* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Powerpoint - Chapter 1
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Communication protocol wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
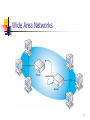
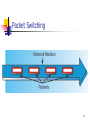
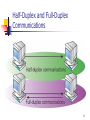
Chapter Overview Network Communications The OSI Reference Model 1 Signals and Protocols A data network is a group of computers connected by a network medium. The network medium carries signals between computers. Signals reduce complex information to the simplest possible form. Computers communicate by using a language called a protocol. 2 Protocol Services Packet acknowledgment Segmentation Flow control Error detection Error correction Data compression Data encryption 3 A Protocol Stack 4 Protocol Interaction 5 Local Area Networks A local area network (LAN) is a collection of computers located in a relatively small area and connected by a common medium. The pattern in which computers in a LAN are connected is called the topology. LAN topologies include bus, star, and ring. The defining protocols for a LAN are the datalink layer protocols. 6 Wide Area Networks 7 Packet Switching 8 Half-Duplex and Full-Duplex Communications 9 Backbone Network 10 Client/Server and Peer-to-Peer Networking On a client/server network, computers function as either clients or servers. On a peer-to-peer network, computers can function as both clients and servers. Microsoft Windows, UNIX, and Linux are peer-to-peer operating systems. Novell NetWare is a client/server operating system. 11 The OSI Reference Model 12 Data Encapsulation 13 PDU Names at Different OSI Layers OSI Layer Application Protocol Data Unit (PDU) Name Message Transport Segment or datagram Network Datagram Data-link Frame (Any layer) Packet 14 The Physical Layer Defines the hardware elements of the network, including The network medium How the network is installed The type of signaling Includes the following elements: Cables Network interface adapters (also called network interface cards, or NICs) Hubs 15 The Data-Link Layer Includes the following protocols: Ethernet Token Ring Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP) Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) 16 The Data-Link Layer (Cont.) Includes the following protocol components: Frame format Media Access Control (MAC) mechanism Physical layer specifications Performs the following functions: Hardware addressing Error detection and correction Protocol identification 17 The Network Layer Includes the following protocols: Internet Protocol (IP) Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX) NetBIOS Extended User Interface (NetBEUI) AppleTalk Performs the following functions: Addressing Fragmenting Routing Protocol identification 18 The Transport Layer Includes the following protocols: Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) User Datagram Protocol (UDP) IPX NetWare Core Protocol (NCP) Sequenced Packet Exchange (SPX) Performs the following functions: Packet acknowledgment Data segmentation Flow control Error detection 19 Connection-Oriented and Connectionless Protocols Connection-Oriented (CO) Protocols Connectionless (CL) Protocols Require a handshake Do not require a handshake Have larger headers and more overhead Have smaller headers and less overhead Provide packet acknowledgments, data segmentation, flow control, and error detection and correction Do not provide additional services Acknowledge transmitted packets, so they are considered reliable Do not acknowledge transmitted packets, so they are considered unreliable 20 The Session Layer The two most important functions at this layer are Dialog control Dialog separation 21 The Presentation Layer The presentation layer uses the following translation process: 1. The sender translates its abstract syntax to transfer syntax. 2. The sender transmits data to the receiver. 3. The receiver translates transfer syntax to it in abstract syntax. 22 The Application Layer Includes the following protocols: File Transfer Protocol (FTP) Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) Post Office Protocol, Version 3 (POP3) Internet Mail Access Protocol (IMAP) Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Domain Name System (DNS) Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) 23 Lesson 1 Summary: Network Communications Computers communicate by using languages called protocols. Protocols provide services to other protocols operating above and below them. A LAN uses a common network medium to connect computers in a relatively small area. A WAN uses an external network provider to connect LANs. Broadband networks carry multiple signals at once, while baseband networks carry only one signal. A backbone network connects segments together, forming an internetwork. Most operating systems today use the peer-to-peer model, which allows computers to function as both clients and servers. 24 Lesson 2 Summary: The OSI Reference Model OSI Model Layer Function Physical Defines the hardware elements and structure of the network installation Data-link Provides addressing, data encapsulation, and media access control Network Provides end-to-end routing and addressing Transport Provides packet acknowledgment, flow control, and error detection Session Provides dialog control and dialog separation Presentation Translates syntaxes between different systems Application Provides an interface to applications running on the computer 25