Which of the following muscles attaches to the olecranon process
... d. Vomer Concha are all in the ethmoid; olfactory runs through cribriform plate in ethmoid bone 6. The ________ nerve innervates the teres major muscle a. Lower subscapular – to teres major ...
... d. Vomer Concha are all in the ethmoid; olfactory runs through cribriform plate in ethmoid bone 6. The ________ nerve innervates the teres major muscle a. Lower subscapular – to teres major ...
Unit 1 Review
... Pleura parietal (outer layer), visceral (on lungs) layers Costodiaphragmatic recess fills when you breathe – at the inferior of the lungpotential space LungRoot- just the arteries, veins, bronchi Hilum- root + pulmonary ligament Pulmonary Arteries (deoxygenated blood) – superior – run with bronch ...
... Pleura parietal (outer layer), visceral (on lungs) layers Costodiaphragmatic recess fills when you breathe – at the inferior of the lungpotential space LungRoot- just the arteries, veins, bronchi Hilum- root + pulmonary ligament Pulmonary Arteries (deoxygenated blood) – superior – run with bronch ...
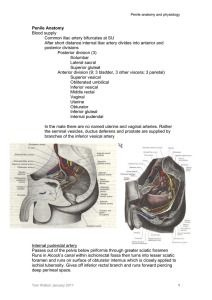
Penile Anatomy
... attached to the inferior surface of the perineal membrane and consists of central bulb of the penis with a crus on each side Bulb is on the posterior end of the corpus spongiosum, crus at the end of the corpus cavernosa Crus attached to the angle between the perineal membrane and pubic ramus. ...
... attached to the inferior surface of the perineal membrane and consists of central bulb of the penis with a crus on each side Bulb is on the posterior end of the corpus spongiosum, crus at the end of the corpus cavernosa Crus attached to the angle between the perineal membrane and pubic ramus. ...
Atlanto-occipital and Atlantoaxial joints
... • Posterior part between dens and transverse ligament is continuous with one of the atlanto occipital joint • Main support is transverse ligament which forms part of the cruciform ligament ...
... • Posterior part between dens and transverse ligament is continuous with one of the atlanto occipital joint • Main support is transverse ligament which forms part of the cruciform ligament ...
1. CNS tissue is enclosed within the vertebral column from the
... There are 4 major branches of this plexus (See chart for branches) 1. Root – 5 ventral rami (C5 and C6 form the upper trunk) (C7 forms the middle trunk) (C8 and T1 form the lower trunk) 2. Trunks – upper, middle, and lower (form divisions) 3. Divisions – anterior and posterior serve the front and ba ...
... There are 4 major branches of this plexus (See chart for branches) 1. Root – 5 ventral rami (C5 and C6 form the upper trunk) (C7 forms the middle trunk) (C8 and T1 form the lower trunk) 2. Trunks – upper, middle, and lower (form divisions) 3. Divisions – anterior and posterior serve the front and ba ...
The Pons - Dentistry 09
... On the anterolateral surface of the pons , the trigeminal nerve emerges on each side Each nerve consist of a smaller ,medial part ,known as the motor root, and a larger, lateral part, known as the sensory root. In the groove between the pons and the medulla ablongata there emerge, from medial to lat ...
... On the anterolateral surface of the pons , the trigeminal nerve emerges on each side Each nerve consist of a smaller ,medial part ,known as the motor root, and a larger, lateral part, known as the sensory root. In the groove between the pons and the medulla ablongata there emerge, from medial to lat ...
The Suboccipital Region
... transverse process of the 6th cervical vertebra and passes upward through all foramina transversaria until it reaches the top of the posterior arch of the atlas. At this point it lies in a groove there and then enters the cranial cavity through the foramen magnum. One of its primary supplies is ...
... transverse process of the 6th cervical vertebra and passes upward through all foramina transversaria until it reaches the top of the posterior arch of the atlas. At this point it lies in a groove there and then enters the cranial cavity through the foramen magnum. One of its primary supplies is ...
Penile Anatomy Blood supply Common iliac artery bifurcates
... After short distance internal iliac artery divides into anterior and posterior divisions Posterior division (3) Iliolumbar Lateral sacral Superior gluteal Anterior division (9; 3 bladder, 3 other viscera; 3 parietal) Superior vesical Obliterated umbilical Inferior vesical Middle rectal Vaginal Uteri ...
... After short distance internal iliac artery divides into anterior and posterior divisions Posterior division (3) Iliolumbar Lateral sacral Superior gluteal Anterior division (9; 3 bladder, 3 other viscera; 3 parietal) Superior vesical Obliterated umbilical Inferior vesical Middle rectal Vaginal Uteri ...
