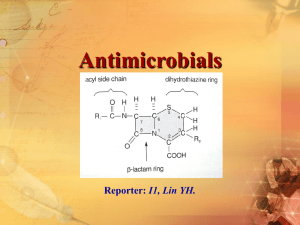
Antibacterials II: Vancomycin, Linezolid, Daptomycin, Macrolides
... 1st of ketolide class Designed to target macrolide-resistant respiratory tract pathogens Compared to macrolidemore highly concentrated in tissue Not currently recommended in guidelines due to hepatotoxicity ...
... 1st of ketolide class Designed to target macrolide-resistant respiratory tract pathogens Compared to macrolidemore highly concentrated in tissue Not currently recommended in guidelines due to hepatotoxicity ...
Slide 1
... - 1st line tx: azithromycin 500 mg OD or clarithromycin 500 mg BID + ethambutol 15 mgkd or Clofazimine or Ciprofloxacin 750mg BID or Amikacin - 2nd line tx: Rifabutin 300 mg OD; Rifampicin; ...
... - 1st line tx: azithromycin 500 mg OD or clarithromycin 500 mg BID + ethambutol 15 mgkd or Clofazimine or Ciprofloxacin 750mg BID or Amikacin - 2nd line tx: Rifabutin 300 mg OD; Rifampicin; ...
Pharmacokinetics and doses of anti-TB drugs in children
... • To rapidly kill most bacilli in order to: - prevent disease progression - prevent transmission of infection - prevent development of drug resistance Continuation phase • To effect cure and prevent relapse (eliminate dormant bacilli) ...
... • To rapidly kill most bacilli in order to: - prevent disease progression - prevent transmission of infection - prevent development of drug resistance Continuation phase • To effect cure and prevent relapse (eliminate dormant bacilli) ...
File
... • Corticosteroid:used occassionaly in severe cases and in angioedema and urticarial vasculitis. Prednisone • Immunosuppressant for treatment of autoimmune disorders; may decrease inflammation by reversing increased capillary permeability .Stabilizes lysosomal membranes and suppresses lymphocytes an ...
... • Corticosteroid:used occassionaly in severe cases and in angioedema and urticarial vasculitis. Prednisone • Immunosuppressant for treatment of autoimmune disorders; may decrease inflammation by reversing increased capillary permeability .Stabilizes lysosomal membranes and suppresses lymphocytes an ...
Carbapenem
... susceptible to b-lactamases. • Their antibacterial spectrum is the same as the broadspectrum drugs plus pseudomonads. • These antibiotics are used in the treatment of lung, and bloodstream infections caused by ampicillin-resistant enteric gram-negative pathogens. ...
... susceptible to b-lactamases. • Their antibacterial spectrum is the same as the broadspectrum drugs plus pseudomonads. • These antibiotics are used in the treatment of lung, and bloodstream infections caused by ampicillin-resistant enteric gram-negative pathogens. ...
Enrofloxacin is a synthetic, broad spectrum antimicrobial substance
... The safety of the product has not been established in calves when administered by the intravenous route and use of this route of administration in calves is therefore not recommended. Official and local antimicrobial policies should be taken into account when the product is used. Fluoroquinolones sh ...
... The safety of the product has not been established in calves when administered by the intravenous route and use of this route of administration in calves is therefore not recommended. Official and local antimicrobial policies should be taken into account when the product is used. Fluoroquinolones sh ...
Drug Therapy of Urinary Tract Infections
... Prototype: ciprofloxacin (Cipro) – broad spectrum bactericidal agent that have multiple applications (oral or IV agents) MOA: Inhibit bacterial DNA gyrase so that DNA replication cannot take place Adverse Effects: GI reactions (N/V, diarrhea, abd pain), CNS effects (dizziness, HA, confusion et restl ...
... Prototype: ciprofloxacin (Cipro) – broad spectrum bactericidal agent that have multiple applications (oral or IV agents) MOA: Inhibit bacterial DNA gyrase so that DNA replication cannot take place Adverse Effects: GI reactions (N/V, diarrhea, abd pain), CNS effects (dizziness, HA, confusion et restl ...
General Outline for Antibiotics
... of Quinolones • Nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort (common) • Diarrhea and antibiotic-associated colitis (uncommon to rare) • CNS side effects • Mild headache and dizziness (common to rare) • Hallucinations, delirium, and seizures (rare) ...
