IJFTR 12(2) 100-102
... (3) Light polarized parallel to the axis of the fibre must be used for these measurements, because calculation of the combined fresnel coefficients shows that light polarized perpendicular to the axis of the fibre has a minimum irradiance when it emerges from the fibre at angles very close to m' ...
... (3) Light polarized parallel to the axis of the fibre must be used for these measurements, because calculation of the combined fresnel coefficients shows that light polarized perpendicular to the axis of the fibre has a minimum irradiance when it emerges from the fibre at angles very close to m' ...
Modal and Material Dispersion
... in the refractive indices would change the phase difference between these two components & thereby the state of the polarization of the mode. However after certain length referred to as fiber beat length, the modal wave will produce its original state of polarization. This length is simply given by: ...
... in the refractive indices would change the phase difference between these two components & thereby the state of the polarization of the mode. However after certain length referred to as fiber beat length, the modal wave will produce its original state of polarization. This length is simply given by: ...
Materialanalytik Praktikum Ellipsometry B508
... Figure 3: Schematic illustration of the ellipsometer working principle (after [1]). One question remains: How are the properties of a wave changed when propagating through a dielectric material? Since answering this question in detail would exceed the time limitations of this lab course, we will giv ...
... Figure 3: Schematic illustration of the ellipsometer working principle (after [1]). One question remains: How are the properties of a wave changed when propagating through a dielectric material? Since answering this question in detail would exceed the time limitations of this lab course, we will giv ...
Lecture8 - UMD Physics
... larger than the critical angle, it is totally internally reflected: No loss of light from escaping! Thus the light can be used to transmit information through the optical fibers. ...
... larger than the critical angle, it is totally internally reflected: No loss of light from escaping! Thus the light can be used to transmit information through the optical fibers. ...
DG Papazoglou et al.
... Optical aberrations can be envisioned as a way to impose polynomial phase distributions on plane wave! Coma aberration Cubic phase ! ...
... Optical aberrations can be envisioned as a way to impose polynomial phase distributions on plane wave! Coma aberration Cubic phase ! ...
Experimental method for reliably establishing the refractive index of
... and Miller’s values were “so far outside the range of refractive indices ever measured for insect cuticles (1.5 and 1.6) that they should be carefully checked”. However, Caveney later conducted experiments on the cuticle of an iridescent scarab beetle and determined the average refractive index of i ...
... and Miller’s values were “so far outside the range of refractive indices ever measured for insect cuticles (1.5 and 1.6) that they should be carefully checked”. However, Caveney later conducted experiments on the cuticle of an iridescent scarab beetle and determined the average refractive index of i ...
ray_optics_su2014
... 2a. Total Reflection (Snell’s Window) • At the “critical angle” the refracted beam is at 90, so it can’t get out. • Greater than this “critical angle” there is 100% reflection • Snell’s Window: from underwater a fish sees the entire area above surface in a cone. Outside the cone light is totally r ...
... 2a. Total Reflection (Snell’s Window) • At the “critical angle” the refracted beam is at 90, so it can’t get out. • Greater than this “critical angle” there is 100% reflection • Snell’s Window: from underwater a fish sees the entire area above surface in a cone. Outside the cone light is totally r ...
PHYS 242 BLOCK 11 NOTES Sections 33.1 to 33.7 Geometrical
... c is the speed of light in vacuum, defined to equal exactly 299,792,458 m/s ≈ 2.998 × 108 m/s. υ is the speed of light in the material (in m/s) and υ ≤ c. Thus n has no unit, n ≥ 1, n = KKm (from Block 10) , n = 1 in vacuum, and n ≈ 1 in air. Traditionally called Snell’s law, the law of refraction i ...
... c is the speed of light in vacuum, defined to equal exactly 299,792,458 m/s ≈ 2.998 × 108 m/s. υ is the speed of light in the material (in m/s) and υ ≤ c. Thus n has no unit, n ≥ 1, n = KKm (from Block 10) , n = 1 in vacuum, and n ≈ 1 in air. Traditionally called Snell’s law, the law of refraction i ...
