes that promote the range and intensity of FGF signals in ...
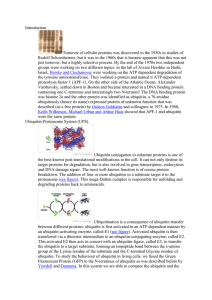
Introduction
... Turnover of cellular proteins was discovered in the 1930s in studies of Rudolf Schoenheimer, but it was in the 1960s that is became apparent that this was not just turnover, but a highly selective process. By the end of the 1970s two independent groups were working on two different topics: in the la ...
... Turnover of cellular proteins was discovered in the 1930s in studies of Rudolf Schoenheimer, but it was in the 1960s that is became apparent that this was not just turnover, but a highly selective process. By the end of the 1970s two independent groups were working on two different topics: in the la ...
Type-IV Antifreeze Proteins are Essential for Epiboly
... (YSL). Interestingly, afp4a expression continues in YSL and digestive system from early embryos to adults, whereas afp4b expression is restricted to embryogenesis. Importantly, we have shown by using afp4a-specific and afp4b-specifc morpholino knockdown and cell lineage tracing approaches that AFP4a ...
... (YSL). Interestingly, afp4a expression continues in YSL and digestive system from early embryos to adults, whereas afp4b expression is restricted to embryogenesis. Importantly, we have shown by using afp4a-specific and afp4b-specifc morpholino knockdown and cell lineage tracing approaches that AFP4a ...
ab initio
... – In living organisms, the specific steps of the folding process have been hard to discern experimentally and characterize theoretically. – It seems that all the information needed to get to a precise three-dimensional shape is "in there already," contained in the one-dimensional amino acid sequence ...
... – In living organisms, the specific steps of the folding process have been hard to discern experimentally and characterize theoretically. – It seems that all the information needed to get to a precise three-dimensional shape is "in there already," contained in the one-dimensional amino acid sequence ...
Progressive resistance exercise training decreases ribosomal
... training (RT) or sedentary (SED) group. RT animals were trained to climb a ladder apparatus with progressively heavier loads over a 10 week period. SED animals were not given any exercise training. Following this period, the flexor hallucis longus (FHL) muscle was excised and analyzed for protein le ...
... training (RT) or sedentary (SED) group. RT animals were trained to climb a ladder apparatus with progressively heavier loads over a 10 week period. SED animals were not given any exercise training. Following this period, the flexor hallucis longus (FHL) muscle was excised and analyzed for protein le ...
CHAPTER 2 FUNDAMENTAL CHEMISTRY FOR MICROBIOLOGY
... group of substances that includes fats, phospholipids, and steroids. • They are relatively insoluble in water which makes them very useful as elements of cellular structure. • Some lipids contain more energy than carbohydrates but are harder to break down. ...
... group of substances that includes fats, phospholipids, and steroids. • They are relatively insoluble in water which makes them very useful as elements of cellular structure. • Some lipids contain more energy than carbohydrates but are harder to break down. ...
Chapt 5 - Workforce Solutions
... “This workforce solution was funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community-Based Job Training Grants as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration. The solution was created by the grantee and does not necessarily reflect the official position of ...
... “This workforce solution was funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community-Based Job Training Grants as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration. The solution was created by the grantee and does not necessarily reflect the official position of ...
mRNA translation
... structure which are unique for microbes and are not found in eukaryotes There are slight differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic ribosomes and these differences are targeted by antibiotics There are antibiotics (eg. kanamycin) kanamycin) which specifically block bacterial ribosomes ...
... structure which are unique for microbes and are not found in eukaryotes There are slight differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic ribosomes and these differences are targeted by antibiotics There are antibiotics (eg. kanamycin) kanamycin) which specifically block bacterial ribosomes ...
