2 Pyramids on the Nile - Mr. Villines` History Page
... build, the pyramid builders scratched messages for the ages inside the pyramids. Who were the pyramid builders? The ancient Greek historian Herodotus claimed that the pharaohs worked an army of laborers to death. However, it was actually peasants who provided most of the labor. They had to work for ...
... build, the pyramid builders scratched messages for the ages inside the pyramids. Who were the pyramid builders? The ancient Greek historian Herodotus claimed that the pharaohs worked an army of laborers to death. However, it was actually peasants who provided most of the labor. They had to work for ...
Exploring Ancient Egypt Unit Summary
... the Nile but were not a uniformed group. The land was only known as Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Between 3000 and 2649 BC, Upper and Lower Egypt united together to form Egypt. The capital was located in Memphis. Now discuss the different Kingdoms. First there was the Old Kingdom, which was form at t ...
... the Nile but were not a uniformed group. The land was only known as Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Between 3000 and 2649 BC, Upper and Lower Egypt united together to form Egypt. The capital was located in Memphis. Now discuss the different Kingdoms. First there was the Old Kingdom, which was form at t ...
Diapositiva 1 - Ancient Egypt
... merged into two kingdoms of Upper and Lower Egypt, in doing so founded what was to become the first “Dynasty” Of Ancient Egypt. • The rulers of the early farming communities are thought to have been religious leaders, “rainmakers” and controllers of the “flood”. • The majority of the population of E ...
... merged into two kingdoms of Upper and Lower Egypt, in doing so founded what was to become the first “Dynasty” Of Ancient Egypt. • The rulers of the early farming communities are thought to have been religious leaders, “rainmakers” and controllers of the “flood”. • The majority of the population of E ...
PACKET #2 River Valley Civilizations PART I: Egypt and
... o Old Kingdom—2686-2125 bce; construction of largest pyramids. After collapse there was a period of chaos. Ruled by a pharaoh with absolute power. Considered a divine institution o Middle Kingdom—new royal dynasty lasted from 2055-1650 bce Golden age of Egypt Invaded by the Hyksos who used hor ...
... o Old Kingdom—2686-2125 bce; construction of largest pyramids. After collapse there was a period of chaos. Ruled by a pharaoh with absolute power. Considered a divine institution o Middle Kingdom—new royal dynasty lasted from 2055-1650 bce Golden age of Egypt Invaded by the Hyksos who used hor ...
Ancient Egypt
... The River in the Sand Desert covers most of Egypt. The sands spread for hundreds of miles to the west and the south, discouraging outsiders from invading. The Nile River, which runs through the desert, is sometimes called “the river in the sand.” The Nile’s yearly floods deposited tons of silt in th ...
... The River in the Sand Desert covers most of Egypt. The sands spread for hundreds of miles to the west and the south, discouraging outsiders from invading. The Nile River, which runs through the desert, is sometimes called “the river in the sand.” The Nile’s yearly floods deposited tons of silt in th ...
File - Mrs. Sumner`s Social Science Course Website
... Pyramids were tombs for the mummified bodies of pharaohs. The largest and most magnificent of all pyramids was built under King Khufu. Constructed at Giza around 2540 B.C., the famous Great Pyramid of King Khufu covers 13 acres measure 756 ft at each side of its base and stands 481 ft high. Guardin ...
... Pyramids were tombs for the mummified bodies of pharaohs. The largest and most magnificent of all pyramids was built under King Khufu. Constructed at Giza around 2540 B.C., the famous Great Pyramid of King Khufu covers 13 acres measure 756 ft at each side of its base and stands 481 ft high. Guardin ...
Moses - Exodus - WordPress.com
... --God called Moses at the “burning bush” and told him he would be the leader of the children of Israel. (Ex. 3:10) --Before Israel’s deliverance was accomplished, God had to send ten national calamities to overcome the obstinate refusal of Pharaoh. These are called the 10 Plagues of Egypt. (Ex. 7:4) ...
... --God called Moses at the “burning bush” and told him he would be the leader of the children of Israel. (Ex. 3:10) --Before Israel’s deliverance was accomplished, God had to send ten national calamities to overcome the obstinate refusal of Pharaoh. These are called the 10 Plagues of Egypt. (Ex. 7:4) ...
File - History Scholars
... A. Unlike Sumeria, no independent city-states in Egypt B. Menes, the king of Upper Egypt, 1. united the two regions – Upper and Lower – in 3,100 B.C.E. 2. Capital: Memphis 3. Creates first Egyptian dynasty C. The Pharaoh [means, royal house] – the ruler of Egypt 1. were considered gods; served both ...