AHD Darwich Apr 15
... 8,000 Hz, and the most sensitive part of the range is between 1,000 and 3,000 Hz • Intensity of sound is related to the perception of loudness and is usually measured in decibels (dB). • Intensity is also related to a measure of sound pressure level at the tympanic membrane. A sound that has 10 time ...
... 8,000 Hz, and the most sensitive part of the range is between 1,000 and 3,000 Hz • Intensity of sound is related to the perception of loudness and is usually measured in decibels (dB). • Intensity is also related to a measure of sound pressure level at the tympanic membrane. A sound that has 10 time ...
213: human functional anatomy
... For each of the major nerves of the lumbosacral and brachial plexuses, state its distribution and classify it as "dorsal" or "ventral". ...
... For each of the major nerves of the lumbosacral and brachial plexuses, state its distribution and classify it as "dorsal" or "ventral". ...
Laboratory 10: Thalamus MCB 163 Fall 2005 Slide #80 1. MLF: The
... 2. Red Nucleus: The red nucleus is classified as a motor nucleus. The red nucleus has two major subdivisions: the caudal magnocellular part gives rise to the rubrospinal tract and the rostral parvocellular part gives rise to the rubrothalamic tract. In humans, the rubrospinal tract is very small and ...
... 2. Red Nucleus: The red nucleus is classified as a motor nucleus. The red nucleus has two major subdivisions: the caudal magnocellular part gives rise to the rubrospinal tract and the rostral parvocellular part gives rise to the rubrothalamic tract. In humans, the rubrospinal tract is very small and ...
Practice Exam for Anatomy Exam 2 Extrinsic muscles are
... decided to go out with your friends to the bar for a couple of drinks to relax a bit. You relax a bit too much and end up passing out at the bar with your arm over the back of your chair. What would your arm look like when you came to class on Friday morning for Pharm? a. Flexed b. Forearm flexion c ...
... decided to go out with your friends to the bar for a couple of drinks to relax a bit. You relax a bit too much and end up passing out at the bar with your arm over the back of your chair. What would your arm look like when you came to class on Friday morning for Pharm? a. Flexed b. Forearm flexion c ...
Test #2
... Section 2: “Think Section” Carefully read the scenario below. Within it are several anatomical statements. In the space below you are to (a) one-by-one list the anatomical statements, (b) state whether or not the statements are true or false, and (c) if any of the statements are false state why they ...
... Section 2: “Think Section” Carefully read the scenario below. Within it are several anatomical statements. In the space below you are to (a) one-by-one list the anatomical statements, (b) state whether or not the statements are true or false, and (c) if any of the statements are false state why they ...
unit 4. dissection: vertebral column and spinal cord
... 6. Slit the arachnoid longitudinally to expose the spinal pia mater, the spinal cord and the roots of the spinal nerves. Notice the arachnoid trabeculae that traverse the subarachnoid space to attach to the pia. 7. Identify the tapering inferior end of the spinal cord, from which the lumbar and sac ...
... 6. Slit the arachnoid longitudinally to expose the spinal pia mater, the spinal cord and the roots of the spinal nerves. Notice the arachnoid trabeculae that traverse the subarachnoid space to attach to the pia. 7. Identify the tapering inferior end of the spinal cord, from which the lumbar and sac ...
Nerves of Forearm LO6
... 6. Apply principles NP3, NP6 & NP7 to describe the course and distribution of the following nerves median, anterior interosseous, ulnar, radial, posterior interosseous and superficial branch of radial. On the basis of the course of each nerve identify potential sites for injury in the forearm. For a ...
... 6. Apply principles NP3, NP6 & NP7 to describe the course and distribution of the following nerves median, anterior interosseous, ulnar, radial, posterior interosseous and superficial branch of radial. On the basis of the course of each nerve identify potential sites for injury in the forearm. For a ...
FlexioN
... Other actions: None. Palpation sites: Upper rectus: both sides of the midline between the umbilicus and xiphoid process. Lower rectus: both sides of the midline between the umbilicus and symphysis pubis. ...
... Other actions: None. Palpation sites: Upper rectus: both sides of the midline between the umbilicus and xiphoid process. Lower rectus: both sides of the midline between the umbilicus and symphysis pubis. ...
- Ameghiniana
... 2. Location of the mental foramen on the anterior region of the dentary: close to the dorsal margin of the dentary and opening dorsolaterally (0); at the dorsoventral midpoint of the lateral surface of the dentary and opening laterally (1). 3. Position of the mandibular foramen: behind the retromola ...
... 2. Location of the mental foramen on the anterior region of the dentary: close to the dorsal margin of the dentary and opening dorsolaterally (0); at the dorsoventral midpoint of the lateral surface of the dentary and opening laterally (1). 3. Position of the mandibular foramen: behind the retromola ...
