Information Sheet D7
... When the temperature increased approximately 12,000 years ago, the last ice age ended. As the ice melted it dropped its load of sediment, rocks and stones. This load was dropped in different ways and created different features on the landscape which are still visible today. Common glacial deposition ...
... When the temperature increased approximately 12,000 years ago, the last ice age ended. As the ice melted it dropped its load of sediment, rocks and stones. This load was dropped in different ways and created different features on the landscape which are still visible today. Common glacial deposition ...
grade 5 presentation Kalli, iona , Anica , Claire
... When the grade 8 went to visit the Stein Glacier last year, they said they were able to walk on the glacier. This year we were not allowed to because of the increase In Crevasses (big cracks in the ice) and because the glaciers from had melted and changed so much from the year before. ...
... When the grade 8 went to visit the Stein Glacier last year, they said they were able to walk on the glacier. This year we were not allowed to because of the increase In Crevasses (big cracks in the ice) and because the glaciers from had melted and changed so much from the year before. ...
focus What can we learn from past warm periods?
... be—and after the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster in 2011 maybe not so many—or how many green vehicles will people use, or how many people will there be on the planet? These are very uncertain issues. And so the IPCC presented a series of possible scenarios with outcomes for the year 2100, ranging ...
... be—and after the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster in 2011 maybe not so many—or how many green vehicles will people use, or how many people will there be on the planet? These are very uncertain issues. And so the IPCC presented a series of possible scenarios with outcomes for the year 2100, ranging ...
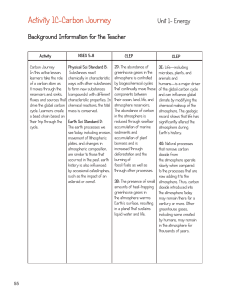
Activity 1C-Carbon Journey
... Carbon (C) is the 12th element on the Periodic Table and is most familiar to us as graphite in pencils. Another form of pure carbon, in a different structure, is diamond. Both are made up of atoms of carbon. All of the carbon on Earth today was present when Earth was formed, some 4.5 billion years a ...
... Carbon (C) is the 12th element on the Periodic Table and is most familiar to us as graphite in pencils. Another form of pure carbon, in a different structure, is diamond. Both are made up of atoms of carbon. All of the carbon on Earth today was present when Earth was formed, some 4.5 billion years a ...
PALEOZOIC ERA:
... The Earth’s surface: the Earth had water at the end of the Hadean Era. any surface material was very thin and unstable as the interior was still very hot causing magma to rise to the surface. Archean Era 4.0-2.5bya: Summary: Archean means “ancient” referring to the oldest known rocks Some sedi ...
... The Earth’s surface: the Earth had water at the end of the Hadean Era. any surface material was very thin and unstable as the interior was still very hot causing magma to rise to the surface. Archean Era 4.0-2.5bya: Summary: Archean means “ancient” referring to the oldest known rocks Some sedi ...
No immediate reason to expect another Ice Age.
... • “Climate change will wipe out most life on earth by the end of this century and man is too late to avert catastrophe.” James Lovelock, Feb.26, 2009 • “The time for delay is over; the time for denial is over." President-elect Obama, December 14, 2008 ...
... • “Climate change will wipe out most life on earth by the end of this century and man is too late to avert catastrophe.” James Lovelock, Feb.26, 2009 • “The time for delay is over; the time for denial is over." President-elect Obama, December 14, 2008 ...
Quaternary of South-West England
... 1989). However, the change may be related to variations in the behaviour of the ice sheets themselves. It is known that after this time, marine-based ice sheets developed on continental shelf areas such as Hudson’s Bay and the Baltic and Irish seas. They grew rapidly and reached considerable thickne ...
... 1989). However, the change may be related to variations in the behaviour of the ice sheets themselves. It is known that after this time, marine-based ice sheets developed on continental shelf areas such as Hudson’s Bay and the Baltic and Irish seas. They grew rapidly and reached considerable thickne ...
CO2: The Thermostat that Controls Earth`s
... surface still remains ice-free, even though the global surface temperature is colder than –21 C. At tropical latitudes, incident solar radiation is enough to keep the ocean from freezing. While this thermal oasis within an otherwise icebound Earth appears to be stable, at least on the short timesca ...
