The veins in the plantar foot run back up the leg
... comitantes vv. along the path of the posterior tibial a. and peroneal a. ...
... comitantes vv. along the path of the posterior tibial a. and peroneal a. ...
Gi tract embryology 1
... • The epithelial buds will go through repeated branching to form solid ducts ...
... • The epithelial buds will go through repeated branching to form solid ducts ...
Pregnancy and Human Development
... (Figure 28.2, 2 ). The acrosomal reaction involves the breakdown of the plasma membrane and the acrosomal membrane, and release of acrosomal enzymes (hyaluronidase, acrosin, proteases, and others) that digest holes through the zona pellucida (Figure 28.2, 3 ). Hundreds of acrosomes must undergo exoc ...
... (Figure 28.2, 2 ). The acrosomal reaction involves the breakdown of the plasma membrane and the acrosomal membrane, and release of acrosomal enzymes (hyaluronidase, acrosin, proteases, and others) that digest holes through the zona pellucida (Figure 28.2, 3 ). Hundreds of acrosomes must undergo exoc ...
compartments of the middle ear
... Inferior Incudal Space: It extends from inferior surface of incus laterally upto posterior mallear fold. It is medially limited by medial incudal fold and anteriorly limited by interossicular fold; Thus this space lies between long crus of the incus and upper two third of malleus handle. Posterior P ...
... Inferior Incudal Space: It extends from inferior surface of incus laterally upto posterior mallear fold. It is medially limited by medial incudal fold and anteriorly limited by interossicular fold; Thus this space lies between long crus of the incus and upper two third of malleus handle. Posterior P ...
Michigan Fishes II
... Bowfins: family characteristics • Bony (gular) plate between lower jaw bones • Single long dorsal fin • Cycloid scales • Caudal fin abbreviate heterocercal Amia calva: bowfin • A.k.a. dogfish, grinnel • Black spot at caudal fin base • Mottled coloration • Similar to burbot, mudminnow • Only species ...
... Bowfins: family characteristics • Bony (gular) plate between lower jaw bones • Single long dorsal fin • Cycloid scales • Caudal fin abbreviate heterocercal Amia calva: bowfin • A.k.a. dogfish, grinnel • Black spot at caudal fin base • Mottled coloration • Similar to burbot, mudminnow • Only species ...
Development of the Gastrointestinal Tract
... of mesoderm, but this need not be pancreatic mesoderm. Differentiation of the islets of Langerhans does not require the presence of mesoderm or of pancreatic acini. It was originally thought that the Islets were derived from the neural crest. Evidence from quail-chick chimera cell tracers and transg ...
... of mesoderm, but this need not be pancreatic mesoderm. Differentiation of the islets of Langerhans does not require the presence of mesoderm or of pancreatic acini. It was originally thought that the Islets were derived from the neural crest. Evidence from quail-chick chimera cell tracers and transg ...
anterior tibial artery
... Regio cruris - Leg o between knee & ankle joint o includes most of tibia & fibula Distally, structures pass between the leg & foot mainly through tarsal tunnel on the posteromedial side of the ankle, Except anterior tibial artery & ends of the deep and superficial fibular nerves ...
... Regio cruris - Leg o between knee & ankle joint o includes most of tibia & fibula Distally, structures pass between the leg & foot mainly through tarsal tunnel on the posteromedial side of the ankle, Except anterior tibial artery & ends of the deep and superficial fibular nerves ...
Somatosensory Systems: Proprioception - Dr. Jacobs
... this conveys information about the lower body. In the upper thoracic and cervical segments (T6 and above) they occupy the fasciculus cuneatus. The posterior intermediate sulcus separates the gracile and cuneate fasciculi in the upper thoracic and cervical spinal cord regions. A lesion eliminating on ...
... this conveys information about the lower body. In the upper thoracic and cervical segments (T6 and above) they occupy the fasciculus cuneatus. The posterior intermediate sulcus separates the gracile and cuneate fasciculi in the upper thoracic and cervical spinal cord regions. A lesion eliminating on ...
