An introduction to Optics
... incidence θ1 and angle of refraction θ2 is equivalent to the ratio of phase velocities (v1 / v2) in the two media, or equivalently, to the opposite ratio of the indices of refraction (n2 / n1): In optics, refraction is a phenomenon that often occurs when waves travel from a medium with a given refr ...
... incidence θ1 and angle of refraction θ2 is equivalent to the ratio of phase velocities (v1 / v2) in the two media, or equivalently, to the opposite ratio of the indices of refraction (n2 / n1): In optics, refraction is a phenomenon that often occurs when waves travel from a medium with a given refr ...
4.Bending Light PhET
... Make sure your materials are “air” on top and “water” on the bottom again, before starting this next part. 7. What happens to the refracted ray’s angle when you make the laser’s angle equal to zero? ...
... Make sure your materials are “air” on top and “water” on the bottom again, before starting this next part. 7. What happens to the refracted ray’s angle when you make the laser’s angle equal to zero? ...
Ref. “Optical Materials”
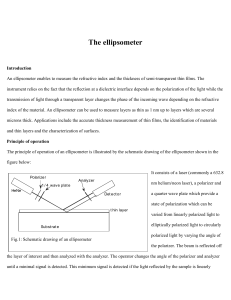
... The reflected light is then detected through an analyser (Glan-Thomson calcite prism) and both the polarizer and the analyser angles are varied to find the maximum extinction of the reflected light. The values obtained consist of the polarizer angle (P), the analyser angle (A) and the angle of incid ...
... The reflected light is then detected through an analyser (Glan-Thomson calcite prism) and both the polarizer and the analyser angles are varied to find the maximum extinction of the reflected light. The values obtained consist of the polarizer angle (P), the analyser angle (A) and the angle of incid ...
PHYS 1111 Mechanics, Waves, & Thermodynamics
... Dispersion and Prisms For a given material (and nearly all materials), the index of fraction is a function of the wavelength of the incident light, n=n() This implies that the speed of light inside the medium depends on The dependence of wave speed v and n on is called dispersion Since n=n(), ...
... Dispersion and Prisms For a given material (and nearly all materials), the index of fraction is a function of the wavelength of the incident light, n=n() This implies that the speed of light inside the medium depends on The dependence of wave speed v and n on is called dispersion Since n=n(), ...
08-Michelson
... pattern. When 100 have disappeared, record the new micrometer reading and calculate the mean wavelength. Repeat the procedure a few times and calculate an average. (You will probably need some practice for this. It is very easy to miss a fringe.) [Hint: To find the average distance, be sure to remem ...
... pattern. When 100 have disappeared, record the new micrometer reading and calculate the mean wavelength. Repeat the procedure a few times and calculate an average. (You will probably need some practice for this. It is very easy to miss a fringe.) [Hint: To find the average distance, be sure to remem ...
Full-field refractive index measurement with simultaneous phase
... Therefore, this setup can avoid errors caused by non-simultaneous capturing of images and offers the benefits of high stability, ease of operation, and real-time measurement. Furthermore, using the phenomenon of total internal reflection, the phase difference between p- and s-polarized light varies co ...
... Therefore, this setup can avoid errors caused by non-simultaneous capturing of images and offers the benefits of high stability, ease of operation, and real-time measurement. Furthermore, using the phenomenon of total internal reflection, the phase difference between p- and s-polarized light varies co ...
Chapter 37 Wave Optics (I)
... interfaces, which means that only (0.96)12=0.61 or 61% of the incident energy is transmitted. How to optimize the transmission of signal intensity? Lens coating. The loss due to the reflection is minimized by coating each lens surface with a thin film. The thickness and refractive index of the thin ...
... interfaces, which means that only (0.96)12=0.61 or 61% of the incident energy is transmitted. How to optimize the transmission of signal intensity? Lens coating. The loss due to the reflection is minimized by coating each lens surface with a thin film. The thickness and refractive index of the thin ...
