Egypt
... became Menmaatre Seti which was his pharaoh name. He married Tuya and they had four children their third was Ramses II who became pharaoh in about 1279 B.C. ...
... became Menmaatre Seti which was his pharaoh name. He married Tuya and they had four children their third was Ramses II who became pharaoh in about 1279 B.C. ...
Ancient Egypt Edit File
... level to the next. This theory has been DISPUTED, since the Egyptians did not have access to trees that were strong enough for this type of work. The average weight of the STONE BLOCKS used to build the Great Pyramid at Giza has been estimated at 2.5 TONS. Such an enormous weight would undoubtedly b ...
... level to the next. This theory has been DISPUTED, since the Egyptians did not have access to trees that were strong enough for this type of work. The average weight of the STONE BLOCKS used to build the Great Pyramid at Giza has been estimated at 2.5 TONS. Such an enormous weight would undoubtedly b ...
4 - Images
... • Invades Palestine, Syria, and Nubia—region around the upper Nile River • Egypt most powerful and wealthy during reign of New Kingdom pharaohs ...
... • Invades Palestine, Syria, and Nubia—region around the upper Nile River • Egypt most powerful and wealthy during reign of New Kingdom pharaohs ...
Question - Mr Powell`s History Pages
... Historians divide Egyptian history into three major periods of stability, peace, and cultural flourishing: the Old Kingdom, the Middle Kingdom, and the New Kingdom. Periods of upheaval fell between them. Egyptian history began around 3100 B.C. when Menes created the first royal dynasty in Egypt. ...
... Historians divide Egyptian history into three major periods of stability, peace, and cultural flourishing: the Old Kingdom, the Middle Kingdom, and the New Kingdom. Periods of upheaval fell between them. Egyptian history began around 3100 B.C. when Menes created the first royal dynasty in Egypt. ...
Slide 1
... level to the next. This theory has been DISPUTED, since the Egyptians did not have access to trees that were strong enough for this type of work. The average weight of the STONE BLOCKS used to build the Great Pyramid at Giza has been estimated at 2.5 TONS. Such an enormous weight would undoubtedly b ...
... level to the next. This theory has been DISPUTED, since the Egyptians did not have access to trees that were strong enough for this type of work. The average weight of the STONE BLOCKS used to build the Great Pyramid at Giza has been estimated at 2.5 TONS. Such an enormous weight would undoubtedly b ...
Ancient Egypt
... level to the next. This theory has been DISPUTED, since the Egyptians did not have access to trees that were strong enough for this type of work. The average weight of the STONE BLOCKS used to build the Great Pyramid at Giza has been estimated at 2.5 TONS. Such an enormous weight would undoubtedly b ...
... level to the next. This theory has been DISPUTED, since the Egyptians did not have access to trees that were strong enough for this type of work. The average weight of the STONE BLOCKS used to build the Great Pyramid at Giza has been estimated at 2.5 TONS. Such an enormous weight would undoubtedly b ...
Ancient Egypt
... level to the next. This theory has been DISPUTED, since the Egyptians did not have access to trees that were strong enough for this type of work. The average weight of the STONE BLOCKS used to build the Great Pyramid at Giza has been estimated at 2.5 TONS. Such an enormous weight would undoubtedly b ...
... level to the next. This theory has been DISPUTED, since the Egyptians did not have access to trees that were strong enough for this type of work. The average weight of the STONE BLOCKS used to build the Great Pyramid at Giza has been estimated at 2.5 TONS. Such an enormous weight would undoubtedly b ...
Introduction to Egyptian Civilization
... and two in Easter term. Mode of Assessment: There will be a three-hour written examination at the end of the academic year. The paper is divided into two sections: Section A consists of five comparative questions in which candidates are expected to refer to both Egyptian and Mesopotamian cultures; S ...
... and two in Easter term. Mode of Assessment: There will be a three-hour written examination at the end of the academic year. The paper is divided into two sections: Section A consists of five comparative questions in which candidates are expected to refer to both Egyptian and Mesopotamian cultures; S ...
