Document
... 2. Cytoscape-rendered view of a portion of the peptide-protein network generated by our software from ProteinProphet results Peptide nodes are represented by small triangles; those with thick borders map only to a single protein or indistinguishable protein group. Protein nodes are represented by la ...
... 2. Cytoscape-rendered view of a portion of the peptide-protein network generated by our software from ProteinProphet results Peptide nodes are represented by small triangles; those with thick borders map only to a single protein or indistinguishable protein group. Protein nodes are represented by la ...
Buffers
... a) No change in blood pH. b) A decrease in [CO2], causing an increase in [H+] and decrease in pH. c) An increase in [CO2], causing an increase in [H+] and decrease in pH. d) A decrease in [CO2], causing an increase in [H+] and increase in pH. e) An increase in [CO2], causing a decrease in [H+] and i ...
... a) No change in blood pH. b) A decrease in [CO2], causing an increase in [H+] and decrease in pH. c) An increase in [CO2], causing an increase in [H+] and decrease in pH. d) A decrease in [CO2], causing an increase in [H+] and increase in pH. e) An increase in [CO2], causing a decrease in [H+] and i ...
Cell Free Protein Synthesis
... – Interestingly, when comparing the total amount of protein produced, dispersions with smaller particles (170 or 250 nm) produced more protein than dispersions with larger (400 nm) – the exact reason for this phenomenon is unclear but it seems: possible that the close proximity of the “reacting” com ...
... – Interestingly, when comparing the total amount of protein produced, dispersions with smaller particles (170 or 250 nm) produced more protein than dispersions with larger (400 nm) – the exact reason for this phenomenon is unclear but it seems: possible that the close proximity of the “reacting” com ...
What do Prions, Viruses and Viroids reveal about the formation of
... temperatures to that seen in hydrothermal systems. One problem with the formation of DNA and RNA in such environments is their survival in that system. Interactions between primitive prion like particles and RNA for example benefits both. Survivability in harsh conditions for proto RNA constructs wh ...
... temperatures to that seen in hydrothermal systems. One problem with the formation of DNA and RNA in such environments is their survival in that system. Interactions between primitive prion like particles and RNA for example benefits both. Survivability in harsh conditions for proto RNA constructs wh ...
Introduction to Proteins
... Stabilize tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins Create an organic solvent-like environment in the interior ...
... Stabilize tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins Create an organic solvent-like environment in the interior ...
Biochemistry Course #: - College of Pharmacy at Howard University
... 1. Typically fibrous proteins consist largely of a single type of secondary structure. Globular proteins often contain several types of secondary structure. 2. The two groups differ functionally in that the structures that provide support, shape, and external protection to vertebrates are made of fi ...
... 1. Typically fibrous proteins consist largely of a single type of secondary structure. Globular proteins often contain several types of secondary structure. 2. The two groups differ functionally in that the structures that provide support, shape, and external protection to vertebrates are made of fi ...
MCB100A/CHEM130A In-Section Quiz #2 (Aathavan Karunakaran)
... mutated one of the cysteines into a serine (there are now only 7 cysteines), but the mutant protein is just as active as the wild-type. You now repeat the Anfinsen experiment on this mutant protein: i.e, unfolded the protein with urea, reduced all the disulfide bonds, put the protein in oxidizing en ...
... mutated one of the cysteines into a serine (there are now only 7 cysteines), but the mutant protein is just as active as the wild-type. You now repeat the Anfinsen experiment on this mutant protein: i.e, unfolded the protein with urea, reduced all the disulfide bonds, put the protein in oxidizing en ...
How are the proteins built up
... Sometimes the secondary structures are closely related to the tertiary contacts between the different parts of the protein that are far away along the sequence (think of the β-sheet contacts, which had H-bonding between the β -strands, and the β -strands are located at different parts of the polymer ...
... Sometimes the secondary structures are closely related to the tertiary contacts between the different parts of the protein that are far away along the sequence (think of the β-sheet contacts, which had H-bonding between the β -strands, and the β -strands are located at different parts of the polymer ...
Protein Enriched Porridge High Protein Porridge
... © 2016. Univar BV. All rights reserved. UNIVAR, the hexagon, and other identified trademarks are the property of Univar Inc., Univar USA Inc., Univar Ltd., or affiliated companies. All other trademarks not owned by Univar Inc., Univar USA Inc., Univar Ltd., or affiliated companies that appear in thi ...