Properties of Multilayer Optics
... one, Brewster’s angle is near 45 degrees. Adjusting the spacing between layers (d) in the Bragg equation one can place this Bragg reflection peak also near 45 degrees This causes the ML optic to be highly reflective (due to the multilayer reflections) and especially to the s-component since the angl ...
... one, Brewster’s angle is near 45 degrees. Adjusting the spacing between layers (d) in the Bragg equation one can place this Bragg reflection peak also near 45 degrees This causes the ML optic to be highly reflective (due to the multilayer reflections) and especially to the s-component since the angl ...
Dispersion Relation of Defect Structure Containing Negative Index
... Photonic crystals are also known as the electromagnetic wave band gap materials because the electromagnetic wave cannot propagate through the photonic crystal if the incident wavelength is equivalent to the thickness of the unit cell of the crystals. Photonic crystals are the artificial periodic co ...
... Photonic crystals are also known as the electromagnetic wave band gap materials because the electromagnetic wave cannot propagate through the photonic crystal if the incident wavelength is equivalent to the thickness of the unit cell of the crystals. Photonic crystals are the artificial periodic co ...
Tutorial 2
... In the dielectric model, take N = 1028/m3 for the density of bound electrons in an insulator, a resonant frequency = 6 × 1015 rad/sec (in the UV), and damping = /5 (quite broad). Assume |E0| is 104 V/m. You don’t need to worry about vector directions. For three frequencies = − 2, = ...
... In the dielectric model, take N = 1028/m3 for the density of bound electrons in an insulator, a resonant frequency = 6 × 1015 rad/sec (in the UV), and damping = /5 (quite broad). Assume |E0| is 104 V/m. You don’t need to worry about vector directions. For three frequencies = − 2, = ...
PDF Link
... The dispersion relation is fundamental to a physical phenomenon that develops in both space and time. This equation connects the spatial and temporal frequencies involved in the dynamic process through the material constants. Electromagnetic plane waves propagating in homogeneous media are bound by ...
... The dispersion relation is fundamental to a physical phenomenon that develops in both space and time. This equation connects the spatial and temporal frequencies involved in the dynamic process through the material constants. Electromagnetic plane waves propagating in homogeneous media are bound by ...
Chapter 2 Classical propagation
... refractive index and the absorption coefficient are not independent parameters but are related to each other. If we invoke the law of causality (that an effect may not precede its cause) and apply complex number analysis, we can derive general relationships between the real and imaginary parts of th ...
... refractive index and the absorption coefficient are not independent parameters but are related to each other. If we invoke the law of causality (that an effect may not precede its cause) and apply complex number analysis, we can derive general relationships between the real and imaginary parts of th ...
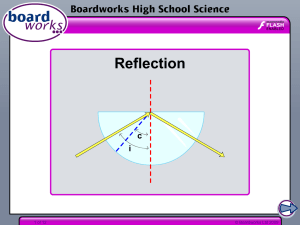
law of reflection
... reflect rays of light towards a focal point (F). If a light source is placed at the focal point, the mirror will produce a beam of parallel light rays. The distance between the mirror and the focal point is called the focal length (ƒ). ƒ becomes smaller as the mirror’s curve increases. 6 of 12 ...
... reflect rays of light towards a focal point (F). If a light source is placed at the focal point, the mirror will produce a beam of parallel light rays. The distance between the mirror and the focal point is called the focal length (ƒ). ƒ becomes smaller as the mirror’s curve increases. 6 of 12 ...
1076
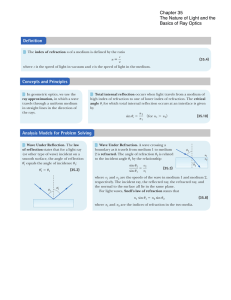
... the indices of refraction of the media, and the angles of incidence and refraction? More than one statement may be correct. (a) v1 /sin u1 5 v 2 /sin u2 (b) csc u1 /n 1 5 csc u2 /n 2 (c) l1 /sin u1 5 l2 /sin u2 (d) f 1 /sin u1 5 f 2 /sin u2 (e) n 1 /cos u1 5 n 2 /cos u2 ...