... of Quinolones • Nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort (common) • Diarrhea and antibiotic-associated colitis (uncommon to rare) • CNS side effects • Mild headache and dizziness (common to rare) • Hallucinations, delirium, and seizures (rare) ...
... If the resistance of S. pneumoniae to penicillin is particularly worrisome, then the resistance to macrolides implies that great care is needed when using these drugs as the first-line empirical treatment against nonsevere and nonhospitalized CAP patients [7, 14, 15]. Although no prospective studies ...
Antibiotics - DENTISTRY 2012
... tubules, so administered with cilastatin (inhibitor of renal dehydropeptidase) for UTI. A carbapenem is indicated for infections caused by organisms that are resistant to other drugs, e.g., P aeruginosa, and for treatment of mixed aerobic and anaerobic infections. A carbapenem is the beta-lactam ant ...
... tubules, so administered with cilastatin (inhibitor of renal dehydropeptidase) for UTI. A carbapenem is indicated for infections caused by organisms that are resistant to other drugs, e.g., P aeruginosa, and for treatment of mixed aerobic and anaerobic infections. A carbapenem is the beta-lactam ant ...
ANTIMICROBIAL DRUGS
... Spectrum: Gr+,Gr-, anaerobes Inhibit Pseudomonas Reserve drug for the treatment of serious nosocomial ...
... Spectrum: Gr+,Gr-, anaerobes Inhibit Pseudomonas Reserve drug for the treatment of serious nosocomial ...
penicillins
... 3) prophylaxis against susceptible meningococcal strains, in ulcerative colitis (as sulfasalazine), in burns (as silver sulfadiazine or mafenide), in chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum infection, and in combination with trimethoprim ...
... 3) prophylaxis against susceptible meningococcal strains, in ulcerative colitis (as sulfasalazine), in burns (as silver sulfadiazine or mafenide), in chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum infection, and in combination with trimethoprim ...
Special Bulletin - Review of Antibiotics
... cover a broader spectrum of organisms, including H. influenzae, Mycobacterium sp, and H. pylori, but do not offer an advantage over erythromycin against penicillin resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae. These drugs are administered once or twice daily but are significantly more expensive than erythromy ...
... cover a broader spectrum of organisms, including H. influenzae, Mycobacterium sp, and H. pylori, but do not offer an advantage over erythromycin against penicillin resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae. These drugs are administered once or twice daily but are significantly more expensive than erythromy ...
Treating Respiratory Tract Infections In The Era Of Antibiotic
... resistance in other pathogens (such as Staphylococcus aureus and many gram-negative pathogens).13,14 Finally, new strategies to combat the potential impact of antimicrobial resistance must be formulated. ASiP: Can you list treatment strategies for community-acquired RTIs that attempt to address the ...
... resistance in other pathogens (such as Staphylococcus aureus and many gram-negative pathogens).13,14 Finally, new strategies to combat the potential impact of antimicrobial resistance must be formulated. ASiP: Can you list treatment strategies for community-acquired RTIs that attempt to address the ...
QuinTMP_Lowy
... replication. 2) They also block topoisomerase IV interfering with the separation of interlocked, replicated DNA molecules. 3) There appear to be other, as yet undefined, mechanisms of killing that may involve RNA and protein synthesis. Mechanism of Resistance: Because of the widespread use of these ...
... replication. 2) They also block topoisomerase IV interfering with the separation of interlocked, replicated DNA molecules. 3) There appear to be other, as yet undefined, mechanisms of killing that may involve RNA and protein synthesis. Mechanism of Resistance: Because of the widespread use of these ...
Formulary Updates Volume 13, Issue 3 · March 2015
... through a Medication Assistance Program (MAP) and CareLink will subsidize pending obtainment through MAP. 3. Dapagliflozin 5 mg and 10 mg oral tablet (Farxiga) - a sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor added to formulary for use according to the UHS Outpatient Glycemic Control Algorithm f ...
... through a Medication Assistance Program (MAP) and CareLink will subsidize pending obtainment through MAP. 3. Dapagliflozin 5 mg and 10 mg oral tablet (Farxiga) - a sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor added to formulary for use according to the UHS Outpatient Glycemic Control Algorithm f ...
Slides_2
... Not active against tissue trophozoites. In the gut, it splits into diloxanide and furoic acid; about 90% of the diloxanide is rapidly absorbed. The unabsorbed diloxanide is the active antiamebic The mechanism of action is unknown. Used with a tissue amebicide, usually metronidazole, to treat serious ...
