Chapter 9 Stoichiometry
... How many moles of carbon dioxide, CO2, can be made from Fe2O3 by the use of 1.90 moles of carbon monoxide, CO, in the following reaction? Fe2O3 + 3 CO -----------> 2 Fe + 3 CO2 ...
... How many moles of carbon dioxide, CO2, can be made from Fe2O3 by the use of 1.90 moles of carbon monoxide, CO, in the following reaction? Fe2O3 + 3 CO -----------> 2 Fe + 3 CO2 ...
Chemistry - Department of Education and Skills
... provision of these subjects has improved, especially in girls’ schools. However, the most recent analysis of provision indicates the persistence of the problem. Although provision for girls is now best in single-sex schools, girls’ secondary schools are less likely to provide Physics to their pupils ...
... provision of these subjects has improved, especially in girls’ schools. However, the most recent analysis of provision indicates the persistence of the problem. Although provision for girls is now best in single-sex schools, girls’ secondary schools are less likely to provide Physics to their pupils ...
Chemistry I Chapter 5 Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the
... One-half the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms that are bonded together is called the a. atomic radius. c. atomic volume. b. atomic diameter. d. electron cloud. The element that has the greatest electronegativity is a. oxygen. c. chlorine. b. sodium. d. fluorine. In a row in the periodi ...
... One-half the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms that are bonded together is called the a. atomic radius. c. atomic volume. b. atomic diameter. d. electron cloud. The element that has the greatest electronegativity is a. oxygen. c. chlorine. b. sodium. d. fluorine. In a row in the periodi ...
Chemistry (Revised)
... 3 Check that the answer sheet you have been given has your name, date of birth, SCN (Scottish Candidate Number) and Centre Name printed on it. Do not change any of these details. 4 If any of this information is wrong, tell the Invigilator immediately. 5 If this information is correct, print ...
... 3 Check that the answer sheet you have been given has your name, date of birth, SCN (Scottish Candidate Number) and Centre Name printed on it. Do not change any of these details. 4 If any of this information is wrong, tell the Invigilator immediately. 5 If this information is correct, print ...
2013 - SQA
... 3 Check that the answer sheet you have been given has your name, date of birth, SCN (Scottish Candidate Number) and Centre Name printed on it. Do not change any of these details. 4 If any of this information is wrong, tell the Invigilator immediately. 5 If this information is correct, print ...
... 3 Check that the answer sheet you have been given has your name, date of birth, SCN (Scottish Candidate Number) and Centre Name printed on it. Do not change any of these details. 4 If any of this information is wrong, tell the Invigilator immediately. 5 If this information is correct, print ...
Amines - ncert
... Aliphatic and aromatic primary and secondary amines react with acid chlorides, anhydrides and esters by nucleophilic substitution reaction. This reaction is known as acylation. You can consider this reaction as the replacement of hydrogen atom of –NH2 or >N–H group by the acyl group. The products ob ...
... Aliphatic and aromatic primary and secondary amines react with acid chlorides, anhydrides and esters by nucleophilic substitution reaction. This reaction is known as acylation. You can consider this reaction as the replacement of hydrogen atom of –NH2 or >N–H group by the acyl group. The products ob ...
Cookies and Chemistry…Huh!?!?
... How many moles of reactants are needed? What if we wanted 4 moles of water? What if we had 3 moles of oxygen, how much hydrogen would we need to react and how much water would we get? What if we had 50 moles of hydrogen, how much oxygen would we need and how much water produced? ...
... How many moles of reactants are needed? What if we wanted 4 moles of water? What if we had 3 moles of oxygen, how much hydrogen would we need to react and how much water would we get? What if we had 50 moles of hydrogen, how much oxygen would we need and how much water produced? ...
Chapter+12
... How many moles of reactants are needed? What if we wanted 4 moles of water? What if we had 3 moles of oxygen, how much hydrogen would we need to react and how much water would we get? What if we had 50 moles of hydrogen, how much oxygen would we need and how much water produced? ...
... How many moles of reactants are needed? What if we wanted 4 moles of water? What if we had 3 moles of oxygen, how much hydrogen would we need to react and how much water would we get? What if we had 50 moles of hydrogen, how much oxygen would we need and how much water produced? ...
Supplementary Exercise 1B Topic 5
... In the electrochemical series, the position of calcium is higher than that of sodium. The order is different from that in the reactivity series. This is because calcium atom loses electrons more readily in cell reactions than in reaction with air, water and dilute acids. ...
... In the electrochemical series, the position of calcium is higher than that of sodium. The order is different from that in the reactivity series. This is because calcium atom loses electrons more readily in cell reactions than in reaction with air, water and dilute acids. ...
