Protein © 2009 Cengage - Wadsworth
... Protein turnover is the continual making and breaking down of protein. Amino acid pool is the supply of amino acids that are available. Amino acids from food are called ...
... Protein turnover is the continual making and breaking down of protein. Amino acid pool is the supply of amino acids that are available. Amino acids from food are called ...
Ruboyianes - University of Arizona
... have yet to be observed during the X174 life cycle. However, past studies of this low-copy protein have focused on its association with assembly intermediates. The protein appears as a monomer in early assembly intermediates (6), and its incorporation into these intermediates appears to be mediated ...
... have yet to be observed during the X174 life cycle. However, past studies of this low-copy protein have focused on its association with assembly intermediates. The protein appears as a monomer in early assembly intermediates (6), and its incorporation into these intermediates appears to be mediated ...
Peptides and Protein Primary Structure
... • Write the chemical equation for formation of a peptide bond. • Draw a peptide bond and describe its conformation (3dimensional arrangement of atoms). • Explain the relation between the N- and C-terminal residues of a peptide or protein and the numbering of the amino acid residues in the chain, and ...
... • Write the chemical equation for formation of a peptide bond. • Draw a peptide bond and describe its conformation (3dimensional arrangement of atoms). • Explain the relation between the N- and C-terminal residues of a peptide or protein and the numbering of the amino acid residues in the chain, and ...
Peptides and Protein Primary Structure
... φ,ψ: φ,ψ What’s it all about? • Polypeptides are made from amino acids. • Each amino acid has a R-group. • Each R-group has its own chemical character (steric volume and shape, hydrophobicity, hydrophilicity, charge, etc.) • Adjacent R-groups interact with each other. • This interaction leads to the ...
... φ,ψ: φ,ψ What’s it all about? • Polypeptides are made from amino acids. • Each amino acid has a R-group. • Each R-group has its own chemical character (steric volume and shape, hydrophobicity, hydrophilicity, charge, etc.) • Adjacent R-groups interact with each other. • This interaction leads to the ...
Extension and Enrichment
... In this exercise you will fold a “real” protein. You will fold a model of the first of three Zinc fingers of the Zif228 protein. Zinc finger proteins regulate the transcription of DNA into mRNAby binding to DNA and attracting RNA polymerase. A zinc finger protein contains two cysteines and two histi ...
... In this exercise you will fold a “real” protein. You will fold a model of the first of three Zinc fingers of the Zif228 protein. Zinc finger proteins regulate the transcription of DNA into mRNAby binding to DNA and attracting RNA polymerase. A zinc finger protein contains two cysteines and two histi ...
answers_ch04
... that region of the active site for COX-1 than there is in the corresponding region in COX-2. Drugs can be designed that take advantage of this difference such that they fit into the active site of COX-2 but cannot fit the active site of COX-1 ...
... that region of the active site for COX-1 than there is in the corresponding region in COX-2. Drugs can be designed that take advantage of this difference such that they fit into the active site of COX-2 but cannot fit the active site of COX-1 ...
Broder et al Curr biol 98
... Yehoshua C. Broder*, Sigal Katz* and Ami Aronheim The yeast two-hybrid system represents one of the most efficient approaches currently available for identifying and characterizing protein–protein interactions [1–4]. Although very powerful, this procedure exhibits several problems and inherent limit ...
... Yehoshua C. Broder*, Sigal Katz* and Ami Aronheim The yeast two-hybrid system represents one of the most efficient approaches currently available for identifying and characterizing protein–protein interactions [1–4]. Although very powerful, this procedure exhibits several problems and inherent limit ...
Infrared spectroscopy: a tool for protein characterization Chenge Li
... positively or negatively charged, depending on its composition, structure and properties. In total, there are mainly 20 natural protein-building amino acids, which combine into peptide chains via peptide bonds (-CO-NH-). To be able to perform biological functions, proteins have to fold to defined an ...
... positively or negatively charged, depending on its composition, structure and properties. In total, there are mainly 20 natural protein-building amino acids, which combine into peptide chains via peptide bonds (-CO-NH-). To be able to perform biological functions, proteins have to fold to defined an ...
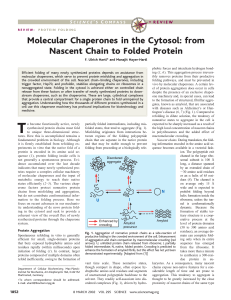
Molecular Chaperones in the Cytosol: from Nascent Chain to Folded
... synthesized protein chains must fold to unique three-dimensional structures. How this is accomplished remains a fundamental problem in biology. Although it is firmly established from refolding experiments in vitro that the native fold of a protein is encoded in its amino acid sequence (1), protein f ...