... surface still remains ice-free, even though the global surface temperature is colder than –21 C. At tropical latitudes, incident solar radiation is enough to keep the ocean from freezing. While this thermal oasis within an otherwise icebound Earth appears to be stable, at least on the short timesca ...
The Oceans, the Atmosphere and Climate Change - EUR
... with quantities mostly measured by meteorological instruments. We say that the weather is windy, rainy, sunny, warm, cold etc. Climate represents average weather conditions, regular weather sequences (like winter, spring, summer, and fall), and extreme weather events (like tornadoes and floods). Thu ...
... with quantities mostly measured by meteorological instruments. We say that the weather is windy, rainy, sunny, warm, cold etc. Climate represents average weather conditions, regular weather sequences (like winter, spring, summer, and fall), and extreme weather events (like tornadoes and floods). Thu ...
Team Earth Cycle B Ice Sheets B>E>H>A As air temperatures warm
... snow and ice is its high surface albedo. Because up to 90% of the incident solar radiation is reflected by snow and ice surfaces, while as low as about 10% is reflected by the open ocean or forested lands, changes in snow and ice cover are important feedback mechanisms in climate change. In addition ...
... snow and ice is its high surface albedo. Because up to 90% of the incident solar radiation is reflected by snow and ice surfaces, while as low as about 10% is reflected by the open ocean or forested lands, changes in snow and ice cover are important feedback mechanisms in climate change. In addition ...
Global Warming Frontcover - Saddleback Educational Publishing
... Increasing temperatures have led to the outbreak of diseases such as malaria and dengue fever in areas that were previously unexposed to these diseases. Warmer temperatures extend the habitable zone for disease-carrying animals such as insects, rodents, and snails. Mosquitoes are particularly sensit ...
... Increasing temperatures have led to the outbreak of diseases such as malaria and dengue fever in areas that were previously unexposed to these diseases. Warmer temperatures extend the habitable zone for disease-carrying animals such as insects, rodents, and snails. Mosquitoes are particularly sensit ...
How is climate change affecting life on Earth?
... related to climate? Greenhouse gases Carbon dioxide (CO2) Released from burning fossil fuels, from respiration, and volcanoes Taken out of the atmosphere by plants during photosynthesis ...
... related to climate? Greenhouse gases Carbon dioxide (CO2) Released from burning fossil fuels, from respiration, and volcanoes Taken out of the atmosphere by plants during photosynthesis ...
7.1 Lesson
... • the factors that affect the amount of solar energy a particular area receives from the Sun • how factors such as winds, ocean currents, and the shape and size of continents affect climate • an understanding of how albedo can affect global temperatures • an understanding of the effects of volcanic ...
... • the factors that affect the amount of solar energy a particular area receives from the Sun • how factors such as winds, ocean currents, and the shape and size of continents affect climate • an understanding of how albedo can affect global temperatures • an understanding of the effects of volcanic ...
The role of the Southern Ocean in Earth System modelling
... Regions of deep water formation are of great importance for the uptake of CO2 and heat because they are a pathway to the interior ocean, where CO2 and heat can enter the interior ocean and be stored in a vast volume. ...
... Regions of deep water formation are of great importance for the uptake of CO2 and heat because they are a pathway to the interior ocean, where CO2 and heat can enter the interior ocean and be stored in a vast volume. ...
The Science of Climate Change
... Earth' with global average temperatures well over 20°C and a 'snowball Earth' with average temperatures below 10°C. Hothouse conditions were associated with sea levels over 100 metres higher than today's and no polar ice, while in snowball times polar icecaps extended down into Europe and ocean leve ...
... Earth' with global average temperatures well over 20°C and a 'snowball Earth' with average temperatures below 10°C. Hothouse conditions were associated with sea levels over 100 metres higher than today's and no polar ice, while in snowball times polar icecaps extended down into Europe and ocean leve ...
Document
... The inner edge of the HZ • The limiting factor for the inner boundary of the HZ must be the ability of the planet to avoid a runaway greenhouse effect. • Theoretical models predict that an Earthlike planet would convert all its ocean into the water vapor ~0.84 AU • However it is likely that a plane ...
... The inner edge of the HZ • The limiting factor for the inner boundary of the HZ must be the ability of the planet to avoid a runaway greenhouse effect. • Theoretical models predict that an Earthlike planet would convert all its ocean into the water vapor ~0.84 AU • However it is likely that a plane ...