Document
... Optical fibre consists of two concentric layers of different types of glass, core and cladding. core Light entering the inner core always strikes the boundary of the two glasses at an angle that is greater than the critical angle. ...
... Optical fibre consists of two concentric layers of different types of glass, core and cladding. core Light entering the inner core always strikes the boundary of the two glasses at an angle that is greater than the critical angle. ...
Note - The Eclecticon of Dr French
... the focusing effect results from the observation that the total angle of deflection passes through an extremum as the angle between incidence and raindrop surface normal is varied. The large multitude of raindrops within a raincloud allows us to assume that all possible angles of are explored wi ...
... the focusing effect results from the observation that the total angle of deflection passes through an extremum as the angle between incidence and raindrop surface normal is varied. The large multitude of raindrops within a raincloud allows us to assume that all possible angles of are explored wi ...
Part 1
... The sign between kx and t determines the direction the wave travels along the x-axis. + wave travels to left (in the direction of decreasing x) - wave travels to right (in the direction of increasing x) The phase angle shifts the cosine or sine function left or right. This can be used to match ...
... The sign between kx and t determines the direction the wave travels along the x-axis. + wave travels to left (in the direction of decreasing x) - wave travels to right (in the direction of increasing x) The phase angle shifts the cosine or sine function left or right. This can be used to match ...
E/M Waves
... are called electromagnetic radiation, or light. The light wave is a transverse wave, with the electric and magnetic fields both perpendicular to the wave’s velocity and each other. Visible light is a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum. The velocity of light in empty space (c) is related to t ...
... are called electromagnetic radiation, or light. The light wave is a transverse wave, with the electric and magnetic fields both perpendicular to the wave’s velocity and each other. Visible light is a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum. The velocity of light in empty space (c) is related to t ...
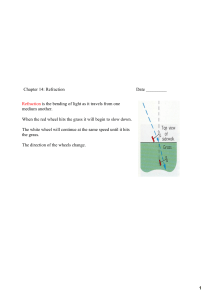
1 Chapter 14: Refraction
... When light moves from one medium to another, part of it is reflected and part is refracted. When light moves from a material in which its speed is higher (air) to a material in which its speed is lower (glass), the ray is bent _________ the normal. When light moves from material in which its speed ...
... When light moves from one medium to another, part of it is reflected and part is refracted. When light moves from a material in which its speed is higher (air) to a material in which its speed is lower (glass), the ray is bent _________ the normal. When light moves from material in which its speed ...
Opt001
... "Light" is a term for those electromagnetic waves that can be detected by the human eye. As with all waves, their speed, v, frequency, f, and wavelength, , are related by v = f , where the speed of light in a vacuum ...
... "Light" is a term for those electromagnetic waves that can be detected by the human eye. As with all waves, their speed, v, frequency, f, and wavelength, , are related by v = f , where the speed of light in a vacuum ...
Refractive indexes of (Al,Ga,In)As epilayers on InP for optoelectronic
... determined from a normalized reflectivity spectrum which oscillates around unity. The data of Pettit et al. [9] was used for the index dispersion of InP in the calculations. The refractive index variation with frequency can be also determined using (l), given the knowledge of the exact epilayer thic ...
... determined from a normalized reflectivity spectrum which oscillates around unity. The data of Pettit et al. [9] was used for the index dispersion of InP in the calculations. The refractive index variation with frequency can be also determined using (l), given the knowledge of the exact epilayer thic ...
PPT-icon - cloudfront.net
... * Hao Xu, Xianyao Li, Xi Xiao, Zhiyong Li, Yude Yu and Jinzhong Yu, "Demonstration and Characterization of High-Speed Silicon Depletion-Mode Mach–Zehnder Modulators," in IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, vol. 20, no. 4, pp. 23-32, July-Aug. 2014. ...
