2.22 Protein Synthesis.docx
... polypeptide. As shown below, this is a fairly involved process. DNA contains the genetic code that is used as a template to create mRNA in a process known as transcription. The mRNA then moves out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm where it serves as the template for translation, where tRNAs bring in ...
... polypeptide. As shown below, this is a fairly involved process. DNA contains the genetic code that is used as a template to create mRNA in a process known as transcription. The mRNA then moves out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm where it serves as the template for translation, where tRNAs bring in ...
Quantitative protein abundance measurements
... drug transporters in drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, elimination, and as such toxicity and efficacy has generally been established and recognized. Making use of recent developments we are now able to accurately measure the concentration of membrane transporters within the plasma membrane ...
... drug transporters in drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, elimination, and as such toxicity and efficacy has generally been established and recognized. Making use of recent developments we are now able to accurately measure the concentration of membrane transporters within the plasma membrane ...
Syllabus: Biochem 104b
... About the course: The course will provide an introduction to the physico-chemical principles that govern the structure, dynamics and function of biological macromolecules. We will then use those principles to look at and understand the structures and physical properties of proteins and nucleic acids ...
... About the course: The course will provide an introduction to the physico-chemical principles that govern the structure, dynamics and function of biological macromolecules. We will then use those principles to look at and understand the structures and physical properties of proteins and nucleic acids ...
The Biology of
... helix and beta sheets • (A) is example of an alpha helix. The hydrogen bonds (dotted lines) are between oxygen atoms (red) and hydrogen atoms (white) (shown in this case as occurring every fourth pair of amino acids along the protein). • (B) shows examples of beta-sheets held together by hydrogen bo ...
... helix and beta sheets • (A) is example of an alpha helix. The hydrogen bonds (dotted lines) are between oxygen atoms (red) and hydrogen atoms (white) (shown in this case as occurring every fourth pair of amino acids along the protein). • (B) shows examples of beta-sheets held together by hydrogen bo ...
Fluorine-Adding Bacteria May Transform Natural Product Medicines
... and structural biologist Barry Stoddard of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle report that they’ve designed a protein to tightly grab a heart drug steroid called digoxigenin, while excluding similar steroids such as digitoxigenin (even the name is almost indistinguishable) and prog ...
... and structural biologist Barry Stoddard of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle report that they’ve designed a protein to tightly grab a heart drug steroid called digoxigenin, while excluding similar steroids such as digitoxigenin (even the name is almost indistinguishable) and prog ...
Organelles Worksheet
... 7. a. Which structure is selectively permeable? b. What substance is permeable to cell membranes? 8. What is the difference between plant cell vacuoles and animal cell vacuoles? ...
... 7. a. Which structure is selectively permeable? b. What substance is permeable to cell membranes? 8. What is the difference between plant cell vacuoles and animal cell vacuoles? ...
New partners for protein kinases - Journal of Molecular Cell Biology
... (Wu, 2011). Among these modifications, protein phosphorylation may be the most important one that involves in the regulation of almost all biological functions. Protein kinases are the major enzymes that are responsible for the protein phosphorylation. On the other hand, protein kinases require othe ...
... (Wu, 2011). Among these modifications, protein phosphorylation may be the most important one that involves in the regulation of almost all biological functions. Protein kinases are the major enzymes that are responsible for the protein phosphorylation. On the other hand, protein kinases require othe ...
מצגת של PowerPoint - The ICNC PhD Program
... http://pawsonlab.mshri.on.ca/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=30&Itemid=63 ...
... http://pawsonlab.mshri.on.ca/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=30&Itemid=63 ...
Klauda-NCTU-Oct31
... homologues (Osh) with Osh4 known to exchange phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PI4P) lipids regulated by ergosterol. This protein contains a lipid packing sensing peptide classified as an amphipathic lipid packing sensor (ALPS) like motif that is believe to sense membrane curvature. To probe peptide ...
... homologues (Osh) with Osh4 known to exchange phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PI4P) lipids regulated by ergosterol. This protein contains a lipid packing sensing peptide classified as an amphipathic lipid packing sensor (ALPS) like motif that is believe to sense membrane curvature. To probe peptide ...
ppt presentation
... - dsRNA cleavage by DCL, siRNA formation, sequence specific mRNA degradation or block of transcription due to promoter methylation ...
... - dsRNA cleavage by DCL, siRNA formation, sequence specific mRNA degradation or block of transcription due to promoter methylation ...
Lucky Lady Slots Online - How Does Shot Roulette Work
... 10. Proteins are formed by joining amino acids. What type of covalent bond is this? ...
... 10. Proteins are formed by joining amino acids. What type of covalent bond is this? ...
L10 Protein-carbo and protein-lipids interactions - e
... Maximum interaction (about 70% degree of interaction) at pH 6.5. At lower pH, there is a slow decline - to about 50% at pH 3.6. At higher pH, rapid decrease of degree of interaction - 13% at pH 8.3. Explanation: Protein-starch interaction requires (+) charge of protein molecules which decline in alk ...