Controlling complexity and water penetration in functional de novo
... challenge to delineating individual amino acid functions in natural enzymes and raises major barriers to their redesign while engineering new functions in artificial proteins. Two complementary principles (Figure 1) illustrate the roots of natural protein complexity. First, individual amino acids ar ...
... challenge to delineating individual amino acid functions in natural enzymes and raises major barriers to their redesign while engineering new functions in artificial proteins. Two complementary principles (Figure 1) illustrate the roots of natural protein complexity. First, individual amino acids ar ...
Proteins - Explore Biology
... Water-loving amino acids Hydrophillic “water loving” amino acids try to stay in water in cell ...
... Water-loving amino acids Hydrophillic “water loving” amino acids try to stay in water in cell ...
Poster 2: Primary Structure - IMSA Digital Commons
... Fig. 1: The general 3D structure of the primary structure of a protein. Note that not everything is in the same plane. Also note the torsion angles; the measurements of these angles will vary between -180 degrees and 180 degrees depending on the R group. (1) However, it will never go to a conformati ...
... Fig. 1: The general 3D structure of the primary structure of a protein. Note that not everything is in the same plane. Also note the torsion angles; the measurements of these angles will vary between -180 degrees and 180 degrees depending on the R group. (1) However, it will never go to a conformati ...
Scoring Docked Protein Complexes with Hydrogen Bonds
... the interaction between the member proteins so weak that the new structure cannot be determined experimentally, even if the structures of both proteins are already known. In addition to this, these complexes are also often times transient and difficult to isolate. Fortunately, computational determi ...
... the interaction between the member proteins so weak that the new structure cannot be determined experimentally, even if the structures of both proteins are already known. In addition to this, these complexes are also often times transient and difficult to isolate. Fortunately, computational determi ...
Facilitated diffusion is a process by which molecules are
... binds a substance and, in doing so, triggers a change of its own shape, moving the bound molecule from the outside of the cell to its interior; depending on the gradient, the material may move in the opposite direction . Carrier proteins are typically specific for a single substance. This adds to th ...
... binds a substance and, in doing so, triggers a change of its own shape, moving the bound molecule from the outside of the cell to its interior; depending on the gradient, the material may move in the opposite direction . Carrier proteins are typically specific for a single substance. This adds to th ...
BIOLOGICAL MACROMOLECULES
... structure and function of proteins, nucleic acids, and their complexes. The topics addressed are a selection of modern biophysical methods applied to current questions in macromolecular biochemistry. In particular, the interplay of structure and function of biological macromolecules will be highligh ...
... structure and function of proteins, nucleic acids, and their complexes. The topics addressed are a selection of modern biophysical methods applied to current questions in macromolecular biochemistry. In particular, the interplay of structure and function of biological macromolecules will be highligh ...
HSPIR: a manually annotated heat shock protein information resource
... the conformations of proteins on exposure to various stress conditions. They are a highly conserved group of proteins involved in diverse physiological functions, including de novo folding, disaggregation and protein trafficking. Moreover, their critical role in the control of disease progression ma ...
... the conformations of proteins on exposure to various stress conditions. They are a highly conserved group of proteins involved in diverse physiological functions, including de novo folding, disaggregation and protein trafficking. Moreover, their critical role in the control of disease progression ma ...
Intrinsically disordered proteins

An intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) is a protein that lacks a fixed or ordered three-dimensional structure. IDPs cover a spectrum of states from fully unstructured to partially structured and include random coils, (pre-)molten globules, and large multi-domain proteins connected by flexible linkers. They constitute one of the main types of protein (alongside globular, fibrous and membrane proteins).The discovery of IDPs has challenged the traditional protein structure paradigm, that protein function depends on a fixed three-dimensional structure. This dogma has been challenged over the last decades by increasing evidence from various branches of structural biology, suggesting that protein dynamics may be highly relevant for such systems. Despite their lack of stable structure, IDPs are a very large and functionally important class of proteins. In some cases, IDPs can adopt a fixed three-dimensional structure after binding to other macromolecules.