T.A.W. Chapter 8
... and more than 100 children. He wasn't shy about glorifying himself, either. He had hundreds of statues of himself erected all around Egypt. Some of them were over 60 feet high. Ramses was a fearless soldier from a young age. He fought alongside his father in various battles. He was made a captain in ...
... and more than 100 children. He wasn't shy about glorifying himself, either. He had hundreds of statues of himself erected all around Egypt. Some of them were over 60 feet high. Ramses was a fearless soldier from a young age. He fought alongside his father in various battles. He was made a captain in ...
Ancient egypt - Distribution Access
... research the topic further with the Internet and print resources provided. ...
... research the topic further with the Internet and print resources provided. ...
Ancient Egyptian Art
... Ra is the eagle god of the sun. Anubis god of the dead Bastet is the Cat goddess. Sehkmet goddess of fire, war and plague Nut is the goddess of sky and stars, mother of gods. Geb is the green god of Earth. Horus is the god with falcon's head, god of pharaohs. Osiris is the god of the afterlife. Isi ...
... Ra is the eagle god of the sun. Anubis god of the dead Bastet is the Cat goddess. Sehkmet goddess of fire, war and plague Nut is the goddess of sky and stars, mother of gods. Geb is the green god of Earth. Horus is the god with falcon's head, god of pharaohs. Osiris is the god of the afterlife. Isi ...
Social Std - Nour Al Maaref International School
... like to go to war to capture neighboring kingdoms. It was said that his army defeated Gilgamesh and tore the walls of Uruk down. He was king of the very first empire. 7. What is an Empire? An empire is land with different territories and peoples under a single rule. Sargon was said to be the first k ...
... like to go to war to capture neighboring kingdoms. It was said that his army defeated Gilgamesh and tore the walls of Uruk down. He was king of the very first empire. 7. What is an Empire? An empire is land with different territories and peoples under a single rule. Sargon was said to be the first k ...
Click here to see our finished project.
... This was called monarchy. The pharaoh would pick rich people and assign them to different estates. These rich people would tell other people what to do for the pharaoh, and they would have to do whatever the pharaoh told them. Monarchy : supreme power or sovereignty held by a single person. ...
... This was called monarchy. The pharaoh would pick rich people and assign them to different estates. These rich people would tell other people what to do for the pharaoh, and they would have to do whatever the pharaoh told them. Monarchy : supreme power or sovereignty held by a single person. ...
e ducation k i t
... escaped major looting in antiquity and was disThe scarab beetle is a symbol of intelligence, covered virtually intact. It was filled with goods rebirth and eternal life. for his afterlife: food, clothing, weapons, jewels and gold coated furniture and chariots. He had three coffins, one inside the ot ...
... escaped major looting in antiquity and was disThe scarab beetle is a symbol of intelligence, covered virtually intact. It was filled with goods rebirth and eternal life. for his afterlife: food, clothing, weapons, jewels and gold coated furniture and chariots. He had three coffins, one inside the ot ...
MAJOR PERIODS IN EGYPTIAN HISTORY
... 2278-2184: Reign of Pepi II, last king of Dynasty 6 First Intermediate Period (Dynasties 7-10); general unrest Middle Kingdom Period (Dynasties 11-12) 1991-1962: Amenemhet I rules, first king of Dynasty 12 1971-1926: Senwosert I rules, second king of Dynasty 12 Second Intermediate Period (Dynasties ...
... 2278-2184: Reign of Pepi II, last king of Dynasty 6 First Intermediate Period (Dynasties 7-10); general unrest Middle Kingdom Period (Dynasties 11-12) 1991-1962: Amenemhet I rules, first king of Dynasty 12 1971-1926: Senwosert I rules, second king of Dynasty 12 Second Intermediate Period (Dynasties ...
CH. 4 Assyrians WH PPt
... New Empire Semitic-speaking people who exploited the use of iron weapons to build an empire by 700 B.C. Semitic-Speaking Spoke Semitic language Included Territory From including Mesopotamia, some of the Iranian Plateau, Asia Minor, Syria, Palestine, and Egypt. ...
... New Empire Semitic-speaking people who exploited the use of iron weapons to build an empire by 700 B.C. Semitic-Speaking Spoke Semitic language Included Territory From including Mesopotamia, some of the Iranian Plateau, Asia Minor, Syria, Palestine, and Egypt. ...
Egypt-Study
... C. The Nile rushed through rocky, hilly lands south of Egypt. At several points, this terrain caused cataracts, or strong rapids, to form. These rapids made sailing through the Upper Egypt portion of the Nile very difficult. D. In Lower Egypt, the Nile divided into several branches that fanned out a ...
... C. The Nile rushed through rocky, hilly lands south of Egypt. At several points, this terrain caused cataracts, or strong rapids, to form. These rapids made sailing through the Upper Egypt portion of the Nile very difficult. D. In Lower Egypt, the Nile divided into several branches that fanned out a ...
Emerging
... During this time, the Egyptians created some of the greatest works of ancient Egypt. They built the pyramids. The first was Djoser’s Stepped Pyramid at Sakkara. As time passed, they built smoother and larger pyramids. These in time included the Great Pyramid of Khufu at Giza. They also carved the Gr ...
... During this time, the Egyptians created some of the greatest works of ancient Egypt. They built the pyramids. The first was Djoser’s Stepped Pyramid at Sakkara. As time passed, they built smoother and larger pyramids. These in time included the Great Pyramid of Khufu at Giza. They also carved the Gr ...
Egypt-Geography-Notes-Outline
... C. The Nile rushed through rocky, hilly lands south of Egypt. At several points, this terrain caused cataracts, or strong rapids, to form. These rapids made sailing through the Upper Egypt portion of the Nile very difficult. D. In Lower Egypt, the Nile divided into several branches that fanned out a ...
