Name Period Date Chapter 5: Egypt Review Packet Lesson 1 ____
... 2. More than 30 dynasties ruled ancient Egypt. Historians divide Egypt’s history into the ____________________ Kingdom, ____________________ Kingdom, and ____________________ Kingdom. 3. Because Egyptians believed that the pharaoh was a child of the ____________________, hard times were a sign that ...
... 2. More than 30 dynasties ruled ancient Egypt. Historians divide Egypt’s history into the ____________________ Kingdom, ____________________ Kingdom, and ____________________ Kingdom. 3. Because Egyptians believed that the pharaoh was a child of the ____________________, hard times were a sign that ...
classroom tutorials
... cutting through the sands of the Egyptian desert. Each spring, excess rain from the highlands carried rich soil deposits downriver. As the waters entered Egypt every year, they overflowed the river’s banks and left a fresh, wet layer of fertile soil along a stretch of land some 10 miles wide and 650 ...
... cutting through the sands of the Egyptian desert. Each spring, excess rain from the highlands carried rich soil deposits downriver. As the waters entered Egypt every year, they overflowed the river’s banks and left a fresh, wet layer of fertile soil along a stretch of land some 10 miles wide and 650 ...
Ancient Egypt Part 2 - Crest Ridge R-VII
... A United Egypt 1. Because the people in Egypt had plenty of food, some people became artisans instead of farmers. Remember, artisans made stuff such as pottery, weapons, and tools. ...
... A United Egypt 1. Because the people in Egypt had plenty of food, some people became artisans instead of farmers. Remember, artisans made stuff such as pottery, weapons, and tools. ...
Intro Ancient Egypt - Lake Oswego High School
... Geography of the Ancient Nile Valley “Egypt is wholly the gift of the Nile.” >Herodotus Settled & established farming villages along Nile. Egyptians depended on annual floods to soak the land & deposit a layer of silt or rich soil. Egyptians had to cooperate to control the Nile, building dikes, res ...
... Geography of the Ancient Nile Valley “Egypt is wholly the gift of the Nile.” >Herodotus Settled & established farming villages along Nile. Egyptians depended on annual floods to soak the land & deposit a layer of silt or rich soil. Egyptians had to cooperate to control the Nile, building dikes, res ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Egypt: Middle and New Kingdoms
... mathematics, literature and writing. Girls learned household skills and weaving from their mothers ...
... mathematics, literature and writing. Girls learned household skills and weaving from their mothers ...
Ancient Egypt Vocabulary
... 1. Cataracts- rapids along a river, such as those along the Nile in Egypt. 2. Delta-a triangle-shaped area of land made from soil deposited by a river. 3. Menes- Legendary Egyptian ruler, he unified the kingdoms of Upper and Lower Egypt and built the new capital city of Memphis. 4. Pharaoh-the title ...
... 1. Cataracts- rapids along a river, such as those along the Nile in Egypt. 2. Delta-a triangle-shaped area of land made from soil deposited by a river. 3. Menes- Legendary Egyptian ruler, he unified the kingdoms of Upper and Lower Egypt and built the new capital city of Memphis. 4. Pharaoh-the title ...
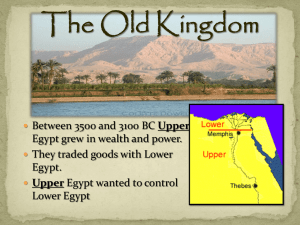
The Old Kingdom - Kingdom of Reese
... mystery In 1799 AD, a large stone was discovered near the city of Rosetta, on this stone were written three different languages; Egyptian hieroglyphics, Egyptian demotic (kind of like Egyptian cursive), and Greek. In 1822, Jean-Francois Champollion decoded the writing, based on his knowledge of ...
... mystery In 1799 AD, a large stone was discovered near the city of Rosetta, on this stone were written three different languages; Egyptian hieroglyphics, Egyptian demotic (kind of like Egyptian cursive), and Greek. In 1822, Jean-Francois Champollion decoded the writing, based on his knowledge of ...
Document
... Invaders Control Egypt Changes to Egyptian Society • Power of Pharaohs declines about 2180 B.C.; end of Old Kingdom • In Middle Kingdom (2040 to 1640 B.C.), some pharaohs regain control • Improve trade, dig canal from Nile to Red Sea, drain ...
... Invaders Control Egypt Changes to Egyptian Society • Power of Pharaohs declines about 2180 B.C.; end of Old Kingdom • In Middle Kingdom (2040 to 1640 B.C.), some pharaohs regain control • Improve trade, dig canal from Nile to Red Sea, drain ...
Theme: Geography
... Flooded, provided silt (Nile Delta 2/3 farms) Fertile soil, irrigation, for farming Stable food supply (surplus) Provided for division of labor and civilization Like Mesopotamia ...
... Flooded, provided silt (Nile Delta 2/3 farms) Fertile soil, irrigation, for farming Stable food supply (surplus) Provided for division of labor and civilization Like Mesopotamia ...
File
... which means hidden. So Ammun eventually merged with Ra to form the god Ammun-Ra, all the Middle Kingdom pharaohs made temples for him and devoted their entire surplus to his glory. The Middle Kingdom also developed an interest in conquering; they were able to conquer much of Egypt using superior mil ...
... which means hidden. So Ammun eventually merged with Ra to form the god Ammun-Ra, all the Middle Kingdom pharaohs made temples for him and devoted their entire surplus to his glory. The Middle Kingdom also developed an interest in conquering; they were able to conquer much of Egypt using superior mil ...