Oral clinical examination
... on the buccal mucosa (opening of the stensen’ duct) Linea alba: hyperkeratotic line corresponding to the line of occlusion of the teeth Caliculus angularis: a small palpable nodule at the anterior termination of the linea alba Pterygomandibular raphe: a fold of tissue at the posterior boundary ...
... on the buccal mucosa (opening of the stensen’ duct) Linea alba: hyperkeratotic line corresponding to the line of occlusion of the teeth Caliculus angularis: a small palpable nodule at the anterior termination of the linea alba Pterygomandibular raphe: a fold of tissue at the posterior boundary ...
Medial surface Central sulcus on axial imaging cs cs pM pocs
... area) (acoustic portion of Cr. N. VIII) cavities and chemoreceptors in the taste buds on Figure 5-7 Right internal auditory canal (porus acusticus) & nerves the anterior 2/3 of * NI = nervus intermedius the tongue 3. acoustic portion of the VIII nerve (mnemonic: “Coke down” for cochlear portion) 4. ...
... area) (acoustic portion of Cr. N. VIII) cavities and chemoreceptors in the taste buds on Figure 5-7 Right internal auditory canal (porus acusticus) & nerves the anterior 2/3 of * NI = nervus intermedius the tongue 3. acoustic portion of the VIII nerve (mnemonic: “Coke down” for cochlear portion) 4. ...
L13-vestibulocochlear pathways2014-08-23 10
... Medial Longitudinal fasciculus: formed of both descending & ascending fibers: 1.Descending (medial vestibulospinal tract) to anterior horns cells for control of body posture & balance. 2.Ascending to Occulomotor, Trochlear & Abducent Nuclei (Motor Nuclei for extraoccular muscles) for coordination o ...
... Medial Longitudinal fasciculus: formed of both descending & ascending fibers: 1.Descending (medial vestibulospinal tract) to anterior horns cells for control of body posture & balance. 2.Ascending to Occulomotor, Trochlear & Abducent Nuclei (Motor Nuclei for extraoccular muscles) for coordination o ...
L12- CN VIII (vestibulocochlear pathways)
... Medial Longitudinal fasciculus: formed of both descending & ascending fibers: 1.Descending (medial vestibulospinal tract) to anterior horns cells for control of body posture & balance. 2.Ascending to Occulomotor, Trochlear & Abducent Nuclei (Motor Nuclei for extraoccular muscles) for coordination o ...
... Medial Longitudinal fasciculus: formed of both descending & ascending fibers: 1.Descending (medial vestibulospinal tract) to anterior horns cells for control of body posture & balance. 2.Ascending to Occulomotor, Trochlear & Abducent Nuclei (Motor Nuclei for extraoccular muscles) for coordination o ...
File - Vertebrate Embryology TA Help Site Welcome Bio
... micromeres and has a darker pigmented edge at the top. Opposite the vegetal pole Establishes Pole contains the larger Cranial/Caudal/Dorsal/Ventral yolky macromeres and Axis. Will be future caudal cells are less compacted. area. Cells are extremely Opposite the animal pole yolky at vegetal pole Esta ...
... micromeres and has a darker pigmented edge at the top. Opposite the vegetal pole Establishes Pole contains the larger Cranial/Caudal/Dorsal/Ventral yolky macromeres and Axis. Will be future caudal cells are less compacted. area. Cells are extremely Opposite the animal pole yolky at vegetal pole Esta ...
Reticular formation
... system (originate from reticular nuclei to thalamus rather than to whole cerebral) increases general level of sensory stimulation thus lead to increased level of neuronal activities and increased arousal level. The noradrenergic neurons and histamine secreting neurons also stimulate arousal level. • ...
... system (originate from reticular nuclei to thalamus rather than to whole cerebral) increases general level of sensory stimulation thus lead to increased level of neuronal activities and increased arousal level. The noradrenergic neurons and histamine secreting neurons also stimulate arousal level. • ...
Brainstem
... pale-staining region of gray matter called, appropriately enough, the periaqueductal gray. The periaqueductal gray is part of an important descending pain-control system discussed later in this chapter In the caudal midbrain, the basal pons gives way to a cerebral peduncle on each side, through ...
... pale-staining region of gray matter called, appropriately enough, the periaqueductal gray. The periaqueductal gray is part of an important descending pain-control system discussed later in this chapter In the caudal midbrain, the basal pons gives way to a cerebral peduncle on each side, through ...
Drosophila embryogenesis

Drosophila embryogenesis, the process by which Drosophila (fruit fly) embryos form, is a favorite model system for geneticists and developmental biologists studying embryogenesis. The small size, short generation time, and large brood size make it ideal for genetic studies. Transparent embryos facilitate developmental studies. Drosophila melanogaster was introduced into the field of genetic experiments by Thomas Hunt Morgan in 1909.