High-resolution Measurement of Refractive Index Based on Resonant Tunneling Effect
... propagation of electromagnetic waves and be utilized to quantize the continuous states of a suitably chosen quantum well material into a series of photonic bound states, much like the way potential barriers are used to quantize the electronic states of a semiconductor; while “ ( D)n ” may be thought ...
... propagation of electromagnetic waves and be utilized to quantize the continuous states of a suitably chosen quantum well material into a series of photonic bound states, much like the way potential barriers are used to quantize the electronic states of a semiconductor; while “ ( D)n ” may be thought ...
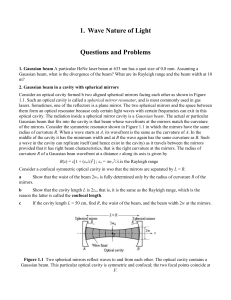
1. Wave Nature of Light
... GaAs becomes incident on AlGaAs. The refractive index of GaAs is 3.60, that of AlGaAs is 3.30. a Consider normal incidence. What are the reflection and transmission coefficients and the reflectance and transmittance? (From GaAs into AlGaAs) b What is the Brewster angle (the polarization angle p) an ...
... GaAs becomes incident on AlGaAs. The refractive index of GaAs is 3.60, that of AlGaAs is 3.30. a Consider normal incidence. What are the reflection and transmission coefficients and the reflectance and transmittance? (From GaAs into AlGaAs) b What is the Brewster angle (the polarization angle p) an ...
+ a
... increasingly recognizable ( from left to right in the upper row and then from the left to right in the lower row). What can you conclude about the behavior of light fiom the photograph demonstration. ( Note: The answer is quite simple and just use a ...
... increasingly recognizable ( from left to right in the upper row and then from the left to right in the lower row). What can you conclude about the behavior of light fiom the photograph demonstration. ( Note: The answer is quite simple and just use a ...
Total Internal Reflection and Critical Angle File
... pulsed lasers to encode information rather than fluctuating electric currents. •Unlike currents the signals do not interfere with each other •Less data loss occurs •They are immune from e.m. interference ...
... pulsed lasers to encode information rather than fluctuating electric currents. •Unlike currents the signals do not interfere with each other •Less data loss occurs •They are immune from e.m. interference ...
This Week`s Stuff: EM Waves Today – No Lecture – We will solve
... A laser beam shines along the surface of a block of transparent material. (See the figure .) Half of the beam goes straight to a detector, while the other half travels through the block and then hits the detector. The time delay between the arrival of the two light beams at the detector is 6.25 . W ...
... A laser beam shines along the surface of a block of transparent material. (See the figure .) Half of the beam goes straight to a detector, while the other half travels through the block and then hits the detector. The time delay between the arrival of the two light beams at the detector is 6.25 . W ...
The frequency dependence of polarization
... Figure 7. In a dispersive prism, material dispersion (a wavelength-dependent refractive index) causes different colors to refract at different angles, splitting white light into a rainbow. The difference in deviation of blue and red for a particular prism is the measure of dispersion. ...
... Figure 7. In a dispersive prism, material dispersion (a wavelength-dependent refractive index) causes different colors to refract at different angles, splitting white light into a rainbow. The difference in deviation of blue and red for a particular prism is the measure of dispersion. ...
File
... 3. A bi convex lens is made of glass of ref index 1.5.The radius of curvature of each face is 30 cm. Calculate the focal length of the lens in air. 4. Explain why white light is dispersed when passing through a prism? 5. For the same angle of incidence, the angles of refraction in three different me ...
... 3. A bi convex lens is made of glass of ref index 1.5.The radius of curvature of each face is 30 cm. Calculate the focal length of the lens in air. 4. Explain why white light is dispersed when passing through a prism? 5. For the same angle of incidence, the angles of refraction in three different me ...
Past Questions On Stationary Waves and Refractive Index
... A small loudspeaker emitting sound of constant frequency is positioned a short distance above a long glass tube containing water. When water is allowed to run slowly out of the tube, the intensity of the sound heard increases whenever the length l (shown in Figure 1) takes certain values. (a) Explai ...