The Egyptian, Nubian, and Assyrian Empires (2.2, 4.1, 4.2) DATE
... 2. We will be able to analyze the rise of the Kingdoms in Egypt, the Nubian Empire and their decline Looking at Ancient Egypt (OLD KINGDOM EGYPT2660 to 2180 BC) o The Nile River was vital to Egypt King Menes united Upper and Lower Egypt in 3100 BC o Egypt’s Rulers, Pharaohs were equal to Gods ...
... 2. We will be able to analyze the rise of the Kingdoms in Egypt, the Nubian Empire and their decline Looking at Ancient Egypt (OLD KINGDOM EGYPT2660 to 2180 BC) o The Nile River was vital to Egypt King Menes united Upper and Lower Egypt in 3100 BC o Egypt’s Rulers, Pharaohs were equal to Gods ...
The Egyptian Civilization
... The Middle Kingdom • 2055-1650 B.C. – Egypt began expanding and establishing trade. • Expanded to the North and South. • Traded with the Mediterranean and Mesopotamia. ...
... The Middle Kingdom • 2055-1650 B.C. – Egypt began expanding and establishing trade. • Expanded to the North and South. • Traded with the Mediterranean and Mesopotamia. ...
Location and Physical Features
... Kings Unify Egypt • In about 3,100 B.C. Menes becomes king of Upper Egypt • He invaded and took control of Lower Egypt • He is considered to be the first pharaoh (means “great house”) • He also founded Egypt’s first dynasty, or series of rulers from the same family ...
... Kings Unify Egypt • In about 3,100 B.C. Menes becomes king of Upper Egypt • He invaded and took control of Lower Egypt • He is considered to be the first pharaoh (means “great house”) • He also founded Egypt’s first dynasty, or series of rulers from the same family ...
Egypt Old Kingdom
... desertification, and, in time, groups began to settle permanently along the waters of the river. By around 4000 B.C., the Nile Valley and Delta was surrounded by agricultural communities that had come to live in harmony with the river, waiting for the annual floods before planting their crops in th ...
... desertification, and, in time, groups began to settle permanently along the waters of the river. By around 4000 B.C., the Nile Valley and Delta was surrounded by agricultural communities that had come to live in harmony with the river, waiting for the annual floods before planting their crops in th ...
File
... Asia and take over part of Egypt. 16. Bring new weapons and ____________- rule until around 1650 B.C. ushering in the Second Intermediate Period 17. Leaders in Upper Egypt drive the Hyksos out of the country. 18. A line of strong pharaohs began to rule a reunited Egypt. This period is called the New ...
... Asia and take over part of Egypt. 16. Bring new weapons and ____________- rule until around 1650 B.C. ushering in the Second Intermediate Period 17. Leaders in Upper Egypt drive the Hyksos out of the country. 18. A line of strong pharaohs began to rule a reunited Egypt. This period is called the New ...
Egypt - Bonar Law Memorial
... • Early system of writing • Picture symbols represent words and ideas • Similar to cuneiform ...
... • Early system of writing • Picture symbols represent words and ideas • Similar to cuneiform ...
Egypt Badarian By 5000 BC simple farming based on cattle herding
... profited from Plum Red pottery. Image from one tomb: ruler smiting enemies and sitting under an awning. About 3500 BC: fragile ecological balance of desert and grassland collapsed. Why? Most likely overgrazing by sheep and goats and deforestation resulting from firing of kilns. May have created an o ...
... profited from Plum Red pottery. Image from one tomb: ruler smiting enemies and sitting under an awning. About 3500 BC: fragile ecological balance of desert and grassland collapsed. Why? Most likely overgrazing by sheep and goats and deforestation resulting from firing of kilns. May have created an o ...
ANCIENT EGYPT (NILE RIVER VALLEY) Geography Today: Desert
... Mediterranean sea from north to south, so travel was possible both ways, meaning a faster trade link which enabled the civilization to expand. 3000 B.C- People had been living in the Nile River valley for over 9,000 years. However, at this time people in the valley had developed hieroglyphics( a for ...
... Mediterranean sea from north to south, so travel was possible both ways, meaning a faster trade link which enabled the civilization to expand. 3000 B.C- People had been living in the Nile River valley for over 9,000 years. However, at this time people in the valley had developed hieroglyphics( a for ...
Ancient Egypt
... food and drink. Each person also had a ba, the set of spiritual characteristics unique to each individual.[30] Unlike the ka, the ba remained attached to the body after death. Egyptian funeral rituals were intended to release the ba from the body so that it could move freely, and to rejoin it with t ...
... food and drink. Each person also had a ba, the set of spiritual characteristics unique to each individual.[30] Unlike the ka, the ba remained attached to the body after death. Egyptian funeral rituals were intended to release the ba from the body so that it could move freely, and to rejoin it with t ...
Ancient Egyptian Leadership
... •Northern border of Nubia @ 1st cataract at Aswan -known as “Wawat.” •Southern end at 2nd cataract (now inundated by Lake Nasser) was referred to as “Cush” by the Egyptians, and as Ethiopia by the ancient Greeks. •“Nubia” either comes from the Nubian word “nob”,
or “nugur” / “nub”
... •Northern border of Nubia @ 1st cataract at Aswan -known as “Wawat.” •Southern end at 2nd cataract (now inundated by Lake Nasser) was referred to as “Cush” by the Egyptians, and as Ethiopia by the ancient Greeks. •“Nubia” either comes from the Nubian word “nob”