Unit 10 complete 2016-2017
... Moles of A to Moles of B Work the following out on a separate sheet of paper. 1. Hydrogen and oxygen react under certain conditions to product water. a. How many moles of hydrogen would be needed to produce 5.0 moles of water? b. How many moles of oxygen would be needed to produce 5.0 moles of water ...
... Moles of A to Moles of B Work the following out on a separate sheet of paper. 1. Hydrogen and oxygen react under certain conditions to product water. a. How many moles of hydrogen would be needed to produce 5.0 moles of water? b. How many moles of oxygen would be needed to produce 5.0 moles of water ...
teaching and learning materials - UNESDOC
... Since all the chemicals used in the ester preparations are colourless, it is a good idea to advise students to label their propettes prior to the experiment to prevent these from becoming muddled. Two or three students can share one propette of alcohol/acid per ester made because only three or four ...
... Since all the chemicals used in the ester preparations are colourless, it is a good idea to advise students to label their propettes prior to the experiment to prevent these from becoming muddled. Two or three students can share one propette of alcohol/acid per ester made because only three or four ...
C H A P T E R
... compounds are white solids that dissolve in water to form solutions that conduct electricity. Similarly, the elements fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine can combine with sodium in a 1:1 ratio to form NaF, NaCl, NaBr, and NaI. These compounds are also white solids that can dissolve in water to f ...
... compounds are white solids that dissolve in water to form solutions that conduct electricity. Similarly, the elements fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine can combine with sodium in a 1:1 ratio to form NaF, NaCl, NaBr, and NaI. These compounds are also white solids that can dissolve in water to f ...
Mole-Volume Conversion Assignment
... atoms molar mass. We do this for each atom in the compound. o We then take the lowest number we get and divide each other number by this number and round our answers to the 1’s place. This will give us the lowest ratio that these elements combine in. ...
... atoms molar mass. We do this for each atom in the compound. o We then take the lowest number we get and divide each other number by this number and round our answers to the 1’s place. This will give us the lowest ratio that these elements combine in. ...
Stoichiometry Notes
... A) How many grams of carbon are found in 33 grams of CO2? B) How many grams of hydrogen are found in 36 grams of H2O? C) If a sample that contains only C, H, & O is originally 30 grams and is found to have 12 grams of carbon and 2 grams of hydrogen. How many grams are oxygen and what is the e ...
... A) How many grams of carbon are found in 33 grams of CO2? B) How many grams of hydrogen are found in 36 grams of H2O? C) If a sample that contains only C, H, & O is originally 30 grams and is found to have 12 grams of carbon and 2 grams of hydrogen. How many grams are oxygen and what is the e ...
organic problems - St. Olaf College
... 25 Which of the following molecular formulas is reasonable for a stable compound? A) C8H14O2Cl B) C6H14Br2 C) C7H10NF D) C30H54N2Cl 26 What formal charges are present in the molecule C6H5C≡N-O? ( all heavy atoms have a valence shell octet, and C6H5- is a phenyl group) A) N is -1 and C is +1 B) N is ...
... 25 Which of the following molecular formulas is reasonable for a stable compound? A) C8H14O2Cl B) C6H14Br2 C) C7H10NF D) C30H54N2Cl 26 What formal charges are present in the molecule C6H5C≡N-O? ( all heavy atoms have a valence shell octet, and C6H5- is a phenyl group) A) N is -1 and C is +1 B) N is ...
hydrogen storage
... Chemical oxidation of metals with water and liberation of hydrogen, not directly reversible? ...
... Chemical oxidation of metals with water and liberation of hydrogen, not directly reversible? ...
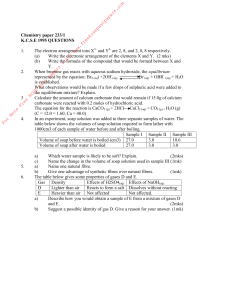
kcse chemistry questions
... Write the formula of the compound that would be formed between X and Y. When bromine gas reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide, the equilibrium represented by the equation: Br2 (aq) +2OH-(aq) Br-(aq) + OBR- (aq) + H2O is established. What observations would be made if a few drops of sulphuric acid we ...
... Write the formula of the compound that would be formed between X and Y. When bromine gas reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide, the equilibrium represented by the equation: Br2 (aq) +2OH-(aq) Br-(aq) + OBR- (aq) + H2O is established. What observations would be made if a few drops of sulphuric acid we ...