Frontal Lobe
... subdividing the spinal gray matter into layers or laminae, based upon differences in cytoarchitecture • Scheme was initially developed for animal models, but is widely used in discussions of the human spinal cord • Ten different laminae described for the human spinal cord Laminae I-VI ...
... subdividing the spinal gray matter into layers or laminae, based upon differences in cytoarchitecture • Scheme was initially developed for animal models, but is widely used in discussions of the human spinal cord • Ten different laminae described for the human spinal cord Laminae I-VI ...
Phylum Platyhelminthes
... • A coelom is a fluid-filled body cavity that is lined with tissue derived from mesoderm. • The digestive cavity is the only body cavity in a flatworm. ...
... • A coelom is a fluid-filled body cavity that is lined with tissue derived from mesoderm. • The digestive cavity is the only body cavity in a flatworm. ...
Unit 2. Suboccipital Triangle, Vertebral Column, Spinal Cord
... Remove the semispinalis capitis muscle from both sides to expose the suboccipital triangle (Plates 171; 4.35-4.36, Table 4.5 and figures-p.318) keeping the greater occipital nerve intact. Carefully clean the surface of the rectus capitis posterior major and minor muscles and the superior and inferio ...
... Remove the semispinalis capitis muscle from both sides to expose the suboccipital triangle (Plates 171; 4.35-4.36, Table 4.5 and figures-p.318) keeping the greater occipital nerve intact. Carefully clean the surface of the rectus capitis posterior major and minor muscles and the superior and inferio ...
Document
... – Difficulty turning head to side (with resistance) SCM – Shoulders droop/cannot raise and retract shoulder/cannot raise arm above horizontal Trapezius ...
... – Difficulty turning head to side (with resistance) SCM – Shoulders droop/cannot raise and retract shoulder/cannot raise arm above horizontal Trapezius ...
Reticular Formation of the Brain Stem
... infront of aqueduct, it consists of three parts: a. Crus cerebri: the most anterior part which consists of pyramidal and corticonuclear fibers. b. Substantia Nigra: a thick lamina of gray mater. It is an extrapyramidal center. c. Tegmentum: the posterior part of the cerebral peduncle. It contains as ...
... infront of aqueduct, it consists of three parts: a. Crus cerebri: the most anterior part which consists of pyramidal and corticonuclear fibers. b. Substantia Nigra: a thick lamina of gray mater. It is an extrapyramidal center. c. Tegmentum: the posterior part of the cerebral peduncle. It contains as ...
Neuro Pathways
... taste buds solitary tract nucleus of the solitary tract anterior insula Note: This pathway doesn’t relay in the thalamus or cross the midline Vestibular: vestibulocochlear n. vestibular nuclei medial vestibulospinal tract (in MLF) head posture lateral vestibulospinal tract (in MLF) ...
... taste buds solitary tract nucleus of the solitary tract anterior insula Note: This pathway doesn’t relay in the thalamus or cross the midline Vestibular: vestibulocochlear n. vestibular nuclei medial vestibulospinal tract (in MLF) head posture lateral vestibulospinal tract (in MLF) ...
Slide 1
... On the upper surface between the anterior part of the jugular foramen and the hypoglossal canal Laterally the condylar part fused with the posterior part of the temporal bone. ...
... On the upper surface between the anterior part of the jugular foramen and the hypoglossal canal Laterally the condylar part fused with the posterior part of the temporal bone. ...
Slide 1 - AccessSurgery
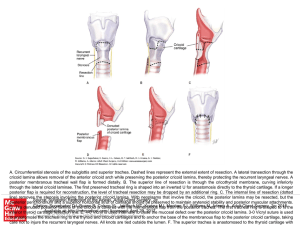
... A. Circumferential stenosis of the subglottis and superior trachea. Dashed lines represent the external extent of resection. A lateral transection through the cricoid lamina allows removal of the anterior cricoid arch while preserving the posterior cricoid lamina, thereby protecting the recurrent la ...
... A. Circumferential stenosis of the subglottis and superior trachea. Dashed lines represent the external extent of resection. A lateral transection through the cricoid lamina allows removal of the anterior cricoid arch while preserving the posterior cricoid lamina, thereby protecting the recurrent la ...