WHICh2Egypt-Sec1-2Ancient Egypt-2016
... • Conquered Palestine & Syria to the east. Conquered more of Nubia in the south. • Now Egypt was a true Empire. Brought Egypt to the height of its ...
... • Conquered Palestine & Syria to the east. Conquered more of Nubia in the south. • Now Egypt was a true Empire. Brought Egypt to the height of its ...
Floodplain Civilization: Egypt WH005 Activity Introduction Hey I`m
... thousands of years. Yes indeed, by one-thousand B.C.E. Egypt supported a population of around three million to four million people… living ones—not mummies like me… ...
... thousands of years. Yes indeed, by one-thousand B.C.E. Egypt supported a population of around three million to four million people… living ones—not mummies like me… ...
WHICh2Egypt-Sec1-2Ancient Egypt-2015
... • Conquered Palestine & Syria to the east. Conquered more of Nubia in the south. • Now Egypt was a true Empire. Brought Egypt to the height of its ...
... • Conquered Palestine & Syria to the east. Conquered more of Nubia in the south. • Now Egypt was a true Empire. Brought Egypt to the height of its ...
Ancient Egypt
... and intestines 4) Treating, cleaning, dehydrating the intestines 5) Packing the body with natron (a natural dehydrating agent) and leaving for 40 days 6) Removal of the natron agent 7) Packing the limbs with clay or sand 8) Packing the body with linen (soaked in resin), myrrh and cinnamon 9) Treatin ...
... and intestines 4) Treating, cleaning, dehydrating the intestines 5) Packing the body with natron (a natural dehydrating agent) and leaving for 40 days 6) Removal of the natron agent 7) Packing the limbs with clay or sand 8) Packing the body with linen (soaked in resin), myrrh and cinnamon 9) Treatin ...
Ancient Egypt stations e15
... Around 3100 BC, there were two separate kingdoms in Egypt, Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Soon afterwards, King Narmer (from Upper Egypt) united the two kingdoms. When the unification happened, it became the world’s first ever nation-state. King Narmer was the first king of Egypt’s first dynasty, and ...
... Around 3100 BC, there were two separate kingdoms in Egypt, Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Soon afterwards, King Narmer (from Upper Egypt) united the two kingdoms. When the unification happened, it became the world’s first ever nation-state. King Narmer was the first king of Egypt’s first dynasty, and ...
Chapter 2:i The Nile Valley
... The Theban kings established a new dynasty that ushered-in the period known as the Middle Kingdom. ...
... The Theban kings established a new dynasty that ushered-in the period known as the Middle Kingdom. ...
Intro to AE Class Notes
... A. The world’s longest river – it flows northward toward the Mediterranean Sea for 4100 miles --- longer than the distance from NJ to CA! 1. Herodotus – The Greek historian said that “Egypt was the gift of the Nile.” B. Upper and Lower Egypt 1. For most of their history ancient Egyptians knew only t ...
... A. The world’s longest river – it flows northward toward the Mediterranean Sea for 4100 miles --- longer than the distance from NJ to CA! 1. Herodotus – The Greek historian said that “Egypt was the gift of the Nile.” B. Upper and Lower Egypt 1. For most of their history ancient Egyptians knew only t ...
Chapter 3 - STA-MrFairesClasses
... Egypt was split into two parts, Upper and Lower Egypt. Each had it’s own king. See crown diagram below. ...
... Egypt was split into two parts, Upper and Lower Egypt. Each had it’s own king. See crown diagram below. ...
Egypt Answer Key
... 1. the chief god, who protected both rich and poor 2. god of the living and dead; god of the afterlife 3. mother figure who protected children; wife of Osiris 4. Answers will vary. 5. a life after death 6. dead body preserved in lifelike condition 7. a huge building with four sloping triangular-shap ...
... 1. the chief god, who protected both rich and poor 2. god of the living and dead; god of the afterlife 3. mother figure who protected children; wife of Osiris 4. Answers will vary. 5. a life after death 6. dead body preserved in lifelike condition 7. a huge building with four sloping triangular-shap ...