The Periodic Table
... chemical properties. However, even with the use of placeholders, there were some elements that did not quite fit the pattern. For example, Mendeleev listed tellurium before iodine even though its atomic mass is higher, because he knew that the properties of iodine were much more similar to those of ...
... chemical properties. However, even with the use of placeholders, there were some elements that did not quite fit the pattern. For example, Mendeleev listed tellurium before iodine even though its atomic mass is higher, because he knew that the properties of iodine were much more similar to those of ...
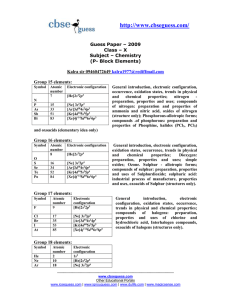
Chapter 5 Section 2 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table
... • beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium • Group 2 metals are less reactive than the alkali metals, but are still too reactive to be found in nature in pure form. ...
... • beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium • Group 2 metals are less reactive than the alkali metals, but are still too reactive to be found in nature in pure form. ...
Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry
... would of course be different. All abundances over 0.1% have been included. The figures reveal that some 99% of the matter in the world around us is made up of as few as 14 elements. Note, however, that many of the remaining elements in the biosphere, despite their low concentration, are essential to ...
... would of course be different. All abundances over 0.1% have been included. The figures reveal that some 99% of the matter in the world around us is made up of as few as 14 elements. Note, however, that many of the remaining elements in the biosphere, despite their low concentration, are essential to ...
Chapter 3 Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions
... 29. The molecular formula of aspirin is C9H8O4. How many aspirin molecules are present in one 500-milligram tablet? A. B. C. D. E. ...
... 29. The molecular formula of aspirin is C9H8O4. How many aspirin molecules are present in one 500-milligram tablet? A. B. C. D. E. ...
enjoy chemistry
... Ans: Both are SP3 hybridised. In PH4+ all the four orbitals are bonded whereas in PH3 there is a lone pair of electrons on P, which is responsible for lone pair-bond pair repulsion in PH3 reducing the bond angle to less than 109° 28′. (xxviii) NO2 dimerises to form N2O4 .Ans:NO2 contains odd number ...
... Ans: Both are SP3 hybridised. In PH4+ all the four orbitals are bonded whereas in PH3 there is a lone pair of electrons on P, which is responsible for lone pair-bond pair repulsion in PH3 reducing the bond angle to less than 109° 28′. (xxviii) NO2 dimerises to form N2O4 .Ans:NO2 contains odd number ...
AVOGADRO EXAMS 1991 - 2002 PRACTICE BOOKLET
... 35. Which solution will have the highest vapor pressure at 25°C? (a) 0.010 M NaCl (b) 0.10 M HBr (c) 0.050M Ca(NO3)2 (d) 0.10 M Na2CO3 (e) 0.020 M CuSO 4 36. What chemical(s) result(s) when NH3(g) reacts with HCl (g)? (a) NH2Cl(g) (b) NH 4Cl(s) (c) NH4OH (aq) and HCl(g) (d) NCl3(g) and H2(g) (e) NH2 ...
... 35. Which solution will have the highest vapor pressure at 25°C? (a) 0.010 M NaCl (b) 0.10 M HBr (c) 0.050M Ca(NO3)2 (d) 0.10 M Na2CO3 (e) 0.020 M CuSO 4 36. What chemical(s) result(s) when NH3(g) reacts with HCl (g)? (a) NH2Cl(g) (b) NH 4Cl(s) (c) NH4OH (aq) and HCl(g) (d) NCl3(g) and H2(g) (e) NH2 ...
Stoichiometry
... Furthermore, instead of using cups and teaspoons, we use moles Lastly, instead of eggs, butter, sugar, etc. we use chemical compounds as ingredients ...
... Furthermore, instead of using cups and teaspoons, we use moles Lastly, instead of eggs, butter, sugar, etc. we use chemical compounds as ingredients ...
Atomic Structure
... Bond order is a concept in the molecular orbital theory. It depends on the number of electrons in the bonding and antibonding orbitals. Which of the following statements is true about it? The bond order (a) Cannot be a negative quantity (b) Always has an integral value (c) Can assume any value, posi ...
... Bond order is a concept in the molecular orbital theory. It depends on the number of electrons in the bonding and antibonding orbitals. Which of the following statements is true about it? The bond order (a) Cannot be a negative quantity (b) Always has an integral value (c) Can assume any value, posi ...
