Week 4: Monetary Transactions in Ecommerce
... • Developed in 1974 by Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn as part of the Arpanet network developed for the US Defense Department. • TCP/IP is the protocol used by the Internet. • Almost 70% of all backbone, metropolitan and wide area networks use TCP/IP. • In 1998, TCP/IP surpassed IPX/SPX to become the most co ...
... • Developed in 1974 by Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn as part of the Arpanet network developed for the US Defense Department. • TCP/IP is the protocol used by the Internet. • Almost 70% of all backbone, metropolitan and wide area networks use TCP/IP. • In 1998, TCP/IP surpassed IPX/SPX to become the most co ...
network Access Layer
... Transporting individual packets of information through the network end-to-end Can route packets according to actual device address or network topology (connectionless) Routing is done according to the network manager or by a dynamic routing protocol Without Network layer all routings will be pointto ...
... Transporting individual packets of information through the network end-to-end Can route packets according to actual device address or network topology (connectionless) Routing is done according to the network manager or by a dynamic routing protocol Without Network layer all routings will be pointto ...
internet overview lecture slides
... request goes to a root nameserver to find out where the appropriate top level domain server (.edu) is, then that server is queried as to where the host (buffalo) is, then the host is queried for the address of the actual computer in question (mediastudy) ...
... request goes to a root nameserver to find out where the appropriate top level domain server (.edu) is, then that server is queried as to where the host (buffalo) is, then the host is queried for the address of the actual computer in question (mediastudy) ...
CS412 Computer Networks - Winona State University
... Q: How can ARP’s performance be improved (i.e., to reduce the broadcasting traffic)? A: one of our favorite mechanisms in CS _________ ...
... Q: How can ARP’s performance be improved (i.e., to reduce the broadcasting traffic)? A: one of our favorite mechanisms in CS _________ ...
Chapter 2 Protocols and TCP/IP
... • Developed by the US Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA) for its packet switched network (ARPANET) • Used by the global Internet • No official model but a working one. —Application layer —Host to host or transport layer —Internet layer —Network access layer —Physical layer ...
... • Developed by the US Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA) for its packet switched network (ARPANET) • Used by the global Internet • No official model but a working one. —Application layer —Host to host or transport layer —Internet layer —Network access layer —Physical layer ...
Class Power Points for Chapter #2
... Host to Host Layer The main purpose of the Host-to-Host layer is to shield the upper-layer applications from the complexities of the network. This layer says to the upper layer, “Just give me your data stream, with any instructions, and I’ll begin the process of getting your information ready to se ...
... Host to Host Layer The main purpose of the Host-to-Host layer is to shield the upper-layer applications from the complexities of the network. This layer says to the upper layer, “Just give me your data stream, with any instructions, and I’ll begin the process of getting your information ready to se ...
Chapter 2 Protocols and TCP/IP
... • Developed by the US Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA) for its packet switched network (ARPANET) • Used by the global Internet • No official model but a working one. —Application layer —Host to host or transport layer —Internet layer —Network access layer —Physical layer ...
... • Developed by the US Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA) for its packet switched network (ARPANET) • Used by the global Internet • No official model but a working one. —Application layer —Host to host or transport layer —Internet layer —Network access layer —Physical layer ...
Introduction
... Transmission Control Protocol(reliable, connection oriented, flow control). User datagram protocol(unreliable connectionless). ...
... Transmission Control Protocol(reliable, connection oriented, flow control). User datagram protocol(unreliable connectionless). ...
02-Protocols and TCP-IP
... • Developed by the US Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA) for its packet switched network (ARPANET) • Used by the global Internet • No official model but a working one. —Application layer —Host to host or transport layer —Internet layer —Network access layer —Physical layer ...
... • Developed by the US Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA) for its packet switched network (ARPANET) • Used by the global Internet • No official model but a working one. —Application layer —Host to host or transport layer —Internet layer —Network access layer —Physical layer ...
Ports and IPv6
... Present IPv4 is used This is 32 bits, and has about 4,300,000,000 address spaces (2^32 – 1) IPv6 is started to be implemented. IPv6 is 128 bits giving 3.4 x 10^38 ...
... Present IPv4 is used This is 32 bits, and has about 4,300,000,000 address spaces (2^32 – 1) IPv6 is started to be implemented. IPv6 is 128 bits giving 3.4 x 10^38 ...
CCNA1 3.0-11 TCPIP Transport & Application Layers
... User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is the connectionless transport protocol in the TCP/IP protocol stack. UDP is a simple protocol that exchanges datagrams, without acknowledgments or guaranteed delivery. Error processing and retransmission must be handled by higher layer protocols. UDP uses no windowing ...
... User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is the connectionless transport protocol in the TCP/IP protocol stack. UDP is a simple protocol that exchanges datagrams, without acknowledgments or guaranteed delivery. Error processing and retransmission must be handled by higher layer protocols. UDP uses no windowing ...
