Chapter 3 The Molecules of Cells
... The amino acid sequence of a polypeptide is programmed by a discrete unit of inheritance known as a gene. Genes consist of DNA(deoxyribonucleic acid), a type of nucleic acid. DNA is inherited from an organism’s parents. ...
... The amino acid sequence of a polypeptide is programmed by a discrete unit of inheritance known as a gene. Genes consist of DNA(deoxyribonucleic acid), a type of nucleic acid. DNA is inherited from an organism’s parents. ...
Metabolism of “surplus” amino acids
... system is also ATP expensive, although the random hydrolysis of tissue proteins by lysosomes is not. Ubiquitin is a small (78 amino acid) protein that targets tissue proteins for uptake by the proteasome; it is not itself catabolized in the proteasome, but is recycled. However, there is apparently r ...
... system is also ATP expensive, although the random hydrolysis of tissue proteins by lysosomes is not. Ubiquitin is a small (78 amino acid) protein that targets tissue proteins for uptake by the proteasome; it is not itself catabolized in the proteasome, but is recycled. However, there is apparently r ...
Building proteins from C, coordinates using the dihedral probability
... automate the process of building a protein model from crystallographic data (Jones et al., 1991), but several other uses have been suggested. Holm and Sander (1991) described how correct and incorrect protein folds can be evaluated by such methods, and Rey and Skolnick (1992) mentioned that their pr ...
... automate the process of building a protein model from crystallographic data (Jones et al., 1991), but several other uses have been suggested. Holm and Sander (1991) described how correct and incorrect protein folds can be evaluated by such methods, and Rey and Skolnick (1992) mentioned that their pr ...
Powerpoint - Wishart Research Group
... EWILLITALLCEASE >P12348 Sequence 3 MQWERTGHFDALKPQWERTYHEREISANTHERS... ...
... EWILLITALLCEASE >P12348 Sequence 3 MQWERTGHFDALKPQWERTYHEREISANTHERS... ...
Table S1.
... The enzymatic activity of all proteins was compared to the activity of wtSOD1 and a commercial recombinant SOD1 protein (hucSOD1). Of the mutant SOD1 purified, three have mutations located away from the metal binding/catalytic region, thus having properties similar to wtSOD1. These mutants are denot ...
... The enzymatic activity of all proteins was compared to the activity of wtSOD1 and a commercial recombinant SOD1 protein (hucSOD1). Of the mutant SOD1 purified, three have mutations located away from the metal binding/catalytic region, thus having properties similar to wtSOD1. These mutants are denot ...
Site-Directed Mutagenesis of the Proposed Catalytic Amino Acids
... the effect of the mutation on proteolysis during translation in vitro. The mutations made in the capsid protein are diagrammed in Fig. 2. Also indicated are the locations of four temperature-sensitive mutations that rendered the proteinase inactive at 40°C. Mutant RNAs were translated in rabbit reti ...
... the effect of the mutation on proteolysis during translation in vitro. The mutations made in the capsid protein are diagrammed in Fig. 2. Also indicated are the locations of four temperature-sensitive mutations that rendered the proteinase inactive at 40°C. Mutant RNAs were translated in rabbit reti ...
2-7 Active-Site Geometry
... orientation and the collision will be non-productive. Thus, if both molecules first bind to an enzyme active site, and do so in such a way that their reactive portions are juxtaposed, the probability of a reaction is optimized. In solution, when two molecules collide but do not react they bounce off ...
... orientation and the collision will be non-productive. Thus, if both molecules first bind to an enzyme active site, and do so in such a way that their reactive portions are juxtaposed, the probability of a reaction is optimized. In solution, when two molecules collide but do not react they bounce off ...
Poster
... measured using SwissPDB Viewer. Chemdraw was used to draw the pharmacophore model and the 2D representations of our ligands. ...
... measured using SwissPDB Viewer. Chemdraw was used to draw the pharmacophore model and the 2D representations of our ligands. ...
supp - Springer Static Content Server
... HnRNP F is an RNA binding protein belonging to the HnRNP H protein family that contains four highly homologous members, namely HnRNP H, HnRNP H’, HnRNP F, and HnRNP 2H9. These proteins contain two (2H9) or three (H, H’, and F) RNA recognition motifs (RRM) and two glycine rich auxiliary domains (Hono ...