... © 2016. Univar BV. All rights reserved. UNIVAR, the hexagon, and other identified trademarks are the property of Univar Inc., Univar USA Inc., Univar Ltd., or affiliated companies. All other trademarks not owned by Univar Inc., Univar USA Inc., Univar Ltd., or affiliated companies that appear in thi ...
LECT09 fibro
... bond covalently to either N or O is attracted by an electron pair from a neighboring N or O. The attracting force is basically electrostatic. Disulfide Bond: A strong covalent bond formed by two –SH groups of cysteines. This bond can only be broken to component -SH groups by reducing agents. Electro ...
... bond covalently to either N or O is attracted by an electron pair from a neighboring N or O. The attracting force is basically electrostatic. Disulfide Bond: A strong covalent bond formed by two –SH groups of cysteines. This bond can only be broken to component -SH groups by reducing agents. Electro ...
Recitation 3 - MIT OpenCourseWare
... patterns in different region of polypeptide chains and is predominantly stabilized by hydrogen bonds. The different interactions between the side chain groups of the amino acids determine the 3dimensional tertiary structure of proteins. Quaternary structure results when two or more polypeptide chain ...
... patterns in different region of polypeptide chains and is predominantly stabilized by hydrogen bonds. The different interactions between the side chain groups of the amino acids determine the 3dimensional tertiary structure of proteins. Quaternary structure results when two or more polypeptide chain ...
Computational Prediction of Beta Structure from Amino Acid
... Sequence in a Class of Pathologically Relevant Proteins Abstract Objectives/Goals Because structure dictates the function of proteins - physiological or pathological - protein structure discovery is of great interest to biological science. Though experimental approaches have yielded good results, th ...
... Sequence in a Class of Pathologically Relevant Proteins Abstract Objectives/Goals Because structure dictates the function of proteins - physiological or pathological - protein structure discovery is of great interest to biological science. Though experimental approaches have yielded good results, th ...
Anti-Ribosomal Protein L26 (N-terminal) (R0655)
... surface of the ribosome while the rRNA components make up the central core. rRNAs play a central part in the ribosome catalytic activities. The proteins’ main function is to hold the ribosomal RNA in place so that it could carry out its catalytic activity.1 However, being at the surface of the ribos ...
... surface of the ribosome while the rRNA components make up the central core. rRNAs play a central part in the ribosome catalytic activities. The proteins’ main function is to hold the ribosomal RNA in place so that it could carry out its catalytic activity.1 However, being at the surface of the ribos ...
PROTEINS
... • Evolution conserves amino acids that are important to protein structure and function across species. Sequence comparison of multiple “homologs” of a particular protein reveals highly conserved regions that are important for function. • Clusters of conserved residues are called “motifs” -- motifs c ...
... • Evolution conserves amino acids that are important to protein structure and function across species. Sequence comparison of multiple “homologs” of a particular protein reveals highly conserved regions that are important for function. • Clusters of conserved residues are called “motifs” -- motifs c ...
REVIEW Protein Synthesis with Analogies
... A Protein Fairytale Once upon a time there were two fraternal twin brothers, Donald N Armstrong and Ronald N. Armstrong. Donald was the smarter of the two and he was a successful inventor with many patents. Although Ronald was not as smart at his brother, he was extremely loyal. One day Donald came ...
... A Protein Fairytale Once upon a time there were two fraternal twin brothers, Donald N Armstrong and Ronald N. Armstrong. Donald was the smarter of the two and he was a successful inventor with many patents. Although Ronald was not as smart at his brother, he was extremely loyal. One day Donald came ...
Pressure - People Server at UNCW
... Effect of P on Km of NADH for M4-LDH in shallow- and deepliving species of teleosts all of which are adapted to similar T (-2 to 8 C) (Siebenaller and Somero, 1979). Note that Sebastolobus ...
... Effect of P on Km of NADH for M4-LDH in shallow- and deepliving species of teleosts all of which are adapted to similar T (-2 to 8 C) (Siebenaller and Somero, 1979). Note that Sebastolobus ...