Topical KCSE Mock-Chemistry Answers(15 Schools)
... b) NaOH(s) absorbs water from the air and forms a solution. It is a deliquescent substance. 1 Anhydrous CuSO4 absorbs water from air to form hydrated Copper (II) sulphate which is blue but no solution is formed 1 it is hygroscopic a)i)Ethanol, acetone (any organic solvent) ii) Its most soluble in ...
... b) NaOH(s) absorbs water from the air and forms a solution. It is a deliquescent substance. 1 Anhydrous CuSO4 absorbs water from air to form hydrated Copper (II) sulphate which is blue but no solution is formed 1 it is hygroscopic a)i)Ethanol, acetone (any organic solvent) ii) Its most soluble in ...
Std 10th, Science and Technology, Maharashtra Board, English
... In addition to this, solved and practice problems are included which not only aim at covering the topic but also make students ready to face the competition. The topic-wise classified “question and answer” format of this book helps students in easy comprehension. Numerical problems included at the e ...
... In addition to this, solved and practice problems are included which not only aim at covering the topic but also make students ready to face the competition. The topic-wise classified “question and answer” format of this book helps students in easy comprehension. Numerical problems included at the e ...
Science - ExamResults.net
... In addition to this, solved and practice problems are included which not only aim at covering the topic but also make students ready to face the competition. The topic-wise classified “question and answer” format of this book helps students in easy comprehension. Numerical problems included at the e ...
... In addition to this, solved and practice problems are included which not only aim at covering the topic but also make students ready to face the competition. The topic-wise classified “question and answer” format of this book helps students in easy comprehension. Numerical problems included at the e ...
F:\Users\Steven\Documents\Chemistry\CHEM120\Problem Set
... Copper is made up of two isotopes 63Cu and 65Cu and they weigh 62.9296 g and 64.9278g respectively. If the average natural abundance mass of copper is 63.5460 g, calculate the percentage of 63Cu and 65Cu in naturally abundant copper. ...
... Copper is made up of two isotopes 63Cu and 65Cu and they weigh 62.9296 g and 64.9278g respectively. If the average natural abundance mass of copper is 63.5460 g, calculate the percentage of 63Cu and 65Cu in naturally abundant copper. ...
A Dictionary of the New Chymical Nomenclature
... Sulphureous acid Volatile sulphureous acid Phlogisticated vitriolic acid Spirit of sulphur ...
... Sulphureous acid Volatile sulphureous acid Phlogisticated vitriolic acid Spirit of sulphur ...
Classification and Periodic Properties of Elements
... could be predicted with a fair accuracy. For example, both gallium and germanium were not discovered at the time when Mendeleev proposed his periodic table. Mendeleevnamed these elements as Eka-Aluminium and Eka·Silicon respectively. Later on, when these elements were discovered, Mendeleev's predict ...
... could be predicted with a fair accuracy. For example, both gallium and germanium were not discovered at the time when Mendeleev proposed his periodic table. Mendeleevnamed these elements as Eka-Aluminium and Eka·Silicon respectively. Later on, when these elements were discovered, Mendeleev's predict ...
General and Inorganic Chemistry I.
... mixture of one or more of four ”roots”. The four elements were earth, water, air and fire. In 1661 Boyle defined an element as a substance that cannot be broken down into a simpler substance by a chemical reaction. Lavoisier published a list of elements in 1789, or substances that could not be broke ...
... mixture of one or more of four ”roots”. The four elements were earth, water, air and fire. In 1661 Boyle defined an element as a substance that cannot be broken down into a simpler substance by a chemical reaction. Lavoisier published a list of elements in 1789, or substances that could not be broke ...
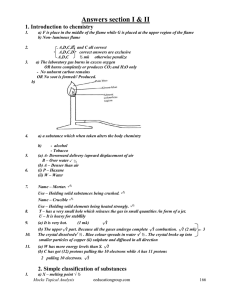
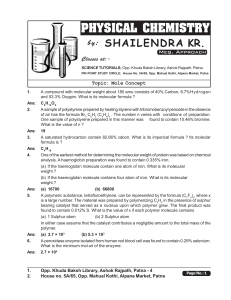
Mole Concept - Shailendra Kumar Chemistry
... (c) 200 ml of 3.0 M NaCl is added to 300 ml of 4.0 M NaCl. (d) 200 ml of 2.0 M BaCl2 is added to 400 ml of 3.0 M BaCl2 and 400 ml of water. (e) 300 ml of 3.0 M NaCl is added to 200 ml of 4.0 M BaCl2. (f) 400 ml of 2.0 M HCl is added to 150 ml of 4.0 M NaOH. (g) 100 ml of 2.0 M HCl and 200 ml of 1.5 ...
... (c) 200 ml of 3.0 M NaCl is added to 300 ml of 4.0 M NaCl. (d) 200 ml of 2.0 M BaCl2 is added to 400 ml of 3.0 M BaCl2 and 400 ml of water. (e) 300 ml of 3.0 M NaCl is added to 200 ml of 4.0 M BaCl2. (f) 400 ml of 2.0 M HCl is added to 150 ml of 4.0 M NaOH. (g) 100 ml of 2.0 M HCl and 200 ml of 1.5 ...