... A. Unlike Sumeria, no independent city-states in Egypt B. Menes, the king of Upper Egypt, 1. united the two regions – Upper and Lower – in 3,100 B.C.E. 2. Capital: Memphis 3. Creates first Egyptian dynasty C. The Pharaoh [means, royal house] – the ruler of Egypt 1. were considered gods; served both ...
Chapter 3: Art of Ancient Egypt In this chapter you will... In this
... ! The Predynastic Period was a time of important social & political transition that comes before the unification of Egypt under a single ruler. ! We will go through periods in time, beginning with the Early Dynastic Period, where we will see Egyptian history as it follows a succession of rulers inhe ...
... ! The Predynastic Period was a time of important social & political transition that comes before the unification of Egypt under a single ruler. ! We will go through periods in time, beginning with the Early Dynastic Period, where we will see Egyptian history as it follows a succession of rulers inhe ...
Chapter 5 - Lesson 4 The New Kingdom A Woman Pharaoh
... (Answer: through conquest and a peace treaty) Ramses II • Ramses II ruled in 1279 B.C., 44 years after Tutankhamen died Empire Builder • Wanted to make Egypt powerful through war • extended territory south into Nubia & to eastern Mediterranean area Military Leader • Ramses led army against old Egypt ...
... (Answer: through conquest and a peace treaty) Ramses II • Ramses II ruled in 1279 B.C., 44 years after Tutankhamen died Empire Builder • Wanted to make Egypt powerful through war • extended territory south into Nubia & to eastern Mediterranean area Military Leader • Ramses led army against old Egypt ...
Atlantis and Egypt : two bound destinies
... Libyan kings, while a new dynasty of Kushite rulers emerged in the region of the Fourth Cataract. They invaded Egypt ca.760 B.C. and reigned on both countries for nearly one century. It is a fact that the black pharaohs of the 25th dynasty always claimed to be the heirs of their ancient Egyptian rul ...
... Libyan kings, while a new dynasty of Kushite rulers emerged in the region of the Fourth Cataract. They invaded Egypt ca.760 B.C. and reigned on both countries for nearly one century. It is a fact that the black pharaohs of the 25th dynasty always claimed to be the heirs of their ancient Egyptian rul ...
Introduction to the Cultures of Egypt and Mesopotamia
... Mode of Assessment: There will be a three-hour written examination at the end of the academic year. The paper is divided into two sections: Section A consists of five comparative questions in which candidates are expected to refer to both Egyptian and Mesopotamian cultures; Section B consists of fi ...
... Mode of Assessment: There will be a three-hour written examination at the end of the academic year. The paper is divided into two sections: Section A consists of five comparative questions in which candidates are expected to refer to both Egyptian and Mesopotamian cultures; Section B consists of fi ...
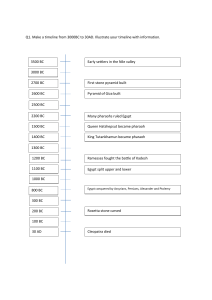
Q1. Make a timeline from 3000BC to 30AD. Illustrate your timeline
... Q6. Who discovered King Tutankhamen’s tomb, what did he find in there and what does this tell us about ancient Egypt? A man called Howard Carter, an archaeologist along with a man called Carnarvon and his wife found King Tutankhamen’s tomb. In the year 1922, when they were looking for King Tutankham ...
... Q6. Who discovered King Tutankhamen’s tomb, what did he find in there and what does this tell us about ancient Egypt? A man called Howard Carter, an archaeologist along with a man called Carnarvon and his wife found King Tutankhamen’s tomb. In the year 1922, when they were looking for King Tutankham ...
Ancient Egypt - Social Studies 210
... The River in the Sand Desert covers most of Egypt. The sands spread for hundreds of miles to the west and the south, discouraging outsiders from invading. The Nile River, which runs through the desert, is sometimes called “the river in the sand.” The Nile’s yearly floods deposited tons of silt in th ...
... The River in the Sand Desert covers most of Egypt. The sands spread for hundreds of miles to the west and the south, discouraging outsiders from invading. The Nile River, which runs through the desert, is sometimes called “the river in the sand.” The Nile’s yearly floods deposited tons of silt in th ...
Ancient Egyptian Timeline
... Few monuments from this period survived. Each king reigned for only a short time. Some of these kings were born commoners. The eastern Delta region broke away during this time. ...
