Serious `XM (That`s W2XM) presents
... Operation of the game is almost intuitive, and you can make up your own rules. Each numeric point value on either game board is a hyperlink which reveals a question. Advancing the game one slide past the question (by clicking the screen) displays the answer. “Back” on the answer slide returns you t ...
... Operation of the game is almost intuitive, and you can make up your own rules. Each numeric point value on either game board is a hyperlink which reveals a question. Advancing the game one slide past the question (by clicking the screen) displays the answer. “Back” on the answer slide returns you t ...
1 ES 6216 – Isotope Geochemistry Problem Set 2 Distributed 9/11
... also radioactive, has a half-life of one month. Because the daughter is not gaseous, it adsorbs onto aerosol particles and is removed by physical processes, mainly precipitation. If the activity ratio for these two isotopes (daughter/parent) in the atmosphere is observed to be 0.3 in steady state, w ...
... also radioactive, has a half-life of one month. Because the daughter is not gaseous, it adsorbs onto aerosol particles and is removed by physical processes, mainly precipitation. If the activity ratio for these two isotopes (daughter/parent) in the atmosphere is observed to be 0.3 in steady state, w ...
Signals, Power and RMS - RS-MET
... we go about evaluating the integral in equation 2? The sole function of the integration (and division by the integration interval afterwards) is to obtain a time averaged value. In the digital world, an average can simply be calculated by summing all values in the interval of interest and dividing b ...
... we go about evaluating the integral in equation 2? The sole function of the integration (and division by the integration interval afterwards) is to obtain a time averaged value. In the digital world, an average can simply be calculated by summing all values in the interval of interest and dividing b ...
net4
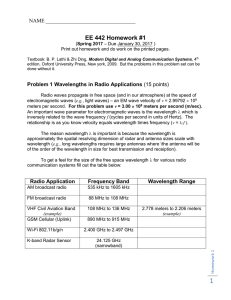
... • All communications systems have some amount of noise. • Even though noise cannot be eliminated, its effects can be minimized if the sources of the noise are understood. • There are many possible sources of noise: ...
... • All communications systems have some amount of noise. • Even though noise cannot be eliminated, its effects can be minimized if the sources of the noise are understood. • There are many possible sources of noise: ...
ELE 100 Electrical Principles Quiz 2 (5 points)
... ELE 100 Electrical Principles Quiz 2 (5 points) April 20, 2005 Name ________________________ ...
... ELE 100 Electrical Principles Quiz 2 (5 points) April 20, 2005 Name ________________________ ...
Homework 3
... operated with a 10 k load resistance at 800 nm where the absorption coefficient α is 1000 cm-1. Which is longer, the carrier drift time or the RC time constant? Is carrier diffusion time important for this device? A transmission system sends signals at 200 kb/s. During the process, fluctuation nois ...
... operated with a 10 k load resistance at 800 nm where the absorption coefficient α is 1000 cm-1. Which is longer, the carrier drift time or the RC time constant? Is carrier diffusion time important for this device? A transmission system sends signals at 200 kb/s. During the process, fluctuation nois ...
PDF (acrobat)
... This is the ratio Pc /(Pn / ∆f ) – where Pc is the carrier power, Pn the noise power, ∆f the corresponding frequency bandwidth. This ratio has a dimension of frequency, it cannot be expressed without caution in terms of decibels, for power is not linked with frequency on a well-defined basis. This r ...
... This is the ratio Pc /(Pn / ∆f ) – where Pc is the carrier power, Pn the noise power, ∆f the corresponding frequency bandwidth. This ratio has a dimension of frequency, it cannot be expressed without caution in terms of decibels, for power is not linked with frequency on a well-defined basis. This r ...
Midterm Study Guide
... Bels = log (P2 / Pref) where Pref is the reference power and P2 is power we’re comparing to that reference. Decibels are literally a tenth of a Bel. So dB becomes 10 log (P2 / Pref) Where Pref is the reference power and P2 is the power you are comparing against that reference. Decibels are dimension ...
... Bels = log (P2 / Pref) where Pref is the reference power and P2 is power we’re comparing to that reference. Decibels are literally a tenth of a Bel. So dB becomes 10 log (P2 / Pref) Where Pref is the reference power and P2 is the power you are comparing against that reference. Decibels are dimension ...
Word - ITU
... Definition: Quotient of a power by another quantity, for example, an area, a bandwidth, a temperature. NOTE 1 – The quotient of a power by an area is called “power flux-density” (“puissance surfacique”) and is commonly expressed in “watts per square metre” (symbol: W · m–2 or W/m2). The quotient of ...
... Definition: Quotient of a power by another quantity, for example, an area, a bandwidth, a temperature. NOTE 1 – The quotient of a power by an area is called “power flux-density” (“puissance surfacique”) and is commonly expressed in “watts per square metre” (symbol: W · m–2 or W/m2). The quotient of ...
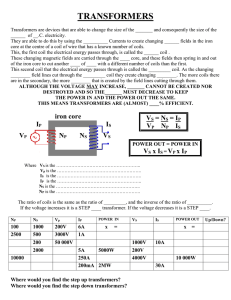
Transformer Turn Ratio IRT-101
... The Transformer Turn Ratio Meter IRT-101 is an instrument designed to accurately measure to the transformer turn ratio providing an easy reading on the panel. It can be used both in the field and laboratory, powered by 127VCA or 220VCA, to test power and distribution single-phase transformers such a ...
... The Transformer Turn Ratio Meter IRT-101 is an instrument designed to accurately measure to the transformer turn ratio providing an easy reading on the panel. It can be used both in the field and laboratory, powered by 127VCA or 220VCA, to test power and distribution single-phase transformers such a ...
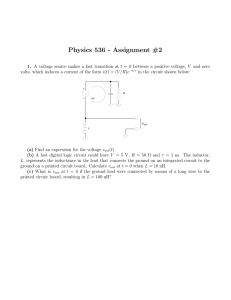
Physics 536 - Assignment #2
... (b) A fast digital logic circuit could have V = 5 V, R = 50 Ω and τ = 1 ns. The inductor, L, represents the inductance in the lead that connects the ground on an integrated circuit to the ground on a printed circuit board. Calculate vout at t = 0 when L = 10 nH. (c) What is vout at t = 0 if the grou ...
... (b) A fast digital logic circuit could have V = 5 V, R = 50 Ω and τ = 1 ns. The inductor, L, represents the inductance in the lead that connects the ground on an integrated circuit to the ground on a printed circuit board. Calculate vout at t = 0 when L = 10 nH. (c) What is vout at t = 0 if the grou ...