... Maximum interaction (about 70% degree of interaction) at pH 6.5. At lower pH, there is a slow decline - to about 50% at pH 3.6. At higher pH, rapid decrease of degree of interaction - 13% at pH 8.3. Explanation: Protein-starch interaction requires (+) charge of protein molecules which decline in alk ...
Proteins
... The shaping of the secondary structure with many twists and folds into a 3D shape. There may be several areas of coiling and pleating with straight chain amino acids in between. Four types of bonds hold these together Disulphide bonds Ionic Bonds Hydrogen bonds Hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactio ...
... The shaping of the secondary structure with many twists and folds into a 3D shape. There may be several areas of coiling and pleating with straight chain amino acids in between. Four types of bonds hold these together Disulphide bonds Ionic Bonds Hydrogen bonds Hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactio ...
SOMAscan™: A Quantitative Multiplex Proteomic
... time-tospin ranges from .5 hours (beige) to 20 hours (blue) ...
... time-tospin ranges from .5 hours (beige) to 20 hours (blue) ...
Cell Parts: Protein Synthesis
... Vesicle: a small molecule within a cell enclosed by a lipid bilayer Image Source: http://karimedalla.files.wordpress.com/2012/09/i60_0322.jpg ...
... Vesicle: a small molecule within a cell enclosed by a lipid bilayer Image Source: http://karimedalla.files.wordpress.com/2012/09/i60_0322.jpg ...
Slide 1
... Porin are major proteins in the outer envelop that form small non-specific hydrophilic channels that allow the diffusion of low molecular weight neutral or charged solutes. Examples are LamB, OmpF, OmpC, Tsx. ...
... Porin are major proteins in the outer envelop that form small non-specific hydrophilic channels that allow the diffusion of low molecular weight neutral or charged solutes. Examples are LamB, OmpF, OmpC, Tsx. ...
BIOCHEMICAL METHODS USED IN PROTEN CHARACTERIZATION
... Increasing salt concentrationn: attracted of the water molecules by the salt ions, which decreases the number of water molecules available to interact with protein. Increasing ionic strength decrease solubility of a protein. In general: a) small proteins more soluble than large proteins b) the lar ...
... Increasing salt concentrationn: attracted of the water molecules by the salt ions, which decreases the number of water molecules available to interact with protein. Increasing ionic strength decrease solubility of a protein. In general: a) small proteins more soluble than large proteins b) the lar ...
BIOCHEMICAL METHODS USED IN PROTEN CHARACTERIZATION
... Increasing salt concentrationn: attracted of the water molecules by the salt ions, which decreases the number of water molecules available to interact with protein. Increasing ionic strength decrease solubility of a protein. In general: a) small proteins more soluble than large proteins b) the lar ...
... Increasing salt concentrationn: attracted of the water molecules by the salt ions, which decreases the number of water molecules available to interact with protein. Increasing ionic strength decrease solubility of a protein. In general: a) small proteins more soluble than large proteins b) the lar ...
Protein: A polymer of amino acids Amino Acid Structure
... Turns nerve and muscle activity “On” or “Off” ...
... Turns nerve and muscle activity “On” or “Off” ...
Slide 1
... Most of the proteins should fold in order to function Misfolding cause some diseases. Cystic Fibrosis ,affects lungs and digestive system and cause early death Alzheimers’s and Parkinson's disease It may help us to understand the structure of proteins which has not been known ...
... Most of the proteins should fold in order to function Misfolding cause some diseases. Cystic Fibrosis ,affects lungs and digestive system and cause early death Alzheimers’s and Parkinson's disease It may help us to understand the structure of proteins which has not been known ...
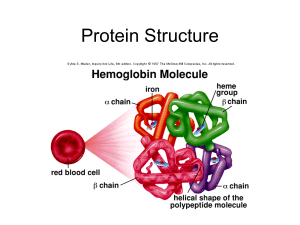
Protein–protein interaction

Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) refer to physical contacts established between two or more proteins as a result of biochemical events and/or electrostatic forces.In fact, proteins are vital macromolecules, at both cellular and systemic levels, but they rarely act alone. Diverse essential molecular processes within a cell are carried out by molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein components organized by their PPIs. Indeed, these interactions are at the core of the entire interactomics system of any living cell and so, unsurprisingly, aberrant PPIs are on the basis of multiple diseases, such as Creutzfeld-Jacob, Alzheimer's disease, and cancer.PPIs have been studied from different perspectives: biochemistry, quantum chemistry, molecular dynamics, signal transduction, among others. All this information enables the creation of large protein interaction networks – similar to metabolic or genetic/epigenetic networks – that empower the current knowledge on biochemical cascades and disease pathogenesis, as well as provide putative new therapeutic targets.