16 Heart flashcards
... the large valves (tricuspid and mitral) End of Systole (ventricles are relaxing): Semilunar valves are closed (aortic and pulmonary) ...
... the large valves (tricuspid and mitral) End of Systole (ventricles are relaxing): Semilunar valves are closed (aortic and pulmonary) ...
Obstructive Congenital Heart Disease
... Remember: It is a competition between Aortic and Pulmonic outlet. As long as systemic resistance is low the LV will eject that way… but, by 4-6 weeks Pulmonary resistance is at its lowest and systemic is at its highest. Ultimately the RV will enlarge as pulmonary HTN develops and it must work agains ...
... Remember: It is a competition between Aortic and Pulmonic outlet. As long as systemic resistance is low the LV will eject that way… but, by 4-6 weeks Pulmonary resistance is at its lowest and systemic is at its highest. Ultimately the RV will enlarge as pulmonary HTN develops and it must work agains ...
Cardiac pathologies
... • Angina pectoris- this is temporary O2 insufficiency. They may have severe pain in the chest. This is not a heart attack, but can feel like one. These usually follow a big meal, trying to exercise, exposure to cold or stress. • Again nitroglycerin under the tongue can help with pain because it dila ...
... • Angina pectoris- this is temporary O2 insufficiency. They may have severe pain in the chest. This is not a heart attack, but can feel like one. These usually follow a big meal, trying to exercise, exposure to cold or stress. • Again nitroglycerin under the tongue can help with pain because it dila ...
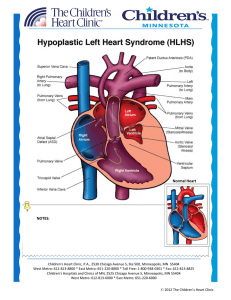
HLHS - Children`s Heart Clinic
... In the normal heart, there are two atria and two ventricles. Blood comes back from the body from the superior vena cava (SVC) and inferior vena cava (IVC) to the right atrium through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. The ventricle contracts and blood is pumped through the pulmonary valve t ...
... In the normal heart, there are two atria and two ventricles. Blood comes back from the body from the superior vena cava (SVC) and inferior vena cava (IVC) to the right atrium through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. The ventricle contracts and blood is pumped through the pulmonary valve t ...
Cardiac Pathophysiology
... • Portions of the heart wall become rigid and lose their flexibility. so it's harder for the ventricles to fill with blood between heartbeats. • Thickening often occurs due to abnormal tissue invading the heart muscle (Amyloid) and in elderly. ...
... • Portions of the heart wall become rigid and lose their flexibility. so it's harder for the ventricles to fill with blood between heartbeats. • Thickening often occurs due to abnormal tissue invading the heart muscle (Amyloid) and in elderly. ...
Sample Questions
... a. The first sound is caused by closure of the tricuspid valve, the second by closure of the mitral valve b. The first sound is caused by closure of the mitral valve, the second by closure of the tricuspid valve c. Both sounds are caused by contraction of the ventricles, followed by c ...
... a. The first sound is caused by closure of the tricuspid valve, the second by closure of the mitral valve b. The first sound is caused by closure of the mitral valve, the second by closure of the tricuspid valve c. Both sounds are caused by contraction of the ventricles, followed by c ...
Heart workbook_Nyboer
... 9. Compare and contrast atherosclerosis and an aneurysm. Include what it is, where it is commonly found, and what it does. ...
... 9. Compare and contrast atherosclerosis and an aneurysm. Include what it is, where it is commonly found, and what it does. ...
The Cardiovascular System Chapter 9
... Capillaries have very thin walls and distribute O2 to tissues while picking up CO2 ...
... Capillaries have very thin walls and distribute O2 to tissues while picking up CO2 ...
cardiovascular system ppt
... The LV contracts, closing the bicuspid valve and pushing blood through the aortic valve into the aorta ...
... The LV contracts, closing the bicuspid valve and pushing blood through the aortic valve into the aorta ...
Sheep Heart Dissection Lab
... ventricular wall until you reach the apex of the heart. b. Find the opening to the pulmonary trunk and use the scissors to cut upward through the wall of the right ventricle. Follow the pulmonary trunk until you have exposed the pulmonary valve. c. Examine the valve and its cusps. 6. Open the left s ...
... ventricular wall until you reach the apex of the heart. b. Find the opening to the pulmonary trunk and use the scissors to cut upward through the wall of the right ventricle. Follow the pulmonary trunk until you have exposed the pulmonary valve. c. Examine the valve and its cusps. 6. Open the left s ...
Circulatory System
... that connect to the Circle of Willis a circuit of arteries that allows blood to flow to the Dura mater in the event of a clot in any one area. Carries in O2, glucose, and cholesterol Takes out CO2 and Growth Hormone ...
... that connect to the Circle of Willis a circuit of arteries that allows blood to flow to the Dura mater in the event of a clot in any one area. Carries in O2, glucose, and cholesterol Takes out CO2 and Growth Hormone ...
Period______ Chapters 10 and 11 Blood and Cardiovascular
... Chapters 10 and 11 Blood and Cardiovascular System Practice 1. Using the key choices, identify the cell type(s) or blood elements that fit the following descriptions. A. Red blood cells B. Megakaryocyte ...
... Chapters 10 and 11 Blood and Cardiovascular System Practice 1. Using the key choices, identify the cell type(s) or blood elements that fit the following descriptions. A. Red blood cells B. Megakaryocyte ...
heart
... amount of myocardium present, which reflects the amount of force each chamber is required to generate. The left ventricle is the largest and strongest chamber ...