PDF sample
... people’s need to expand their access to water and land. Tribal warfare would have been commonplace, although inter-tribal trading between the north and the south was also evident. Centres of power developed in small autonomous political entities in Lower Egypt and at two centres in Upper Egypt, spec ...
... people’s need to expand their access to water and land. Tribal warfare would have been commonplace, although inter-tribal trading between the north and the south was also evident. Centres of power developed in small autonomous political entities in Lower Egypt and at two centres in Upper Egypt, spec ...
Strong government meant people were safe.
... – As a result they could stay in one place, and start to farm. – People were no longer nomadic (moving from place to place). They could now live more settled lives. ...
... – As a result they could stay in one place, and start to farm. – People were no longer nomadic (moving from place to place). They could now live more settled lives. ...
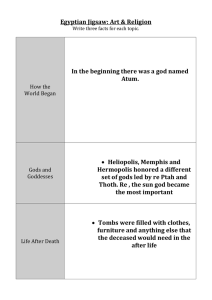
E_Shirley_Egyptian Jigsaw
... rafts that did not have sails and would ride on the rivers currents. By 2900 B.C.E. the Egyptians invented stringer sturdier boats with sails that were made of wood and no longer the reeds of a papyrus plant ...
... rafts that did not have sails and would ride on the rivers currents. By 2900 B.C.E. the Egyptians invented stringer sturdier boats with sails that were made of wood and no longer the reeds of a papyrus plant ...
Worldview - Ms. Westgate's CAWS website
... When the ka acted, all was well, both spiritually and materially Sin was called "an abomination of the ka" The ka could also be seen as the conscience or guide of each individual, urging kindness, quietude, honor and compassion In images and statues of the ka, they are depicted as their owner in an ...
... When the ka acted, all was well, both spiritually and materially Sin was called "an abomination of the ka" The ka could also be seen as the conscience or guide of each individual, urging kindness, quietude, honor and compassion In images and statues of the ka, they are depicted as their owner in an ...
Pharaoh: King of Ancient Egypt Educator`s Resource
... piece depicts Ramses II, a great pharaoh who was born around 1303 BCE. His father was Pharaoh Seti I, and his mother Queen Tuya. Named after his grandfather Ramses I, he became pharaoh at age 25 upon the death of his father. Ramses II was known as a great military ruler, leading Egypt in battle agai ...
... piece depicts Ramses II, a great pharaoh who was born around 1303 BCE. His father was Pharaoh Seti I, and his mother Queen Tuya. Named after his grandfather Ramses I, he became pharaoh at age 25 upon the death of his father. Ramses II was known as a great military ruler, leading Egypt in battle agai ...
Chapter 4, Section 1: Geography and Ancient Egypt
... 19. We are also known as royalty because we have wealth and power. Like the pharaohs, we could often afford to be mummified. Who are we? ...
... 19. We are also known as royalty because we have wealth and power. Like the pharaohs, we could often afford to be mummified. Who are we? ...
Ancient Egypt - Alabama School of Fine Arts
... • Conquered Palestine & Syria to the east. Conquered more of Nubia in the south. • Now Egypt was a true Empire. Brought Egypt to the height of its ...
... • Conquered Palestine & Syria to the east. Conquered more of Nubia in the south. • Now Egypt was a true Empire. Brought Egypt to the height of its ...
ancient egypt
... The flooding of the Nile rendered the narrow strip of land on either side of the river extremely fertile. INTENSIVE AGRICULTURE was practiced by the majority of the peasant population. who played a vital role within the country's STRICT HIERARHICAL SOCIETY. As the flood waters receded, SOWING and ...
... The flooding of the Nile rendered the narrow strip of land on either side of the river extremely fertile. INTENSIVE AGRICULTURE was practiced by the majority of the peasant population. who played a vital role within the country's STRICT HIERARHICAL SOCIETY. As the flood waters receded, SOWING and ...