File
... N2O3, least common of nitrogen oxides, a blue liquid that readily dissociates into NO(g) and NO2(g); NO2: another odd electron species, dimerizes to form N2O4, plays a role in smog production; HNO3: important industrial chemical, used to form nitrogen-based explosives, strong acid and a very strong ...
... N2O3, least common of nitrogen oxides, a blue liquid that readily dissociates into NO(g) and NO2(g); NO2: another odd electron species, dimerizes to form N2O4, plays a role in smog production; HNO3: important industrial chemical, used to form nitrogen-based explosives, strong acid and a very strong ...
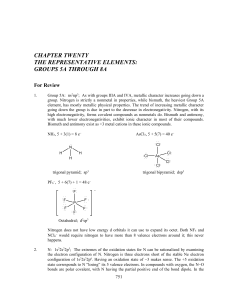
classification of elements and periodicity in properties
... of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), the groups are numbered from 1 to 18 replacing the older notation of groups IA … VIIA, VIII, IB … VIIB and 0. There are altogether seven periods. The period number corresponds to the highest principal quantum number (n) of the elements in the period. The first ...
... of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), the groups are numbered from 1 to 18 replacing the older notation of groups IA … VIIA, VIII, IB … VIIB and 0. There are altogether seven periods. The period number corresponds to the highest principal quantum number (n) of the elements in the period. The first ...
Mole Concept
... coefficients are conversion factors between different species. We define 1 mol of this reaction as the process of mixing a mol of A with b mol of B to form c mol C and d mol D. Thus, if we have Y mol of A, we can convert to mol of reaction by Y x (1 mol reaction / a mol A) = Y/a. Thus, the divisions ...
... coefficients are conversion factors between different species. We define 1 mol of this reaction as the process of mixing a mol of A with b mol of B to form c mol C and d mol D. Thus, if we have Y mol of A, we can convert to mol of reaction by Y x (1 mol reaction / a mol A) = Y/a. Thus, the divisions ...
Periodic Classification of Elements
... properties occurred periodically. In1869, he stated this observation in the following form which is known as Mendeleev’s Periodic Law. A periodic function is the one which repeats itself after a certain interval. Thus, according to the periodic law the chemical and physical properties of elements re ...
... properties occurred periodically. In1869, he stated this observation in the following form which is known as Mendeleev’s Periodic Law. A periodic function is the one which repeats itself after a certain interval. Thus, according to the periodic law the chemical and physical properties of elements re ...
Periodic Table
... table is useful as it is possible to predict the properties of an individual element from its position. -l'he Modern Periodic table is a table of all the chemical elements, in order of their atomic numbers so that elements with similar properties arc close to each other. The Modern Periodic ...
... table is useful as it is possible to predict the properties of an individual element from its position. -l'he Modern Periodic table is a table of all the chemical elements, in order of their atomic numbers so that elements with similar properties arc close to each other. The Modern Periodic ...
LaBrake, Fundamentals Diagnostic Questions
... 17. All of the following are considered subatomic particles, except: a) gamma rays (correct) b) electrons c) protons d) neutrons e) positrons 18. All of the following are statements from Dalton’s atomic hypothesis, except: a) All the atoms of a given element are identical. b) The atoms of different ...
... 17. All of the following are considered subatomic particles, except: a) gamma rays (correct) b) electrons c) protons d) neutrons e) positrons 18. All of the following are statements from Dalton’s atomic hypothesis, except: a) All the atoms of a given element are identical. b) The atoms of different ...
classification of elements and periodicity in properties
... group 1 elements (hydrogen, alkali metals). Elements with two electrons in their outer shells have the configuration of ns2. They belong to group 2 elements (alkaline earth metals). Elements with three electrons (two in ‘s’ orbital and one in ‘p’ orbital) have the configuration of ns2 np2. They belo ...
... group 1 elements (hydrogen, alkali metals). Elements with two electrons in their outer shells have the configuration of ns2. They belong to group 2 elements (alkaline earth metals). Elements with three electrons (two in ‘s’ orbital and one in ‘p’ orbital) have the configuration of ns2 np2. They belo ...
Chapter 3, Elements, Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table Ans
... The ion will be much smaller. In forming the ion, the atom loses all its outermost electrons. The net positive charge on the ion ensures that all the electrons in the ion are strongly attracted to the nucleus, keeping the ion small. Which group of elements has the highest ionization energies? Which ...
... The ion will be much smaller. In forming the ion, the atom loses all its outermost electrons. The net positive charge on the ion ensures that all the electrons in the ion are strongly attracted to the nucleus, keeping the ion small. Which group of elements has the highest ionization energies? Which ...