The Embryology of Patella1
... be seen, PI. I, Fig. 15 and 16, which during the first of the present period increase rapidly in size growing principally inwards toward the animal pole, while in doing so they encroach more and more upon the segmentation cavity and finally nearly obliterate it. PI. I, Fig. 15, shows a surface view ...
... be seen, PI. I, Fig. 15 and 16, which during the first of the present period increase rapidly in size growing principally inwards toward the animal pole, while in doing so they encroach more and more upon the segmentation cavity and finally nearly obliterate it. PI. I, Fig. 15, shows a surface view ...
Brainstem- Midbrain, Pons, Medulla oblongata
... Special Sensory Combination of two or more of above ...
... Special Sensory Combination of two or more of above ...
File
... 5 Enzymes released during the cortical reaction harden the zona pellucida, which now functions as a block to ...
... 5 Enzymes released during the cortical reaction harden the zona pellucida, which now functions as a block to ...
Central Nervous System
... fact that their expression is excluded from ventral regions by SHH at later stages. Thus, they confer on ventral cell types competence to respond appropriately to SHH and other ventralizing signals. Yet another PAX gene, PAX6, is expressed throughout the elevating neural folds except in the midline, ...
... fact that their expression is excluded from ventral regions by SHH at later stages. Thus, they confer on ventral cell types competence to respond appropriately to SHH and other ventralizing signals. Yet another PAX gene, PAX6, is expressed throughout the elevating neural folds except in the midline, ...
Answers to What Did You Learn questions
... The two major triangles of the neck are the anterior triangle and the posterior triangle. The anterior cervical triangle can be subdivided into the carotid (contains the carotid artery), muscular (contains the sternohyoid and sternothyroid muscles), submandibular (contains the submandibular gland), ...
... The two major triangles of the neck are the anterior triangle and the posterior triangle. The anterior cervical triangle can be subdivided into the carotid (contains the carotid artery), muscular (contains the sternohyoid and sternothyroid muscles), submandibular (contains the submandibular gland), ...
Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
... ethmoid bulla form domes that are joined together. It often appears that this is all there is and they might fool you into thinking that one of them is a small frontal sinus. ...
... ethmoid bulla form domes that are joined together. It often appears that this is all there is and they might fool you into thinking that one of them is a small frontal sinus. ...
Sciatic nerve block MGMC
... • The needle should be directed through the entry site toward an imaginary point where the femoral vessels course under the inguinal ligament • Paraesthesia or motor response. • Bone hits . Go towards trochanter but not more than 2 cm ...
... • The needle should be directed through the entry site toward an imaginary point where the femoral vessels course under the inguinal ligament • Paraesthesia or motor response. • Bone hits . Go towards trochanter but not more than 2 cm ...
SPINAL ANATOMY
... BEST WAY TO CLEAN SEPTIC TANK = MICROORGANISMS 22. BEST TERM TO DETERMINE POLLUTION OF WATER = BIOLOGICAL O2 DEMAND 23. SEVERE LACK OF B LYMPHOCYTES AND T LYMPHOCYTES = LEUKEMIA 24. RETROVIRUS = RNA – DNA 25. REASON F & D REQ. PASTEURIZATION OF EGGS = PREVENT SALMONELLA 26. FLUKE CALLED PARAGONIA WE ...
... BEST WAY TO CLEAN SEPTIC TANK = MICROORGANISMS 22. BEST TERM TO DETERMINE POLLUTION OF WATER = BIOLOGICAL O2 DEMAND 23. SEVERE LACK OF B LYMPHOCYTES AND T LYMPHOCYTES = LEUKEMIA 24. RETROVIRUS = RNA – DNA 25. REASON F & D REQ. PASTEURIZATION OF EGGS = PREVENT SALMONELLA 26. FLUKE CALLED PARAGONIA WE ...
Drosophila embryogenesis

Drosophila embryogenesis, the process by which Drosophila (fruit fly) embryos form, is a favorite model system for geneticists and developmental biologists studying embryogenesis. The small size, short generation time, and large brood size make it ideal for genetic studies. Transparent embryos facilitate developmental studies. Drosophila melanogaster was introduced into the field of genetic experiments by Thomas Hunt Morgan in 1909.