Monday March 24 Prof. Sankaran (Thai) Thayumanavan
... “Bottom-up Approaches to Stimuli-sensitive Supramolecular Nanoassemblies” Non-covalent encapsulation of guest molecules and their triggered release is of paramount importance in a variety of areas. Achieving such release characteristics would have significant implications in applications such as dru ...
... “Bottom-up Approaches to Stimuli-sensitive Supramolecular Nanoassemblies” Non-covalent encapsulation of guest molecules and their triggered release is of paramount importance in a variety of areas. Achieving such release characteristics would have significant implications in applications such as dru ...
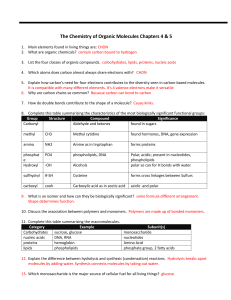
04-05 Biochem review sheet answers ws
... 5. Explain how carbon’s need for four electrons contributes to the diversity seen in carbon-based molecules. It is compatible with many different elements. It’s 4 valence electrons make it versatile 6. Why are carbon chains so common? Because carbon can bond to carbon 7. How do double bonds contribu ...
... 5. Explain how carbon’s need for four electrons contributes to the diversity seen in carbon-based molecules. It is compatible with many different elements. It’s 4 valence electrons make it versatile 6. Why are carbon chains so common? Because carbon can bond to carbon 7. How do double bonds contribu ...
Extend Your Understanding of the Bacterial
... exploited and enhanced this property in the laboratory. Transformation allows scientists to move recombinant plasmids containing DNA from two or more species into bacterial cells to produce many copies of the recombinant plasmid or to produce large amounts of the recombinant protein(s). Through thes ...
... exploited and enhanced this property in the laboratory. Transformation allows scientists to move recombinant plasmids containing DNA from two or more species into bacterial cells to produce many copies of the recombinant plasmid or to produce large amounts of the recombinant protein(s). Through thes ...
ch 4 study guide - Elmwood Park Memorial High School
... 2. Know that diffusion is the movement from high to low concentration. 3. Know that when you place a drop of ink in a beaker of water this is a example of diffusion because the ink moves from high to low until the molecules are equal throughout the water. 4. Know that the diffusion of water is calle ...
... 2. Know that diffusion is the movement from high to low concentration. 3. Know that when you place a drop of ink in a beaker of water this is a example of diffusion because the ink moves from high to low until the molecules are equal throughout the water. 4. Know that the diffusion of water is calle ...
Week 2 Handout with No answers
... determined by the __________________________, (which is determined by the DNA sequence) and __________________ 1 °Primary: simple a.a. sequence read and numbered from _____ to________ terminus. 2° Secondary: recurring structural patterns or folding motifs. Main chain is hydrophilic; interior of prot ...
... determined by the __________________________, (which is determined by the DNA sequence) and __________________ 1 °Primary: simple a.a. sequence read and numbered from _____ to________ terminus. 2° Secondary: recurring structural patterns or folding motifs. Main chain is hydrophilic; interior of prot ...
Sander van Riet 13 June Reviewer Gene co
... IvIiev et al. uses this concept together with Protein Atlas project in order to identify new genes associated with motile cilia. Data from 3 different regions known to harbour motile cilia obtained from the GEO database were used. First they linked with already known motile cilia proteins together w ...
... IvIiev et al. uses this concept together with Protein Atlas project in order to identify new genes associated with motile cilia. Data from 3 different regions known to harbour motile cilia obtained from the GEO database were used. First they linked with already known motile cilia proteins together w ...
Protein–protein interaction

Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) refer to physical contacts established between two or more proteins as a result of biochemical events and/or electrostatic forces.In fact, proteins are vital macromolecules, at both cellular and systemic levels, but they rarely act alone. Diverse essential molecular processes within a cell are carried out by molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein components organized by their PPIs. Indeed, these interactions are at the core of the entire interactomics system of any living cell and so, unsurprisingly, aberrant PPIs are on the basis of multiple diseases, such as Creutzfeld-Jacob, Alzheimer's disease, and cancer.PPIs have been studied from different perspectives: biochemistry, quantum chemistry, molecular dynamics, signal transduction, among others. All this information enables the creation of large protein interaction networks – similar to metabolic or genetic/epigenetic networks – that empower the current knowledge on biochemical cascades and disease pathogenesis, as well as provide putative new therapeutic targets.