... HnRNP F is an RNA binding protein belonging to the HnRNP H protein family that contains four highly homologous members, namely HnRNP H, HnRNP H’, HnRNP F, and HnRNP 2H9. These proteins contain two (2H9) or three (H, H’, and F) RNA recognition motifs (RRM) and two glycine rich auxiliary domains (Hono ...
Aphelenchoides besseyi
... these metabolites from their hosts and the environment through the lipid binding proteins (LBPs) [4,5]. Nematodes have been found to produce a series of unusual proteins that exhibit high affinity binding to lipid, and these proteins can be divided into two different classes according to their molec ...
... these metabolites from their hosts and the environment through the lipid binding proteins (LBPs) [4,5]. Nematodes have been found to produce a series of unusual proteins that exhibit high affinity binding to lipid, and these proteins can be divided into two different classes according to their molec ...
Partial characterization of human complement factor H by protein
... for C3 turnover is regulated in a number of ways, and the principal route is via proteolytic destruction ofC3b. C3b is destroyed by the complement protease factor I. This reaction requires a protein cofactor, which forms a complex with C3b. Only C3b in the C3b-cofactor complex is cleaved by factor I ...
... for C3 turnover is regulated in a number of ways, and the principal route is via proteolytic destruction ofC3b. C3b is destroyed by the complement protease factor I. This reaction requires a protein cofactor, which forms a complex with C3b. Only C3b in the C3b-cofactor complex is cleaved by factor I ...
Transport Between the Endoplasmic Reticulum and Golgi Apparatus
... is in close proximity to Sar1p, which may cause rapid GTP hydrolysis and increase the instability of the vesicular structure. The release of Sar1p from the membrane causes the dissociation of the coat proteins, leaving a membranous vesicle that can fuse with the Golgi apparatus and release its conte ...
... is in close proximity to Sar1p, which may cause rapid GTP hydrolysis and increase the instability of the vesicular structure. The release of Sar1p from the membrane causes the dissociation of the coat proteins, leaving a membranous vesicle that can fuse with the Golgi apparatus and release its conte ...
The Heat-Shock Proteins
... remarkable that this sequence is also found at thc carboxy-tcrminus of the eukaryotic hsp70proteins. In other respects these proteins have little or no homology. The sequence must serve some important purpose, but what the purpose may be is presently unknown. In virtually all cells, proteins of the ...
... remarkable that this sequence is also found at thc carboxy-tcrminus of the eukaryotic hsp70proteins. In other respects these proteins have little or no homology. The sequence must serve some important purpose, but what the purpose may be is presently unknown. In virtually all cells, proteins of the ...
NH 2
... Describe the formation of peptide bonds Describe the four levels of protein organization with reference to primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins using haemoglobin as example Explain how structure of protein determines its function by looking at examples Differentiate betw ...
... Describe the formation of peptide bonds Describe the four levels of protein organization with reference to primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins using haemoglobin as example Explain how structure of protein determines its function by looking at examples Differentiate betw ...
... 1A. (4 pts) True & false (circle the correct answer). T or F: All 20 amino acids contain at least one chiral center. [Glycine has no chiral center] T or F: The peptide bond is planar and usually cis. [Planer and trans] T or F:Non-polar residues are found in the core of globular proteins due to van d ...
updated ppt slides - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... at a time; – Mass spectrometry: Generate small fragments and measure the M/Z ratio. ...
... at a time; – Mass spectrometry: Generate small fragments and measure the M/Z ratio. ...
Gene Section NMT1 (N-myristoyltransferase 1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Gallbladder cancer tends to spread to the liver or small intestine and also spreads to lymph nodes through the lymphatic system in the region of the liver resulting in involvement of other lymph nodes and organs. The treatments available are not particularly effective, unless the tumor is very small ...
... Gallbladder cancer tends to spread to the liver or small intestine and also spreads to lymph nodes through the lymphatic system in the region of the liver resulting in involvement of other lymph nodes and organs. The treatments available are not particularly effective, unless the tumor is very small ...