... Few monuments from this period survived. Each king reigned for only a short time. Some of these kings were born commoners. The eastern Delta region broke away during this time. ...
CH-3-LECTURE
... culture and how are they similar or different in style and cultural context? What would be some reasons for the modification of pyramid scale and institution of rock-cut tombs as seen at Beni Hasan? Why does a change in religion bring about a change in art in ancient Egypt? Describe some specifi ...
... culture and how are they similar or different in style and cultural context? What would be some reasons for the modification of pyramid scale and institution of rock-cut tombs as seen at Beni Hasan? Why does a change in religion bring about a change in art in ancient Egypt? Describe some specifi ...
egyptian art - amorart
... The Beginning- Around 5000 BCE prehistoric hunters and their families settled in the fertile valley of the Nile River. There was an abundance if food in early Egypt. The communities living along the Nile River gradually developed into complex cultures. The earliest dynastic period began around 3100 ...
... The Beginning- Around 5000 BCE prehistoric hunters and their families settled in the fertile valley of the Nile River. There was an abundance if food in early Egypt. The communities living along the Nile River gradually developed into complex cultures. The earliest dynastic period began around 3100 ...
ANCIENT EGYPTIAN FURNITURE Houses
... and King Khufu's ship is well known and demonstrates best how ships were built during that period. ...
... and King Khufu's ship is well known and demonstrates best how ships were built during that period. ...
Section 1 — Introduction
... From a young age, Ramses was a fearless soldier. He fought alongside his father in various battles. At the age of ten, Ramses was made a captain in the Egyptian army. Ramses tried to defend an Egyptian empire that extended north into Canaan. His most famous military campaigns were against the Hittit ...
... From a young age, Ramses was a fearless soldier. He fought alongside his father in various battles. At the age of ten, Ramses was made a captain in the Egyptian army. Ramses tried to defend an Egyptian empire that extended north into Canaan. His most famous military campaigns were against the Hittit ...
Daily Life in Ancient Egypt
... • 27 day festival for all people • Brought people from different social classes together • Honored the god Ra by adorning his statue with jewelry and placing in a shrine on ceremonial boat called a barque. • These various social classes made up the social pyramid of Egypt. ...
... • 27 day festival for all people • Brought people from different social classes together • Honored the god Ra by adorning his statue with jewelry and placing in a shrine on ceremonial boat called a barque. • These various social classes made up the social pyramid of Egypt. ...
Chapter 11 section 1 Power Point Notes
... Menes wanted to unify the kingdoms of Upper and Lower Egypt. Menes wore both the white and red crown to symbolize his leadership over both kingdoms. Many consider Menes to be the first pharaoh of Egypt. Menes also founded Egypt’s first dynasty, or series of rulers from the same family. Egypt’s First ...
... Menes wanted to unify the kingdoms of Upper and Lower Egypt. Menes wore both the white and red crown to symbolize his leadership over both kingdoms. Many consider Menes to be the first pharaoh of Egypt. Menes also founded Egypt’s first dynasty, or series of rulers from the same family. Egypt’s First ...
Egyptian Jeopardy
... Originally, Egyptian writing was done on stone. That was until this Egyptian “paper” was created by flattening and drying out reeds that grew on the banks of the Nile. ...
... Originally, Egyptian writing was done on stone. That was until this Egyptian “paper” was created by flattening and drying out reeds that grew on the banks of the Nile. ...
Ancient Egypt - World Book Encyclopedia
... 4. Hieroglyphics is a system of picture symbols that stood for ideas and sounds that the ancient Egyptians used as their written language. It consisted of over 700 picture symbols. A simpler hieroglyphic form called hieratic and demotic were developed for everyday use. 5. During the New Kingdom, anc ...
... 4. Hieroglyphics is a system of picture symbols that stood for ideas and sounds that the ancient Egyptians used as their written language. It consisted of over 700 picture symbols. A simpler hieroglyphic form called hieratic and demotic were developed for everyday use. 5. During the New Kingdom, anc ...
Ancient Egypt | Student (Word)
... 4. Hieroglyphics is a system of picture symbols that stood for ideas and sounds that the ancient Egyptians used as their written language. It consisted of over 700 picture symbols. A simpler hieroglyphic form called hieratic and demotic were developed for everyday use. 5. During the New Kingdom, anc ...
... 4. Hieroglyphics is a system of picture symbols that stood for ideas and sounds that the ancient Egyptians used as their written language. It consisted of over 700 picture symbols. A simpler hieroglyphic form called hieratic and demotic were developed for everyday use. 5. During the New Kingdom, anc ...