... A small loudspeaker emitting sound of constant frequency is positioned a short distance above a long glass tube containing water. When water is allowed to run slowly out of the tube, the intensity of the sound heard increases whenever the length l (shown in Figure 1) takes certain values. (a) Explai ...
Abstract - University of Dayton
... in the liquid. These bubbles are characterized using the same probe and digital holography. An application of these bubbles to nanoparticle agglomeration and transport for drug delivery systems is proposed. Next, the use of recording materials such as photorefractive lithium niobate for implementing ...
... in the liquid. These bubbles are characterized using the same probe and digital holography. An application of these bubbles to nanoparticle agglomeration and transport for drug delivery systems is proposed. Next, the use of recording materials such as photorefractive lithium niobate for implementing ...
7.1.3 Optimizing Light Confinement and Gain in Laser Diodes
... function of the carrier emissions across some junction. We cannot expect that this is homogeneous everywhere in the active region; g is thus a function of (x,y,z), too. Light is reflected, diffracted, and absorbed according to the (complex) refractive index nr of the medium. This is foremost a funct ...
... function of the carrier emissions across some junction. We cannot expect that this is homogeneous everywhere in the active region; g is thus a function of (x,y,z), too. Light is reflected, diffracted, and absorbed according to the (complex) refractive index nr of the medium. This is foremost a funct ...
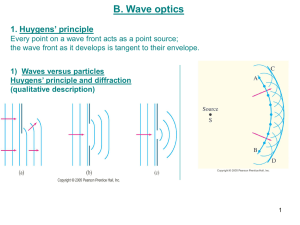
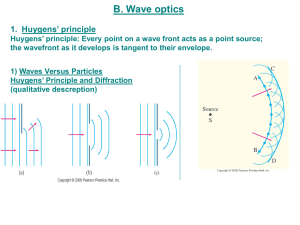
lecture20
... As the wavelets propagate from each point, they propagate more slowly in the medium of higher index of refraction. This leads to a bend in the wavefront and therefore in the ray. The frequency of the light does not change, but the wavelength does as it travels into a new medium. ...
... As the wavelets propagate from each point, they propagate more slowly in the medium of higher index of refraction. This leads to a bend in the wavefront and therefore in the ray. The frequency of the light does not change, but the wavelength does as it travels into a new medium. ...
Laser Vibrometer Measurements of Objects Immersed
... Vibrometry on submerged objects is fundamentally not different from vibrometry in air. In air, the object must be visible; in a fluid, the probing laser must also "see" the object and return enough light from the object to make an accurate measurement. In air, the index of refraction is close to one ...
... Vibrometry on submerged objects is fundamentally not different from vibrometry in air. In air, the object must be visible; in a fluid, the probing laser must also "see" the object and return enough light from the object to make an accurate measurement. In air, the index of refraction is close to one ...
Key Words: Reflection: Light returning from a
... Diffraction: The spreading of waves as they pass through a gap. Concave Lens: A lens that causes light rays to ...
... Diffraction: The spreading of waves as they pass through a gap. Concave Lens: A lens that causes light rays to ...
Waves Revision Booklet
... from one place to another. All electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum, and they all travel at the same speed in a vacuum - the speed of _____. The electromagnetic spectrum is a continuous range of _________. The types of radiation that occur in each part of the spectrum have different use ...
... from one place to another. All electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum, and they all travel at the same speed in a vacuum - the speed of _____. The electromagnetic spectrum is a continuous range of _________. The types of radiation that occur in each part of the spectrum have different use ...
Chapter 3 - People @ EECS at UC Berkeley
... factors of the term e2na/ε0mω2 must be much less than unity. Demonstrate that this approximation is valid, away from the resonance, by considering various atoms, and frequencies corresponding to both EUV and soft X-ray radiation. Atomic densities of atoms in their natural form are given in the Perio ...
... factors of the term e2na/ε0mω2 must be much less than unity. Demonstrate that this approximation is valid, away from the resonance, by considering various atoms, and frequencies corresponding to both EUV and soft X-ray radiation. Atomic densities of atoms in their natural form are given in the Perio ...