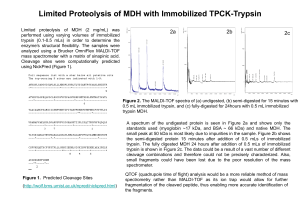
Limited Proteolysis
... 0.5 mL immobilized trypsin, and (c) fully-digested for 24hours with 0.5 mL immobilized trypsin MDH. A spectrum of the undigested protein is seen in Figure 2a and shows only the standards used (myoglobin ~17 kDa, and BSA ~ 66 kDa) and native MDH. The small peak at 50 kDa is most likely due to impurit ...
... 0.5 mL immobilized trypsin, and (c) fully-digested for 24hours with 0.5 mL immobilized trypsin MDH. A spectrum of the undigested protein is seen in Figure 2a and shows only the standards used (myoglobin ~17 kDa, and BSA ~ 66 kDa) and native MDH. The small peak at 50 kDa is most likely due to impurit ...
Trends in Sports Drink Formulations
... saturation of the glucose transport mechanism. Once this metabolic pathway becomes saturated, the body will not absorb any more glucose for the time being. However, this study from U.K. researchers found that combining more than one sugar (in this case glucose and fructose) allowed for greater carbo ...
... saturation of the glucose transport mechanism. Once this metabolic pathway becomes saturated, the body will not absorb any more glucose for the time being. However, this study from U.K. researchers found that combining more than one sugar (in this case glucose and fructose) allowed for greater carbo ...
pO 2
... of, relating to, undergoing, or being a change in the shape and activity of a protein (as an enzyme) that results from combination with another substance at a point other than the chemically active site ...
... of, relating to, undergoing, or being a change in the shape and activity of a protein (as an enzyme) that results from combination with another substance at a point other than the chemically active site ...
Simulation of Enzyme Reaction - diss.fu
... The electrostatic models used today consider these effects, however sometimes only implicitly. In standard empirical force fields used for Molecular Dynamics or Monte Carlo simulations all atoms of a molecular system are represented in detail. All electrostatic interactions between the corresponding ...
... The electrostatic models used today consider these effects, however sometimes only implicitly. In standard empirical force fields used for Molecular Dynamics or Monte Carlo simulations all atoms of a molecular system are represented in detail. All electrostatic interactions between the corresponding ...
Lecture 1 - Doolittle Lab
... In the 1950’s several laboratories were trying to figure out how proteins were made from a biochemical standpoint. The standard biochemical strategy is to purify components and then re-assemble them in the test tube (“in vitro”) to see if they will react to give the expected product. In this case t ...
... In the 1950’s several laboratories were trying to figure out how proteins were made from a biochemical standpoint. The standard biochemical strategy is to purify components and then re-assemble them in the test tube (“in vitro”) to see if they will react to give the expected product. In this case t ...
How Translocons Select Transmembrane Helices
... Membrane protein assembly. (a) The machinery of membrane protein assembly. (Step 1) A ribosome translating the mRNA of a protein targeted for secretion across or insertion into membranes and a signal of a recognition particle (SRP), which is a GTPase. The structures of ribosomes are reviewed in Refe ...
... Membrane protein assembly. (a) The machinery of membrane protein assembly. (Step 1) A ribosome translating the mRNA of a protein targeted for secretion across or insertion into membranes and a signal of a recognition particle (SRP), which is a GTPase. The structures of ribosomes are reviewed in Refe ...
Protein–protein interaction

Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) refer to physical contacts established between two or more proteins as a result of biochemical events and/or electrostatic forces.In fact, proteins are vital macromolecules, at both cellular and systemic levels, but they rarely act alone. Diverse essential molecular processes within a cell are carried out by molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein components organized by their PPIs. Indeed, these interactions are at the core of the entire interactomics system of any living cell and so, unsurprisingly, aberrant PPIs are on the basis of multiple diseases, such as Creutzfeld-Jacob, Alzheimer's disease, and cancer.PPIs have been studied from different perspectives: biochemistry, quantum chemistry, molecular dynamics, signal transduction, among others. All this information enables the creation of large protein interaction networks – similar to metabolic or genetic/epigenetic networks – that empower the current knowledge on biochemical cascades and disease pathogenesis, as well as provide putative new therapeutic targets.