Priem-klima
... Further back in time sediments from the Late Ordovician show that 450 million years ago the atmosphere contained even some 16 times more carbon dioxide than today. Still, this was not accompanied by unusual warm temperatures. On the contrary, at higher latitudes there was widespread glaciation. The ...
... Further back in time sediments from the Late Ordovician show that 450 million years ago the atmosphere contained even some 16 times more carbon dioxide than today. Still, this was not accompanied by unusual warm temperatures. On the contrary, at higher latitudes there was widespread glaciation. The ...
Global Carbon Cycle Change
... H2O can condense and start to form oceans. --- the hot rock will react with hot water + CO2 and make carbonate. Somehow that carbonate needs to be mixed back into the mantle otherwise the mantle would have no water + CO2 today Once the mantle becomes solid (about 4 b.y. ago, viscosity ≈ 1022 Pa-sec) ...
... H2O can condense and start to form oceans. --- the hot rock will react with hot water + CO2 and make carbonate. Somehow that carbonate needs to be mixed back into the mantle otherwise the mantle would have no water + CO2 today Once the mantle becomes solid (about 4 b.y. ago, viscosity ≈ 1022 Pa-sec) ...
CO2 Variations, 1999 Mauna Loa, Hawaii
... Weather – short-term changes in wind, clouds, temperature, and pressure in an atmosphere at a given location Climate – long-term average of the weather at a given location These are Earth’s global wind patterns or circulation ...
... Weather – short-term changes in wind, clouds, temperature, and pressure in an atmosphere at a given location Climate – long-term average of the weather at a given location These are Earth’s global wind patterns or circulation ...
The Realization of Global Warming The Realization of Global Warming
... 1938, Guy Stewart Callendar went before the Royal Meteorological Society to present his argument that contemporary calculations of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere happened to be higher than those in the previous century. This rise in carbon dioxide, he said, could be the cause of warming on the Ear ...
... 1938, Guy Stewart Callendar went before the Royal Meteorological Society to present his argument that contemporary calculations of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere happened to be higher than those in the previous century. This rise in carbon dioxide, he said, could be the cause of warming on the Ear ...
CCTF GLaciers FINAL w logo
... surfaces of the Earth (which reflect much of the sun’s energy back into space) decrease in area, exposing the darker surface of the land (which absorbs more energy) and leading to further increase in global temperatures. (3) The runoff from melting glaciers contributes water for drinking, agricultur ...
... surfaces of the Earth (which reflect much of the sun’s energy back into space) decrease in area, exposing the darker surface of the land (which absorbs more energy) and leading to further increase in global temperatures. (3) The runoff from melting glaciers contributes water for drinking, agricultur ...
Fall07_Exam3
... 3. Life on Earth can be said to be both fragile and robust with respect to climate changes that have occurred throughout the history of the planet, including climate changes that may be caused by human actions. Briefly explain. 4. In the documentary, “An Inconvenient Truth”, Al Gore uses the correla ...
... 3. Life on Earth can be said to be both fragile and robust with respect to climate changes that have occurred throughout the history of the planet, including climate changes that may be caused by human actions. Briefly explain. 4. In the documentary, “An Inconvenient Truth”, Al Gore uses the correla ...
Climate Change
... Earth's temperature has been rising—culminating in this, the hottest decade on record, is abnormal. Sunspot cycles, for example, can increase the sun's output, raising temperature in our atmosphere. But we are seeing a temperature increase in the troposphere, the lower level of our atmosphere, and a ...
... Earth's temperature has been rising—culminating in this, the hottest decade on record, is abnormal. Sunspot cycles, for example, can increase the sun's output, raising temperature in our atmosphere. But we are seeing a temperature increase in the troposphere, the lower level of our atmosphere, and a ...
Earth Systems - Assets - Cambridge University Press
... town, quite a distance up the mountains in the background. What accounts for this dramatic retreat in the century after 1855? One hundred and fifty years ago, the global climate was colder than it is today – about 17C colder. The warming trend over the past century and a half is correlated with a ma ...
... town, quite a distance up the mountains in the background. What accounts for this dramatic retreat in the century after 1855? One hundred and fifty years ago, the global climate was colder than it is today – about 17C colder. The warming trend over the past century and a half is correlated with a ma ...