... amount of myocardium present, which reflects the amount of force each chamber is required to generate. The left ventricle is the largest and strongest chamber ...
NAME______________________________________ What is a
... 1957 First battery pacemaker using transistors small enough to carry 1958 First implanted pacemaker in Sweden 1970s lithium-ion batteries make pacemakers smaller and longer lasting 1990s microprocessors make pacemakers more efficient 2000s pacemakers simultaneously linked to both ventricle ...
... 1957 First battery pacemaker using transistors small enough to carry 1958 First implanted pacemaker in Sweden 1970s lithium-ion batteries make pacemakers smaller and longer lasting 1990s microprocessors make pacemakers more efficient 2000s pacemakers simultaneously linked to both ventricle ...
Anatomy of the Heart
... ____________________ chamber of the heart Forms apex ______________________ attached to _________________ muscles Blood passes through _____________valve (aortic ______________ valve) into ascending aorta Some blood flows into coronary arteries, remainder to body During fetal life ______ ...
... ____________________ chamber of the heart Forms apex ______________________ attached to _________________ muscles Blood passes through _____________valve (aortic ______________ valve) into ascending aorta Some blood flows into coronary arteries, remainder to body During fetal life ______ ...
Cardiovascular System
... – 2/3rds of the heart lies to the left of the mid-line. – It is about the size of a clenched fist. – Pericardium- Sac of connective tissue that covers and protects the heart. ...
... – 2/3rds of the heart lies to the left of the mid-line. – It is about the size of a clenched fist. – Pericardium- Sac of connective tissue that covers and protects the heart. ...
Valvular Heart Disease/Myopathy/Aneurysm
... because of aortic insufficiency (when blood ejected into the aorta regurgitates back through the aortic valve into the left ventricle ). Also called a Corrigan pulse or a cannonball, collapsing, pistol-shot, or trip-hammer pulse. ...
... because of aortic insufficiency (when blood ejected into the aorta regurgitates back through the aortic valve into the left ventricle ). Also called a Corrigan pulse or a cannonball, collapsing, pistol-shot, or trip-hammer pulse. ...
Human Body in health and Disease CV sys
... 6. Trace a drop of blood from the superior vena cava to the lungs and from the lungs to the aorta. 7. Calculate the number of times your heart will beat in your lifetime. ...
... 6. Trace a drop of blood from the superior vena cava to the lungs and from the lungs to the aorta. 7. Calculate the number of times your heart will beat in your lifetime. ...
Bios 1310 SI Final Exam Review Good luck! J VITAL SIGNS: Blood
... d. During isovolumetric contraction the ventricular pressure is less than atrial pressure but greater than the great artery pressure 14. The amount of friction the blood experiences as it is traveling through blood vessels is known as what? a. Cardiac output b. Blood pressure c. Peripheral resistanc ...
... d. During isovolumetric contraction the ventricular pressure is less than atrial pressure but greater than the great artery pressure 14. The amount of friction the blood experiences as it is traveling through blood vessels is known as what? a. Cardiac output b. Blood pressure c. Peripheral resistanc ...
The Cardiac Cycle
... Late Ventricular Systole Once pressure in the ventricles exceeds the pressure in the aorta, the semilunar valve opens and blood flows into the aorta. This is the start of ventricular ejection. About 60 - 70 ml of blood is ejected. This ejected blood is called the stroke volume. Ventricular pressures ...
... Late Ventricular Systole Once pressure in the ventricles exceeds the pressure in the aorta, the semilunar valve opens and blood flows into the aorta. This is the start of ventricular ejection. About 60 - 70 ml of blood is ejected. This ejected blood is called the stroke volume. Ventricular pressures ...
Phonocardiogram
... and is normal in children and adolescents, but usually disappears after age 30. When heard in adults, an S3 is called a “gallop” and indicates left ventricular failure. ...
... and is normal in children and adolescents, but usually disappears after age 30. When heard in adults, an S3 is called a “gallop” and indicates left ventricular failure. ...
Cardiology Jeopardy
... procedure, used to establish coronary perfusion and afterload reduction, is contraindicated in patients with aortic valve regurgitation ...
... procedure, used to establish coronary perfusion and afterload reduction, is contraindicated in patients with aortic valve regurgitation ...
6.2 Transport
... What have we just found out? • Why do arteries have thick elastic walls? Arteries work at high pressure. They have to resist this pressure at the moment of ‘squeeze’ and return it to the blood in between the squeezes. ...
... What have we just found out? • Why do arteries have thick elastic walls? Arteries work at high pressure. They have to resist this pressure at the moment of ‘squeeze’ and return it to the blood in between the squeezes. ...
File
... Describe the substance normally found in the pericardial cavity. Describe the movement of the atria during contraction. …the ventricles. Describe the tissue construction of each of the three layers of the heart wall. How are endocardium and endothelium related? ...
... Describe the substance normally found in the pericardial cavity. Describe the movement of the atria during contraction. …the ventricles. Describe the tissue construction of each of the three layers of the heart wall. How are endocardium and endothelium related? ...
Artificial heart valve

An artificial heart valve is a device implanted in the heart of a patient with valvular heart disease. When one of the four heart valves malfunctions, the medical choice may be to replace the natural valve with an artificial valve. This requires open-heart surgery.Valves are integral to the normal physiological functioning of the human heart. Natural heart valves are evolved to forms that perform the functional requirement of inducing unidirectional blood flow through the valve structure from one chamber of the heart to another. Natural heart valves become dysfunctional for a variety of pathological causes. Some pathologies may require complete surgical replacement of the natural heart valve with a heart valve prosthesis.