... synthesized protein chains must fold to unique three-dimensional structures. How this is accomplished remains a fundamental problem in biology. Although it is firmly established from refolding experiments in vitro that the native fold of a protein is encoded in its amino acid sequence (1), protein f ...
Identification of a family of BspA like surface proteins of Entamoeba
... worldwide [1]. E. histolytica trophozoites invade into submucosal tissues of the colon, which brings them into contact with extracellular matrix proteins, such as collagen, laminin, and fibronectin. Amebic contact with fibronectin induces alterations in actin polymerization, trophozoite motility, an ...
... worldwide [1]. E. histolytica trophozoites invade into submucosal tissues of the colon, which brings them into contact with extracellular matrix proteins, such as collagen, laminin, and fibronectin. Amebic contact with fibronectin induces alterations in actin polymerization, trophozoite motility, an ...
Unit 1.1.2 - Membranes
... e.g. O2 through cell membrane of plant and animal cells or released from ...
... e.g. O2 through cell membrane of plant and animal cells or released from ...
Identification of a novel protein encoded by third conserved gene
... lymphocyte specific genes, encode transposase, an essential component of the V(D)J recombinase which is responsible for the generation of diversity of antigen receptors on T and B lymphocytes (Schatz & Baltimore, 2004). It is believed that the acquisition of RAG genes represented a turning point in ...
... lymphocyte specific genes, encode transposase, an essential component of the V(D)J recombinase which is responsible for the generation of diversity of antigen receptors on T and B lymphocytes (Schatz & Baltimore, 2004). It is believed that the acquisition of RAG genes represented a turning point in ...
BIOCHEMISTRY
... Glycolysis speeds up in the presence of oxygen since more ATP is produced under anaerobic conditions than in aerobic conditions. Glycolysis is slowed down in the presence of oxygen since more ATP is produced under aerobic conditions than in anaerobic conditions. The presence of oxygen does not effec ...
... Glycolysis speeds up in the presence of oxygen since more ATP is produced under anaerobic conditions than in aerobic conditions. Glycolysis is slowed down in the presence of oxygen since more ATP is produced under aerobic conditions than in anaerobic conditions. The presence of oxygen does not effec ...
Slide 1
... • Messenger RNA migrates to ribosomes where it acts as the template for protein • To be used in protein synthesis, amino acids are bound to transfer RNA (specific) • Transfer RNA travels along the messenger RNA to place amino acid in chain • If an given amino acid is not present, synthesis of this p ...
... • Messenger RNA migrates to ribosomes where it acts as the template for protein • To be used in protein synthesis, amino acids are bound to transfer RNA (specific) • Transfer RNA travels along the messenger RNA to place amino acid in chain • If an given amino acid is not present, synthesis of this p ...
Electrophoretic Extraction and Proteomic Characterization of
... of particulate nitrogen in marine sediments [5–8]. In addition to proteins representing the largest fraction of organic nitrogen, within the unique amino acid sequence, proteins also can provide functional and phylogenetic information on the organisms from which they were produced, potentially makin ...
... of particulate nitrogen in marine sediments [5–8]. In addition to proteins representing the largest fraction of organic nitrogen, within the unique amino acid sequence, proteins also can provide functional and phylogenetic information on the organisms from which they were produced, potentially makin ...
ACT Science Practice Test 1 ANSWERS File
... The characteristics common to the studies is that both: a. measured periods of maximum glaciations. b. utilized ancient and modern sedimentary rocks. c. analyzed data from marine sediments. d. measured the depth of the cycles. c. Both studies state that they are analyzing marine sediment. Study 2 ma ...
... The characteristics common to the studies is that both: a. measured periods of maximum glaciations. b. utilized ancient and modern sedimentary rocks. c. analyzed data from marine sediments. d. measured the depth of the cycles. c. Both studies state that they are analyzing marine sediment. Study 2 ma ...
Chemistry 160 Exam 2 Key Pg. Chemistry 160 Exam 2 key Please
... Secondary = simple folding like α helix or beta sheet Supersecondary = patterns of secondary Tertiary = 3 D structure Quaternary = subunit interactions (5) 7. Give two types of forces that hold proteins in their 3-D shape. Draw a diagram for each. ...
... Secondary = simple folding like α helix or beta sheet Supersecondary = patterns of secondary Tertiary = 3 D structure Quaternary = subunit interactions (5) 7. Give two types of forces that hold proteins in their 3-D shape. Draw a diagram for each. ...
Gene Section IDO2 (indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase 2) -
... IDO2 is a presumptive immunomodulatory gene based on its close structural relationship to IDO1 and its expression in a variety of antigen-presenting cell types. Both IDO1 and IDO2 will catabolize tryptophan to kynurenine. Biochemical studies indicate that both enzymes are similarly robust in catabol ...