... Not active against tissue trophozoites. In the gut, it splits into diloxanide and furoic acid; about 90% of the diloxanide is rapidly absorbed. The unabsorbed diloxanide is the active antiamebic The mechanism of action is unknown. Used with a tissue amebicide, usually metronidazole, to treat serious ...
View PDF - Auspherix
... could benefit from a pre-treatment to prevent post-surgical infection from these bacteria,” the executive commented. An estimated one in three people are carriers of nasal Staphylococcus aureus, one of the staphylococcal bacteria. A healthy individual is not harmed by the bacteria. But if he or she ...
... could benefit from a pre-treatment to prevent post-surgical infection from these bacteria,” the executive commented. An estimated one in three people are carriers of nasal Staphylococcus aureus, one of the staphylococcal bacteria. A healthy individual is not harmed by the bacteria. But if he or she ...
Tuberculosis - ichapps.com
... dermatitis and acne. Clofazimine: Clofazimine is a drug with good activity against Mycobacterium leprae and weak activity against M. tuberculosis and M. avium. Adverse reactions: Gastrointestinal distress and skin discoloration. Thiacetazone: It is a weak agent used rarely in parts of the developing ...
... dermatitis and acne. Clofazimine: Clofazimine is a drug with good activity against Mycobacterium leprae and weak activity against M. tuberculosis and M. avium. Adverse reactions: Gastrointestinal distress and skin discoloration. Thiacetazone: It is a weak agent used rarely in parts of the developing ...
Antimicrobial1
... encountered with the tetracyclines. Of course, all drugs should be used only during pregnancy under the supervision of a patient's physician. lactation: Drugs administered to a lactating mother may enter the nursing infant via the breast milk. Although the concentration of an antibiotic in breast mi ...
... encountered with the tetracyclines. Of course, all drugs should be used only during pregnancy under the supervision of a patient's physician. lactation: Drugs administered to a lactating mother may enter the nursing infant via the breast milk. Although the concentration of an antibiotic in breast mi ...
... liver parenchymal damage, blood dyscrasia, severe renal insufficiency, glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. Pregnancy and Lactation : Although Co-trimoxazole has been used during pregnancy without deleterious sequelae, animal studies have indicated a risk of teratogenic effects. Co-trimoxaz ...
PRTK Feb 2015 Cowen Presentation
... No known metabolites No CYP interactions identified No DDI effects anticipated Modest GI effects No nausea-vomiting seen in IV-oral cross-over study ...
... No known metabolites No CYP interactions identified No DDI effects anticipated Modest GI effects No nausea-vomiting seen in IV-oral cross-over study ...
Levofloxacin
Levofloxacin (trade names Levaquin (US), Tavanic (EU), and others) is a broad-spectrum antibiotic of the fluoroquinolone drug class, and the levo isomer of its predecessor ofloxacin. Its spectrum of activity includes most strains of bacterial pathogens responsible for respiratory, urinary tract, gastrointestinal, and abdominal infections, including Gram negative (Escherichia coli, Haemophilus influenzae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Legionella pneumophila, Moraxella catarrhalis, Proteus mirabilis, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa), Gram positive (methicillin-sensitive but not methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, and Streptococcus pyogenes), and atypical bacterial pathogens (Chlamydophila pneumoniae and Mycoplasma pneumoniae). Compared to earlier antibiotics of the fluoroquinoline class such as ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin exhibits greater activity towards Gram-positive bacteria but lesser activity toward Gram-negative bacteria, especially Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Levofloxacin and later generation fluoroquinolones are collectively referred to as ""respiratory quinolones"" to distinguish them from earlier fluoroquinolones which exhibited modest activity toward the important respiratory pathogen Streptococcus pneumoniae.Levofloxacin and other fluoroquinolones are valued for their broad spectrum of activity, excellent tissue penetration, and for their availability in both oral and intravenous formulations. Levofloxacin is used alone or in combination with other antibacterial drugs to treat certain bacterial infections including pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and abdominal infections.Levofloxacin and other fluoroquinolones are generally well tolerated, but in rare instances have produced serious adverse reactions such as spontaneous tendon ruptures and irreversible peripheral neuropathy. Tendon damage may manifest months after therapy had been completed. Levofloxacin may cause worsening of myasthenia gravis symptoms, including muscle weakness and breathing problems.