... C. The Nile rushed through rocky, hilly lands south of Egypt. At several points, this terrain caused cataracts, or strong rapids, to form. These rapids made sailing through the Upper Egypt portion of the Nile very difficult. D. In Lower Egypt, the Nile divided into several branches that fanned out a ...
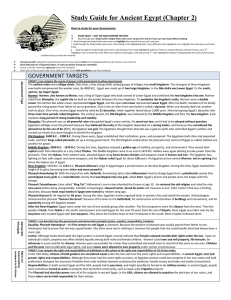
Study Guide for Ancient Egypt
... trade, and their kings called pharaohs set up a strong government. The Old Kingdom ended when the pharaohs lost control of Egypt as nobles battled one another for power. Middle Kingdom: 2050 B.C. - 1670 B.C. During this time, Egyptians enjoyed a golden age of stability, prosperity, and achievement. ...
... trade, and their kings called pharaohs set up a strong government. The Old Kingdom ended when the pharaohs lost control of Egypt as nobles battled one another for power. Middle Kingdom: 2050 B.C. - 1670 B.C. During this time, Egyptians enjoyed a golden age of stability, prosperity, and achievement. ...
Chapter 1
... Suppiluliumas I (c. 1370 – 1330 B.C.E.) The Use of Iron Decline: Internal Strife; the Sea Peoples; the Gasga ...
... Suppiluliumas I (c. 1370 – 1330 B.C.E.) The Use of Iron Decline: Internal Strife; the Sea Peoples; the Gasga ...
Name: _________ Date_________________ Class________
... The Afterlife a. Egyptians believed life after death was better than present life b. One of the most important writing in ancient Egypt was The Book of the Dead, which explained what a person can expect in the afterlife c. Earliest Egyptians believed only the pharaoh could enjoy the afterlife i. The ...
... The Afterlife a. Egyptians believed life after death was better than present life b. One of the most important writing in ancient Egypt was The Book of the Dead, which explained what a person can expect in the afterlife c. Earliest Egyptians believed only the pharaoh could enjoy the afterlife i. The ...
UNITED DIVERS.indd
... Egypt is famous for its ancient civilization and some of the world’s most famous monuments, including the Giza pyramid complex and its Great Sphinx. Its ancient ruins, such as those of Memphis, Thebes, Karnak and the Valley of the Kings, are a significant focus of archaeological study. The artifacts ...
... Egypt is famous for its ancient civilization and some of the world’s most famous monuments, including the Giza pyramid complex and its Great Sphinx. Its ancient ruins, such as those of Memphis, Thebes, Karnak and the Valley of the Kings, are a significant focus of archaeological study. The artifacts ...
The Stability of Ancient Egypt: Flood and Sun - 59-208-201-f10
... political architecture was built • Art was produced not only for religious purposes but to show off wealth and sophistication ...
... political architecture was built • Art was produced not only for religious purposes but to show off wealth and sophistication ...
File - Mr. Murray`s Class
... The final symbol of Pharaonic power was the blue beard of Ptah, the Egyptian god of wisdom. The blue beard of Ptah was also always worn in public. Taken all together, pharaoh was embodiment of life, wisdom and protection. He could strike down his enemies like a deadly cobra and then feast on their p ...
... The final symbol of Pharaonic power was the blue beard of Ptah, the Egyptian god of wisdom. The blue beard of Ptah was also always worn in public. Taken all together, pharaoh was embodiment of life, wisdom and protection. He could strike down his enemies like a deadly cobra and then feast on their p ...
尼罗河的礼物——埃及尼罗河的礼物——埃及
... This pyramid was actually not a pyramid, but a step-pyramid made from a series of mastabas placed one on top of another. It was built under the direction of the architect. Imohtep considered by many historians to be the first known architect of western history. ...
... This pyramid was actually not a pyramid, but a step-pyramid made from a series of mastabas placed one on top of another. It was built under the direction of the architect. Imohtep considered by many historians to be the first known architect of western history. ...
Age of Pharaohs
... repelled the Sea People, who came from the Mediterranean sea. • 8 more kings named ruled, but the country weakened. • The high priests of Thebes took power over Upper Egypt. ...
... repelled the Sea People, who came from the Mediterranean sea. • 8 more kings named ruled, but the country weakened. • The high priests of Thebes took power over Upper Egypt. ...
File
... The Harvesting Season. The fully grown crops had to be cut down (harvested) and removed before the Nile flooded again. It was also the time to repair the canals ready for the next flood. ...
... The Harvesting Season. The fully grown crops had to be cut down (harvested) and removed before the Nile flooded again. It was also the time to repair the canals ready for the next flood. ...
File
... However until now we still read ancient books and study their history, but there are two questions that are always through our mind, what was before the pharaohs? Why did they start to disappear? Where did they go? King Menes was the first official pharaoh to rule Egypt; he combined lower and upper ...
... However until now we still read ancient books and study their history, but there are two questions that are always through our mind, what was before the pharaohs? Why did they start to disappear? Where did they go? King Menes was the first official pharaoh to rule Egypt; he combined lower and upper ...
SSWGEegy - Mr Boayue`s Social Studies site
... The pyramids were built as tombs for Egypt’s pharaohs. The Egyptians believed that burial sites, especially royal tombs, were very important, so they built spectacular monuments in which to bury their rulers. The most spectacular were the pyramids—huge, stone tombs with four triangle-shaped sides th ...
... The pyramids were built as tombs for Egypt’s pharaohs. The Egyptians believed that burial sites, especially royal tombs, were very important, so they built spectacular monuments in which to bury their rulers. The most spectacular were the pyramids—huge, stone tombs with four triangle-shaped sides th ...