... the indices of refraction of the media, and the angles of incidence and refraction? More than one statement may be correct. (a) v1 /sin u1 5 v 2 /sin u2 (b) csc u1 /n 1 5 csc u2 /n 2 (c) l1 /sin u1 5 l2 /sin u2 (d) f 1 /sin u1 5 f 2 /sin u2 (e) n 1 /cos u1 5 n 2 /cos u2 ...
Physics 422 - Spring 2016 - Assignment #8, Due April... 1. Total internal reflection occurs when the angle of incidence, θ
... (a) Describe in detail the polarization states of each of these. (b) Determine the resulting Stokes parameters of the combined beam and describe its polarization state. (c) What is its degree of polarization? (d) What is the resulting light produced by overlapping the incoherent beams (1, 1, 0, 0) a ...
... (a) Describe in detail the polarization states of each of these. (b) Determine the resulting Stokes parameters of the combined beam and describe its polarization state. (c) What is its degree of polarization? (d) What is the resulting light produced by overlapping the incoherent beams (1, 1, 0, 0) a ...
Derive an expression for time dilation and give an
... 3. State Einstein’s postulates of special theory of relativity. Derive inverse Lorentz transformation equations. 4. Show that x2 + y2 + z2 – c2t2 is invariant under Lorentz transformation. 5. Get an expression for Einstein’s mass-energy relationship. How will this expression get modified when the sp ...
... 3. State Einstein’s postulates of special theory of relativity. Derive inverse Lorentz transformation equations. 4. Show that x2 + y2 + z2 – c2t2 is invariant under Lorentz transformation. 5. Get an expression for Einstein’s mass-energy relationship. How will this expression get modified when the sp ...
12.5 Total Internal Reflection
... The critical angle is the angle of incidence which gives an angle of refraction of 90º. If you increase the angle of incidence past the critical angle, the refracted ray no longer exits the medium. This is called total internal reflection. ...
... The critical angle is the angle of incidence which gives an angle of refraction of 90º. If you increase the angle of incidence past the critical angle, the refracted ray no longer exits the medium. This is called total internal reflection. ...
Determination of Absolute Values of Refractive Index of Liquids
... In our experiment the ratio d/∆x is approximately 0.3 so that the resulting relative error of refractive index is 0.3 n̂ · ϕ ~ . Aiming at an overall error of the order 10−5 one would like to keep this contribution smaller than say 5 · 10−6 , which means n̂ · ϕ ~ < 1.7 × 10−5 rad, which is a tight r ...
... In our experiment the ratio d/∆x is approximately 0.3 so that the resulting relative error of refractive index is 0.3 n̂ · ϕ ~ . Aiming at an overall error of the order 10−5 one would like to keep this contribution smaller than say 5 · 10−6 , which means n̂ · ϕ ~ < 1.7 × 10−5 rad, which is a tight r ...
Discussion Note #32
... Reflection and Refraction Reflection is the simplest of these phenomena. For surfaces that are smooth and flat on a scale size of the wavelength of light, specular (mirror) reflection obeys the simple relation that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection for the incident and reflected ...
... Reflection and Refraction Reflection is the simplest of these phenomena. For surfaces that are smooth and flat on a scale size of the wavelength of light, specular (mirror) reflection obeys the simple relation that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection for the incident and reflected ...
File
... At each boundary some light is reflected and some refracted. This is called division by amplitude. Someone looking at rays 1 and 2 would see an interference pattern. This is caused by path difference between the rays. ...
... At each boundary some light is reflected and some refracted. This is called division by amplitude. Someone looking at rays 1 and 2 would see an interference pattern. This is caused by path difference between the rays. ...