... * Hao Xu, Xianyao Li, Xi Xiao, Zhiyong Li, Yude Yu and Jinzhong Yu, "Demonstration and Characterization of High-Speed Silicon Depletion-Mode Mach–Zehnder Modulators," in IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, vol. 20, no. 4, pp. 23-32, July-Aug. 2014. ...
LEP 2.1.01 Measuring the velocity of light
... The mirror displacement Dx is measured; the measurement should be repeated several times. 2. The water-filled tube or the synthetic resin block is placed in the path of the ray so that its end faces are perpendicular to the optic axis; the mirror is placed directly behind them (top of Fig. 3). A sup ...
... The mirror displacement Dx is measured; the measurement should be repeated several times. 2. The water-filled tube or the synthetic resin block is placed in the path of the ray so that its end faces are perpendicular to the optic axis; the mirror is placed directly behind them (top of Fig. 3). A sup ...
Resins for Optics
... 1-1. Brief Description of the Refractive Index The refractive index shows the optical density of a material and it is generally represented by “n”. In other words, the refractive index is the resistance under which light passes through a material. A greater resistance results in an increased refract ...
... 1-1. Brief Description of the Refractive Index The refractive index shows the optical density of a material and it is generally represented by “n”. In other words, the refractive index is the resistance under which light passes through a material. A greater resistance results in an increased refract ...
Chapter1 Fundamental law of geometrical optics 第一章 几何光学的
... Frequency ν: lying between 7.5*10 14 for violet light and 4*10 14 for deep red light. Wavelength λ: dividing the velocity by the frequency. λ=v/ν λ: 0.4μm~0.75μm(micrometer) Velocity v=3*10 10 cm/sec in empty space ...
... Frequency ν: lying between 7.5*10 14 for violet light and 4*10 14 for deep red light. Wavelength λ: dividing the velocity by the frequency. λ=v/ν λ: 0.4μm~0.75μm(micrometer) Velocity v=3*10 10 cm/sec in empty space ...
ETM4106Tutorial3
... coefficient of 0.286. The Boltzman constant is 1.381 10-23 JK-1 . Ans. 5.2 dB/Km, 0.8 dB/Km, 0.3 dB/Km. Q.5 A K2 O-SiO2 glass core optical fiber has an attenuation resulting from Rayleigh scattering 0.46 dB/Km at a wavelength of 1 m. The glass has an estimated fricative temperature of 758 K, isot ...
... coefficient of 0.286. The Boltzman constant is 1.381 10-23 JK-1 . Ans. 5.2 dB/Km, 0.8 dB/Km, 0.3 dB/Km. Q.5 A K2 O-SiO2 glass core optical fiber has an attenuation resulting from Rayleigh scattering 0.46 dB/Km at a wavelength of 1 m. The glass has an estimated fricative temperature of 758 K, isot ...
4.8 Acceptance Angle and Numerical Aperture
... The fibre output is a cone of light that spreads out wider as the distance from the fibre exit increases. The grid slide or screen and ruler can be used to measure diameters. The edges of the cone of light may appear fuzzy so there will be an error introduced into your measurements. Measurement of t ...
... The fibre output is a cone of light that spreads out wider as the distance from the fibre exit increases. The grid slide or screen and ruler can be used to measure diameters. The edges of the cone of light may appear fuzzy so there will be an error introduced into your measurements. Measurement of t ...
The petrographic microscope
... This is a characteristic of the medium in which light is propagated, and is determined by the Refractive index (n), or the relation between the velocity of propagation in a vacuum (c) and in the medium under consideration (v). n=c/v For this reason, the "n" of minerals is always greater than one (ra ...
... This is a characteristic of the medium in which light is propagated, and is determined by the Refractive index (n), or the relation between the velocity of propagation in a vacuum (c) and in the medium under consideration (v). n=c/v For this reason, the "n" of minerals is always greater than one (ra ...