Chapter03
... Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) works at the Network layer and is used by IP for many different services. •ICMP is a management protocol and messaging service provider for IP. •Its messages are carried as IP datagrams. ICMP packets have the following characteristics: • They can provide host ...
... Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) works at the Network layer and is used by IP for many different services. •ICMP is a management protocol and messaging service provider for IP. •Its messages are carried as IP datagrams. ICMP packets have the following characteristics: • They can provide host ...
A Brief history of the Internet BY ZIYUN WANG
... • Internet history revolves around four distinct aspects. • 1.the technological evolution that began with early research on packet switching and the ARPANET (and related technologies), and where current research continues to expand the horizons of the infrastructure along several dimensions, such as ...
... • Internet history revolves around four distinct aspects. • 1.the technological evolution that began with early research on packet switching and the ARPANET (and related technologies), and where current research continues to expand the horizons of the infrastructure along several dimensions, such as ...
Optimal Resume at KAPLAN UNIVERSITY
... protocols, a good place to start would be defining protocols. A Protocol is the rules and standards that define network communication. A protocol stack is the protocol software components running on a computer. And, a protocol suite is a set of related protocols that support network communication at ...
... protocols, a good place to start would be defining protocols. A Protocol is the rules and standards that define network communication. A protocol stack is the protocol software components running on a computer. And, a protocol suite is a set of related protocols that support network communication at ...
Chapter 4 : TCP/IP and OSI
... TCP/IP Network Access • Exchange of data between systems on a shared network • Utilizes address of host and destination • Can also prioritize transmission • Software at this layer depends on network (e.g. X.25 vs. Ethernet) • Segregation means that no other software needs to be concerned about net ...
... TCP/IP Network Access • Exchange of data between systems on a shared network • Utilizes address of host and destination • Can also prioritize transmission • Software at this layer depends on network (e.g. X.25 vs. Ethernet) • Segregation means that no other software needs to be concerned about net ...
A crash course in networking
... • Why Layering? – Flexibility – Extensibility – Divide and conquer ...
... • Why Layering? – Flexibility – Extensibility – Divide and conquer ...
Communication systems
... FTP – (file transfer protocol) is a standard network protocol used to copy a file from one host to another over a TCP/IP – based network, such as the internet. SSL (secure socket layer) are cryptographic protocols that provide security for communications over networks such as the internet. Ether ...
... FTP – (file transfer protocol) is a standard network protocol used to copy a file from one host to another over a TCP/IP – based network, such as the internet. SSL (secure socket layer) are cryptographic protocols that provide security for communications over networks such as the internet. Ether ...
Chapter 1 Data Communications and Networks Overview
... • Developed by the US Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA) for its packet switched network (ARPANET) • Used by the global Internet • No official model but a working one. —Application layer —Host to host or transport layer —Internet layer —Network access layer —Physical layer ...
... • Developed by the US Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA) for its packet switched network (ARPANET) • Used by the global Internet • No official model but a working one. —Application layer —Host to host or transport layer —Internet layer —Network access layer —Physical layer ...
Chapter 1 Data Communications and Networks Overview
... • Developed by the US Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA) for its packet switched network (ARPANET) • Used by the global Internet • No official model but a working one. —Application layer —Host to host or transport layer —Internet layer —Network access layer —Physical layer ...
... • Developed by the US Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA) for its packet switched network (ARPANET) • Used by the global Internet • No official model but a working one. —Application layer —Host to host or transport layer —Internet layer —Network access layer —Physical layer ...
OSI Model
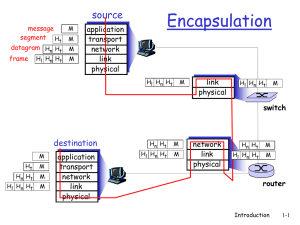
... which contains sufficient information to allow it to be routed from the source to the destination The protocol used at the data link layer encapsulates the datagram into a frame and this is transmitted across the transmission medium. ...
... which contains sufficient information to allow it to be routed from the source to the destination The protocol used at the data link layer encapsulates the datagram into a frame and this is transmitted across the transmission medium. ...
Internet protocol suite

The Internet protocol suite is the computer networking model and set of communications protocols used on the Internet and similar computer networks. It is commonly known as TCP/IP, because among many protocols, the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP) is the accepted and most widely used protocol in Internet. Often also called the Internet model, it was originally also known as the DoD model, because the development of the networking model was funded by DARPA, an agency of the United States Department of Defense.TCP/IP provides end-to-end connectivity specifying how data should be packetized, addressed, transmitted, routed and received at the destination. This functionality is organized into four abstraction layers which are used to sort all related protocols according to the scope of networking involved. From lowest to highest, the layers are the link layer, containing communication technologies for a single network segment (link); the internet layer, connecting hosts across independent networks, thus establishing internetworking; the transport layer handling host-to-host communication; and the application layer, which provides process-to-process application data exchange.The TCP/IP model and related protocol models are maintained by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).