... IDO2 is a presumptive immunomodulatory gene based on its close structural relationship to IDO1 and its expression in a variety of antigen-presenting cell types. Both IDO1 and IDO2 will catabolize tryptophan to kynurenine. Biochemical studies indicate that both enzymes are similarly robust in catabol ...
PPT
... the ability of bacteria to sense and respond to environmental stimuli such as pH, temperature, the presence of nutrients, etc has been long recognized as essential for their continued survival it is now apparent that many bacteria can also sense and respond to signals expressed by other bacteria ...
... the ability of bacteria to sense and respond to environmental stimuli such as pH, temperature, the presence of nutrients, etc has been long recognized as essential for their continued survival it is now apparent that many bacteria can also sense and respond to signals expressed by other bacteria ...
lecture 3
... These molecules are called amphiphilic because they are composed of two parts which differ by their solubility in water: (1) polar «head» possessing high affinity for water, i.e. hydrophilic, and (2) .tail» that is formed by non-polar carbohydrate chains of fatty acids; this part of the molecule has ...
... These molecules are called amphiphilic because they are composed of two parts which differ by their solubility in water: (1) polar «head» possessing high affinity for water, i.e. hydrophilic, and (2) .tail» that is formed by non-polar carbohydrate chains of fatty acids; this part of the molecule has ...
Nucleic acids and their protein partners
... without the help of proteins. Electrostatics is a dominant force in RNA folding, but recent theoretical, computational, and experimental investigations have revealed the interplay of counterions, RNA structure and folding pathways. New structural methods, including timeresolved footprinting, small-a ...
... without the help of proteins. Electrostatics is a dominant force in RNA folding, but recent theoretical, computational, and experimental investigations have revealed the interplay of counterions, RNA structure and folding pathways. New structural methods, including timeresolved footprinting, small-a ...
BCAA 4:1:1 - ProAction
... BCAA 4:1:1 is an innovative product because the special ESTERDRIVE formula ensures that rapidly dissolves and is absorbed at gastrointestinal level. BCAA are metabolized in the mitochondria; valine is converted into a molecule of succinyl-CoA, a Krebs cycle intermediate; isoleucine generates one mol ...
... BCAA 4:1:1 is an innovative product because the special ESTERDRIVE formula ensures that rapidly dissolves and is absorbed at gastrointestinal level. BCAA are metabolized in the mitochondria; valine is converted into a molecule of succinyl-CoA, a Krebs cycle intermediate; isoleucine generates one mol ...
Chapter 3 The Molecules of Cells
... – They can be sold as prescription drugs and used to treat certain diseases – They may also be abused with serious consequences, such as liver damage that can lead to cancer ...
... – They can be sold as prescription drugs and used to treat certain diseases – They may also be abused with serious consequences, such as liver damage that can lead to cancer ...
Membrane pore architecture of the CslF6
... and (1-3,1-4)-b-glucan (also known as mixed linkage glucan or simply b-glucan), mannans, and xyloglucans are synthesized by large integral membrane proteins with a cytoplasmic active site and a membrane pore through which the polysaccharides are transported to exit the cell (1). The biosynthetic gen ...
... and (1-3,1-4)-b-glucan (also known as mixed linkage glucan or simply b-glucan), mannans, and xyloglucans are synthesized by large integral membrane proteins with a cytoplasmic active site and a membrane pore through which the polysaccharides are transported to exit the cell (1). The biosynthetic gen ...
Types of Organic compounds
... Glycoprotein and Proteoglycan • Proteins exist in combination with sugar. • Glycoprotein: Protein + sugar chain. Found in cell membrane. Serve as surface proteins. • Proteoglycan: Protein + sugar chain. Also present in cell membrane. Can have enzymatic activity. ...
... Glycoprotein and Proteoglycan • Proteins exist in combination with sugar. • Glycoprotein: Protein + sugar chain. Found in cell membrane. Serve as surface proteins. • Proteoglycan: Protein + sugar chain. Also present in cell membrane. Can have enzymatic activity. ...
Protein–protein interaction

Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) refer to physical contacts established between two or more proteins as a result of biochemical events and/or electrostatic forces.In fact, proteins are vital macromolecules, at both cellular and systemic levels, but they rarely act alone. Diverse essential molecular processes within a cell are carried out by molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein components organized by their PPIs. Indeed, these interactions are at the core of the entire interactomics system of any living cell and so, unsurprisingly, aberrant PPIs are on the basis of multiple diseases, such as Creutzfeld-Jacob, Alzheimer's disease, and cancer.PPIs have been studied from different perspectives: biochemistry, quantum chemistry, molecular dynamics, signal transduction, among others. All this information enables the creation of large protein interaction networks – similar to metabolic or genetic/epigenetic networks – that empower the current knowledge on biochemical cascades and disease pathogenesis, as well as provide putative new therapeutic targets.