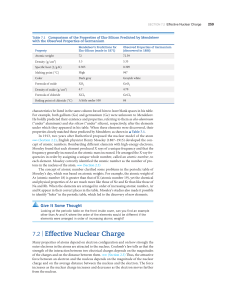
7.2 | Effective Nuclear Charge
... recognize as a chemical bond. We discuss bonding in Chapters 8 and 9. For now, we need to realize that two bonded atoms are closer together than they would be in a nonbonding collision where the atoms ricochet apart. We can therefore define an atomic radius based on the distance between the nuclei w ...
... recognize as a chemical bond. We discuss bonding in Chapters 8 and 9. For now, we need to realize that two bonded atoms are closer together than they would be in a nonbonding collision where the atoms ricochet apart. We can therefore define an atomic radius based on the distance between the nuclei w ...
Naming Compounds - Kowenscience.com
... the symbol for oxygen, but • take the first part of the element name (the root) and add –ide to get the name oxide. • Since chromium can have more than one charge, a Roman numeral must be used to identify that charge. • There are two oxygen ions each with a 2– charge, giving an overall charge of –4. ...
... the symbol for oxygen, but • take the first part of the element name (the root) and add –ide to get the name oxide. • Since chromium can have more than one charge, a Roman numeral must be used to identify that charge. • There are two oxygen ions each with a 2– charge, giving an overall charge of –4. ...
Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry
... would of course be different. All abundances over 0.1% have been included. The figures reveal that some 99% of the matter in the world around us is made up of as few as 14 elements. Note, however, that many of the remaining elements in the biosphere, despite their low concentration, are essential to ...
... would of course be different. All abundances over 0.1% have been included. The figures reveal that some 99% of the matter in the world around us is made up of as few as 14 elements. Note, however, that many of the remaining elements in the biosphere, despite their low concentration, are essential to ...
Chemistry 133 Problem Set Introduction
... 1.81 Antifreeze contains the compound ethylene glycol. This compound not only lowers the freezing point of water but also increases the boiling point of water. The density of ethylene glycol is 9.35 lb/gal, and the density of water is 62.5 lb/ft3. (a) Is the density of water greater than the density ...
... 1.81 Antifreeze contains the compound ethylene glycol. This compound not only lowers the freezing point of water but also increases the boiling point of water. The density of ethylene glycol is 9.35 lb/gal, and the density of water is 62.5 lb/ft3. (a) Is the density of water greater than the density ...
Stoichiometry
... formed. The reaction will stop when all of the limiting reactant is consumed. Example: I want to assemble a gadget that requires one nut, one bolt and two washers for every hole. I have in my garage a bucket filled with 12 washers, 4 bolts and five nuts. What is the LIMITING SMALL METAL ...
... formed. The reaction will stop when all of the limiting reactant is consumed. Example: I want to assemble a gadget that requires one nut, one bolt and two washers for every hole. I have in my garage a bucket filled with 12 washers, 4 bolts and five nuts. What is the LIMITING SMALL METAL ...
Unit 06: Periodic Trends - Lincoln Park High School
... have similar chemical properties are in the same ________________. The elements in Groups 1A through 7A are called the ________________. The ________________ make up Group 0. The elements in Groups 2A and 3A are interrupted in periods 4 and 5 by the ________________ and in periods 6 and 7 by the ...
... have similar chemical properties are in the same ________________. The elements in Groups 1A through 7A are called the ________________. The ________________ make up Group 0. The elements in Groups 2A and 3A are interrupted in periods 4 and 5 by the ________________ and in periods 6 and 7 by the ...
Benzylamine reacts with nitrous acid to form unstable
... 3. How is phenyl hydrazine prepared from aniline? 4. What is the IUPAC name of a tertiary amine containing one methyl, one ethyl and one n-propyl group? 5. Explain why silver chloride is soluble in aqueous solution of methylamine? 6. Write the IUPAC name of C6H5N+(CH3)3Br ? 7. Primary amines have hi ...
... 3. How is phenyl hydrazine prepared from aniline? 4. What is the IUPAC name of a tertiary amine containing one methyl, one ethyl and one n-propyl group? 5. Explain why silver chloride is soluble in aqueous solution of methylamine? 6. Write the IUPAC name of C6H5N+(CH3)3Br ? 7. Primary amines have hi ...