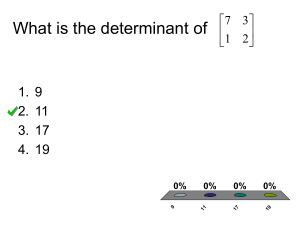
GRE math study group Linear algebra examples
... A 2-dimensional subspace in 4-space is just a plane in 4-space that passes through the origin. How can two planes intersect? In 3-space, your experience gives the answer. If they’re not the same plane, then they must intersect in a line. (They have the origin in common, so they can’t be parallel.) V ...
... A 2-dimensional subspace in 4-space is just a plane in 4-space that passes through the origin. How can two planes intersect? In 3-space, your experience gives the answer. If they’re not the same plane, then they must intersect in a line. (They have the origin in common, so they can’t be parallel.) V ...
11 Cross Product & the Model Matrix
... would produce the local axis of rotation between the two vectors. For example the cross product is used to construct a LookAt() function and to implement shader techniques such as normal mapping and ...
... would produce the local axis of rotation between the two vectors. For example the cross product is used to construct a LookAt() function and to implement shader techniques such as normal mapping and ...
Multivariable Linear Systems and Row Operations
... The algorithm used to transform a system of linear equations into an equivalent system in row-echelon form is called Gaussian elimination. The operations used to produce equivalent systems are given below. ...
... The algorithm used to transform a system of linear equations into an equivalent system in row-echelon form is called Gaussian elimination. The operations used to produce equivalent systems are given below. ...
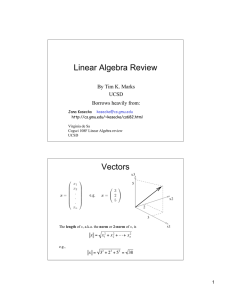
Linear Algebra Review Vectors By Tim K. Marks UCSD
... – D is an m × n diagonal matrix. Its diagonal elements, σ1, σ2, …, are called the singular values of A, and satisfy σ1 ≥ σ2 ≥ … ≥ 0. – V is an n × n orthonormal matrix ...
... – D is an m × n diagonal matrix. Its diagonal elements, σ1, σ2, …, are called the singular values of A, and satisfy σ1 ≥ σ2 ≥ … ≥ 0. – V is an n × n orthonormal matrix ...
Page 1 PES 1110 Fall 2013, Spendier Lecture 31/Page 1 Today
... Calculate the net torque about point O for the two forces applied as in the Fig below. The rod and both forces are in the plane of the page. In what direction will the rod rotate? Which force will result in the larger torque and why? ...
... Calculate the net torque about point O for the two forces applied as in the Fig below. The rod and both forces are in the plane of the page. In what direction will the rod rotate? Which force will result in the larger torque and why? ...
Algebra II Quiz 6
... (2nd) MATRIX 1[A] highlighted EDIT ENTER 2 ENTER x 2 ENTER Then plug in the entries. Now hit 2nd QUIT (2nd) MATRIX EDIT 2[B] highlighted ENTER 2 ENTER x 2 ENTER Then plug in the entries. Then hit 2nd QUIT (2nd) MATRIX 1[A] ENTER times (2nd) MATRIX 2[B] ENTER Record your answer here. ...
... (2nd) MATRIX 1[A] highlighted EDIT ENTER 2 ENTER x 2 ENTER Then plug in the entries. Now hit 2nd QUIT (2nd) MATRIX EDIT 2[B] highlighted ENTER 2 ENTER x 2 ENTER Then plug in the entries. Then hit 2nd QUIT (2nd) MATRIX 1[A] ENTER times (2nd) MATRIX 2[B] ENTER Record your answer here. ...
Slides for Rosen, 5th edition
... • i.e., element (i,j) of AB is given by the vector dot product of the ith row of A and the jth column of B (considered as vectors). • Note: Matrix multiplication is not commutative! ...
... • i.e., element (i,j) of AB is given by the vector dot product of the ith row of A and the jth column of B (considered as vectors). • Note: Matrix multiplication is not commutative! ...
Numerical Analysis
... The eigenvalues of AT are the same as those of A The eigenvectors from A and AT are orthogonal (associated with different eigenvalues) ...
... The eigenvalues of AT are the same as those of A The eigenvectors from A and AT are orthogonal (associated with different eigenvalues) ...